
Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) is an Indian central public sector undertaking and the largest government-owned power generation equipment manufacturer. It is under the ownership of Government of India and administrative control of the Ministry of Heavy Industries. Established in 1956, BHEL is based in New Delhi.

India is the third largest producer of electricity in the world. During the fiscal year (FY) 2019–20, the total electricity generation in the country was 1,598 TWh, of which 1,383.5 TWh generated by utilities. The gross electricity consumption per capita in FY2019 was 1,208 kWh.

Baglihar Dam, also known as Baglihar Hydroelectric Power Project, is a run-of-the-river power project on the Chenab River in the Ramban district of Jammu and Kashmir, India. The first power project executed by the Jammu and Kashmir Power Development Corporation, it was conceived in 1992 and approved in 1996, with construction begun in 1999. The project was estimated to cost US$1 billion. The project consists of two-stage of 450MW each. The first stage of the project was completed in 2008-09 and was dedicated to the nation by the Prime Minister Manmohan Singh of India. The second stage of the project was completed in 2015–16, and was subsequently dedicated to the nation by the Prime Minister Narendra Modi of India.

Tarapur Atomic Power Station (T.A.P.S.) is located in Tarapur, Palghar, India. It was the first commercial nuclear power station built in India.

Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant is the largest nuclear power station in India, situated in Kudankulam in the Tirunelveli district of the southern Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Construction on the plant began on 31 March 2002, but faced several delays due to opposition from local fishermen. KKNPP is scheduled to have six VVER-1000 reactors built in collaboration with Atomstroyexport, the Russian state company and Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL), with an installed capacity of 6,000 MW of electricity.

Solar power is a fast developing industry in India. The country's solar installed capacity was 63.303 GWAC as of 31 December 2022. Solar power generation in India ranks fourth globally in 2021.

Kakrapar Atomic Power Station is a nuclear power station in India, which lies in the proximity of Mandvi, Surat and Tapi river in the state of Gujarat.
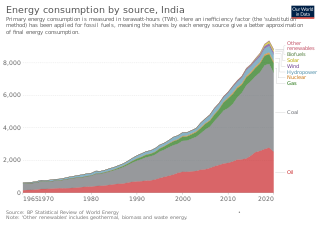
Since 2013, total primary energy consumption in India has been the third highest in the world after China and United States. India is the second-top coal consumer in the year 2017 after China. India ranks third in oil consumption with 22.1 crore tons in 2017 after United States and China. India is net energy importer to meet nearly 47% of its total primary energy in 2019.

India is world's 3rd largest consumer of electricity and world's 3rd largest renewable energy producer with 40% of energy capacity installed in the year 2022 coming from renewable sources. Ernst & Young's (EY) 2021 Renewable Energy Country Attractiveness Index (RECAI) ranked India 3rd behind USA and China. In November 2021, India had a renewable energy capacity of 150 GW consisting of solar, wind, small hydro power, bio-mass, large hydro, and nuclear. India has committed for a goal of 500 GW renewable energy capacity by 2030.

NTPC Limited, formerly known as National Thermal Power Corporation Limited, is an Indian central public sector undertaking under the ownership of the Ministry of Power, Government of India which is engaged in generation of electricity and allied activities. The headquarters of the psu is situated at New Delhi. NTPC's core function is the generation and distribution of electricity to State Electricity Boards in India. The body also undertakes consultancy and turnkey project contracts that involve engineering, project management, construction management, and operation and management of power plants.

Chandrapur Super Thermal Power Station is a thermal power plant located in Chandrapur district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. The power plant is one of the coal based power plants of MAHAGENCO. The coal for the power plant is sourced from Durgapur and Padmapur Collieries of Western Coalfields Limited. The plant was officially inaugurated by the then Prime Minister Indira Gandhi on 8 October 1984.
Khaparkheda Thermal Power Station is located in Khaperkheda Town Nagpur district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. The power plant is one of the oldest coal based power plants of MAHAGENCO. The coal for the power plant is sourced from Saoner and Dumri Khurd mines of Western Coalfields Limited (WCL).Mainly coal transport through the Indian Railways. Now coal india has opened many mines in nearby areas and these mines are also providing coal to the power plant, specially to the new power plant which is of 500 MW. Source of water for the power plant is from Pench reservoir through a pond of Koradi Thermal Power Station (KTPS). Since the new power plant has begun operations, locals have reported increase in dust leading to many health conditions. This is due to low quality equipment used in the power plant

Kanti Thermal Power Station also known as George Fernandes Thermal Power Plant Station is located in Kanti, Muzaffarpur, Bihar. George Fernandes was former Member of Parliament from Muzaffarpur constituency of Bihar. It is wholly owned subsidiary company of NTPC. The share of the company is 100% of the NTPC. The plant was not functional between 2003 and 2013; however, renovation of both older units paved the way for commercial production of electricity by the end of 2013.
The Rampal Power Station is a 1320 megawatt coal-fired power station currently under construction at Rampal Upazila of Bagerhat District in Khulna, Bangladesh. The power plant is being constructed on an area of over 1834 acres of land, is situated 14 kilometres north of the world's largest mangrove forest Sundarbans which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It will be the country's largest power plant.
Sasan Ultra Mega Power Plant or Sasan UMPP is one of the four Ultra Mega Power Projects awarded by the Ministry of Power, Government of India. It is located in Sasan village near Waidhan in Singrauli district of Madhya Pradesh. Sasan UMPP is India's largest integrated power generation and coal mine project with 3,960 MW power plant and 20 MT per year coal mining capacity. It is presently the 4th largest electricity generation power plant in India after NTPC Vindhyachal, Mundra Thermal Power and Mundra UMPP. The total project value of Sasan UMPP is ₹25,186 crores.

Ghatghar Dam refers to two associated gravity dams built using roller-compacted concrete, the first use in India. They are situated in Ghatghar village in Ahmednagar district Maharashtra, India. Both dams create a lower and upper reservoir for the 250 MW pumped-storage hydroelectric power station. The upper Ghatghar dam is 15 m (49 ft) tall and on the Pravara River, a tributary of Godavari river. The lower Ghatghar dam is 86 m (282 ft) tall and located on the Shahi Nalla which is a tributary of Ulhas River to the south west of the upper reservoir in a steep valley. The hydro power project diverts Godavari river basin water outside the basin area to a west flowing river of Western ghats.

Make in India is an initiative by the Government of India to create and encourage companies to develop, manufacture and assemble products made in India and incentivize dedicated investments into manufacturing. The policy approach was to create a conducive environment for investments, develop a modern and efficient infrastructure, and open up new sectors for foreign capital. The initiative targeted 25 economic sectors for job creation and skill enhancement, and aimed "to transform India into a global design and manufacturing export hub."

Kamuthi Solar Power Project is a photovoltaic power station spread over an area of 2,500 acres (10 km2) in Kamuthi, Ramanathapuram district, 90 km from Madurai, in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. The project was commissioned by Adani Power. With a generating capacity of 648 MWp at a single location, it is the world's 12th largest solar park based on capacity.















