Sandomierz Governorate [lower-alpha 1] was an administrative-territorial unit ( guberniya ) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.

Sandomierz Governorate [lower-alpha 1] was an administrative-territorial unit ( guberniya ) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.

It was created in 1837 from the Sandomierz Voivodeship, and had the same borders and capital (Radom) as the voivodeship. Its lower levels of administration were also mostly unchanged, although renamed from obwóds to powiats. Reform of 1844 merged the governorate with Kielce Governorate, creating a new entity, the Radom Governorate.

Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska, is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a separate culture featuring diverse architecture, folk costumes, dances, cuisine, traditions and a rare Lesser Polish dialect. The region is rich in historical landmarks, monuments, castles, natural scenery and UNESCO World Heritage Sites.

Radom is a city in east-central Poland, located approximately 100 kilometres south of the capital, Warsaw. It is situated on the Mleczna River in the Masovian Voivodeship. Radom is the fifteenth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest in its province with a population of 196,918 (30.06.2023)

Sandomierz Voivodeship was a unit of administration and local government in Poland from the 14th century to the partitions of Poland in 1772–1795. It was part of the Lesser Poland region and the Lesser Poland Province. Originally Sandomierz Voivodeship also covered the area around Lublin, but in 1474 its three eastern counties were organized into Lublin Voivodeship. In the 16th century, it had 374 parishes, 100 towns and 2586 villages. The voivodeship was based on the Sandomierz ziemia, which earlier was the Duchy of Sandomierz. The Duchy of Sandomierz was created in 1138 by King Bolesław III Wrymouth, who in his testament divided Poland into five principalities. One of them, with the capital at Sandomierz, was assigned to Krzywousty's son, Henry of Sandomierz. Later on, with southern part of the Seniorate Province, the Duchy of Sandomierz created Lesser Poland, divided into Kraków and Sandomierz Voivodeships.

Radom County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Masovian Voivodeship, east-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat is the city of Radom, although the city is not part of the county. The county contains three towns: Pionki, 22 km (14 mi) north-east of Radom, Iłża, 27 km (17 mi) south of Radom, and Skaryszew, 12 km (7 mi) south-east of Radom.

Zwoleń is a town in eastern Poland, in Masovian Voivodeship, about 30 kilometres east of Radom. It is the capital of Zwoleń County. Population is 8,048 (2009). Zwoleń belongs to Sandomierz Land of the historic province of Lesser Poland, and is located on the Zwoleńka river.
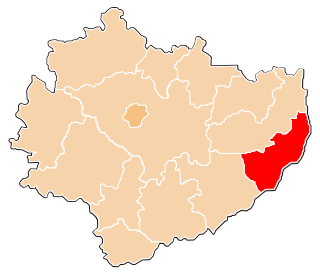
Sandomierz County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, south-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Sandomierz, which lies 83 kilometres (52 mi) east of the regional capital Kielce. The county also contains the towns of Koprzywnica, lying 16 km (10 mi) south-west of Sandomierz, and Zawichost, 16 km (10 mi) north-east of Sandomierz.

Opoczno County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Łódź Voivodeship, south-east Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Opoczno, which lies 72 kilometres (45 mi) south-east of the regional capital Łódź. The only other town in the county is Drzewica, lying 15 km (9 mi) north-east of Opoczno.

Wyśmierzyce is a town in Białobrzegi County, Masovian Voivodeship, Poland, with 884 inhabitants (2004). Until 2017 it was the smallest town in Poland.

Congress Poland was subdivided several times from its creation in 1815 until its dissolution in 1918. Congress Poland was divided into departments, a relic from the times of the French-dominated Duchy of Warsaw. In 1816 the administrative divisions were changed to forms that were more traditionally Polish: voivodeships, obwóds and powiats. Following the November Uprising, the subdivisions were again changed in 1837 to bring the subdivisions closer to the structure of the Russian Empire when guberniyas (governorates) were introduced. In this way, Congress Poland was gradually transformed into the "Vistulan Country". Over the next several decades, various smaller reforms were carried out, either changing the smaller administrative units or merging/splitting various guberniyas.

Lublin Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.

Radom Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.

Kielce Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.

Piotrków Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire, established in 1867 by splitting some areas of Radom and Warsaw Governorates. Its capital was in Petrokov (Piotrków Trybunalski).
Podlasie Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.
Kraków Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.

Kalisz Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of Congress Poland of the Russian Empire.

Volhynia Governorate, also known as Volyn Governorate, was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of the Southwestern Krai of the Russian Empire. It consisted of an area of 71,736 square kilometres (27,697 sq mi) and a population of 2,989,482 inhabitants. The governorate bordered Grodno and Minsk Governorates to the north, Kiev Governorate to the east, Podolia Governorate to the south, Lublin and Siedlce Governorates, and after 1912, Kholm Governorate and Austria to the west. Its capital was in Novograd-Volynsky until 1804, and then Zhitomir. It corresponded to most of modern-day Volyn, Rivne and Zhytomyr Oblasts of Ukraine and some parts of Brest and Gomel Regions of Belarus.

Sandomierz Voivodeship was a proposed voivodeship of the Second Polish Republic, which was never created because of the Nazi and Soviet invasion of Poland in September 1939. The idea of the creation of this unit was the brainchild of the Minister of Industry and Trade Eugeniusz Kwiatkowski, and it was directly linked with creation of one of the biggest economic projects of interbellum Poland, Central Industrial Region. It was intended to cover south-central Poland and be created in late 1939. Its projected size was 24,500 square kilometers, and it was to incorporate 20 or 21 powiats.

The coat of arms that serves as the symbol of the Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, Poland, consists of the Iberian style escutcheon (shield), with square top and rounded base, that is divided in the 2 by 2 chessboard pattern. The top left field features a yellow patriarchal cross. The top right field features a white eagle with yellow crown, beak, legs, stripes on its wings, and a ring on its tail. The bottom left field features eight yellow six-pointed starts, placed in three rows, each with three stars, with the exception of the bottom row, that only had 2 stars, placed to the left.

The historical coat of arms, that served as the symbol of the Sandomierz Land, and the Sandomierz Voivodeship of the Kingdom of Poland, from 14th to 18th centuries, was divided into two fields, with the left field consisting of six stripes, that were alternatining either between red and white, or red and yellow colours, and with the right field consisting of several yellow six-armed stars, which number altered between seven and nine.