Congress Poland or Congress Kingdom of Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. It was established when the French ceded a part of Polish territory to the Russian Empire following France's defeat in the Napoleonic Wars. In 1915, during World War I, it was replaced by the German-controlled nominal Regency Kingdom until Poland regained independence in 1918.

The Vilna Governorate was a province (guberniya) of the Northwestern Krai of the Russian Empire. In 1897, the governorate covered an area of 41,907.9 square kilometres (16,180.7 sq mi) and had a population of 1,591,207 inhabitants. The governorate was defined by the Minsk Governorate to the south, the Grodno Governorate to the southwest, the Suwałki Governorate to the west, the Kovno and Courland Governorates to the north, and the Vitebsk Governorate to the east. The capital was located in Vilna (Vilnius). The city also served as the capital of Vilna Governorate-General, which existed until 1912. The area roughly corresponded to the Vilnius Region, which was later occupied by Germany, Bolsheviks, and Poland.

Grodno Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of the Northwestern Krai of the Russian Empire, with its capital in Grodno. It encompassed 38,671.5 square kilometres (14,931.1 sq mi) in area and consisted of a population of 1,631,645 inhabitants by 1897. Grodno Governorate was bordered by Suwałki Governorate to the north, Vilna Governorate to the northeast, Minsk Governorate to the east, Volhynia Governorate to the south, Kholm Governorate to the west, and Łomża Governorate to the northwest. The governorate covered the areas of modern-day Grodno Region of Belarus, part of the Podlaskie Voivodeship of Poland, and a small part of Druskininkai, Lazdijai and Varėna districts of Lithuania.

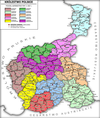
Congress Poland was subdivided several times from its creation in 1815 until its dissolution in 1918. Congress Poland was divided into departments, a relic from the times of the French-dominated Duchy of Warsaw. In 1816 the administrative divisions were changed to forms that were more traditionally Polish: voivodeships, obwóds and powiats. Following the November Uprising, the subdivisions were again changed in 1837 to bring the subdivisions closer to the structure of the Russian Empire when guberniyas (governorates) were introduced. In this way, Congress Poland was gradually transformed into the "Vistulan Country". Over the next several decades, various smaller reforms were carried out, either changing the smaller administrative units or merging/splitting various guberniyas.

Lublin Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.

Sandomierz Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.

Radom Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.

Kielce Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.

Piotrków Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire, established in 1867 by splitting some areas of Radom and Warsaw Governorates. Its capital was in Petrokov (Piotrków Trybunalski).
Augustów Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.

Płock Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.

Warsaw Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.
Podlasie Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.
Kraków Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.

Kalisz Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.

Siedlce Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.

The Russian Partition, sometimes called Russian Poland, constituted the former territories of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that were annexed by the Russian Empire in the course of late-18th-century Partitions of Poland. The Russian acquisition encompassed the largest share of Poland's population, living on 463,200 km2 of land constituting the eastern and central territory of the former commonwealth. The three partitions, which took place in 1772, 1793 and 1795, resulted in the complete loss of Poland's sovereignty, with its territory split between Russia, Prussia and Austria. The Napoleonic Wars saw significant parts of Prussia's and Austria's partitions reconstituted as the Duchy of Warsaw, most of which was then reconstituted as the Kingdom of Poland within the Russian Empire in 1815.

Oryol Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of the Russian Empire and the Russian SFSR, which existed from 1796 to 1928. Its seat was in the city of Oryol.

Irkutsk Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of the Russian Empire, located in Siberia. It existed from 1764 to 1926; its seat was in the city of Irkutsk.

The coat of arms that served as a symbol of the Augustów Voivodeship (1816–1837), and later, the Augustów Governorate (1837–1867), of the Congress Poland, was divided vertically into two red fields. The left half depicted a knight in a white (silver) armor, sitting on a white (silver) horse with a blue saddle and shabrack, standing on its back hoofs. The knight has a blue shield with a yellow (golden) cross of Lorraine on it, put on his left arm, and hold a sword in his right hand. The right half depicted a black bear facing left and standing on its back legs, with a yellow (golden) collar on its neck.