Related Research Articles

The Panhellenic Socialist Movement, known mostly by its acronym PASOK, is a social-democratic political party in Greece. Until 2012 it was one of the two major parties in the country, along with New Democracy, its main political rival. In the June 2023 Greek legislative election it once again held firm on to its position of one of the ”big three” political parties of Greece.

New Democracy is a liberal-conservative political party in Greece. In contemporary Greek politics, New Democracy has been the main centre-right to right-wing political party and one of the two major parties along with its historic rival, the Panhellenic Socialist Movement (PASOK). New Democracy and PASOK were created in the wake of the toppling of the military junta in 1974, ruling Greece in succession for the next four decades. Following the electoral decline of PASOK, New Democracy remained one of the two major parties in Greece, the other being the Coalition of the Radical Left (SYRIZA). The party was founded in 1974 by Konstantinos Karamanlis and in the same year it formed the first cabinet of the Third Hellenic Republic. New Democracy is a member of the European People's Party, the largest European political party since 1999, the Centrist Democrat International, and the International Democracy Union.

Karolos Papoulias was a Greek politician who served as the president of Greece from 2005 to 2015.

Antonis Samaras is a Greek politician who served as 14th Prime Minister of Greece from 2012 to 2015. A member of the New Democracy party, he was its president from 2009 until 2015. Samaras started his national political career as Minister of Finance in 1989; he served as Minister of Foreign Affairs from 1989 to 1992 and Minister of Culture in 2009.

The Coalition of the Radical Left – Progressive Alliance, best known by the syllabic abbreviation SYRIZA, is a centre-left to left-wing political party in Greece. It was founded in 2004 as a political coalition of left-wing and radical left parties, and registered as a political party in 2012.

The Third Hellenic Republic is the period in modern Greek history that stretches from 1974, with the fall of the Greek military junta and the final confirmation of the abolishment of the Greek monarchy, to the present day.

Democratic Left was a social-democratic political party in Greece. Formed as a split from Synaspismós, DIMAR was a minor party supporting the Samaras cabinet from 21 June 2012 to 21 June 2013. After being a member of the Democratic Alignment (DISI) and the Movement for Change (KINAL), it affiliated to Syriza in 2019. The party was dissolved in 2022.
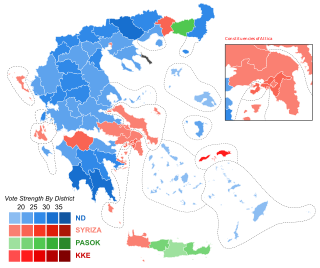
Legislative elections were held in Greece on Sunday, 6 May 2012 to elect all 300 members to the Hellenic Parliament. It was scheduled to be held in late 2013, four years after the previous election; however, an early election was stipulated in the coalition agreement of November 2011 which formed the Papademos Cabinet. The coalition comprised both of Greece's traditional major political parties, PASOK on the left and New Democracy (ND) on the right, as well as the right-wing Popular Orthodox Rally (LAOS). The aim of the coalition was to relieve the Greek government-debt crisis by ratifying and implementing decisions taken with other Eurozone countries and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) a month earlier.

The Independent Greeks – National Patriotic Alliance is a national conservative political party in Greece.

Legislative elections were held in Greece on Sunday, 17 June 2012, to elect all 300 members to the Hellenic Parliament in accordance with the constitution, after all attempts to form a new government failed following the May elections. If all attempts to form a new government fail, the constitution directs the president to dissolve a newly elected parliament, and then to call for new parliamentary elections within 30 days of the dissolution. The president announced at 16 May the date for the new election, and signed the formal decree to dissolve the parliament and call for the election at 19 May.

Legislative elections were held in Greece on Sunday 25 January 2015 to elect all 300 members of the Hellenic Parliament in accordance with the constitution. The election was held earlier than scheduled due to the failure of the Greek parliament to elect a new president on 29 December 2014.
European Parliament elections were held in Greece on 25 May 2014 to elect the 21 Greek members of the European Parliament. The number of seats allocated to Greece declined from 22 to 21, as a result of the 2013 reapportionment of seats in the European Parliament.
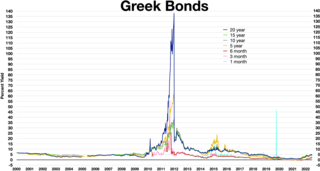
The Greek government-debt crisis began in 2009 and, as of November 2017, was still ongoing. During this period, many changes had occurred in Greece. The income of many Greeks has declined, levels of unemployment have increased, elections and resignations of politicians have altered the country's political landscape radically, the Greek parliament has passed many austerity bills, and protests have become common sights throughout the country.
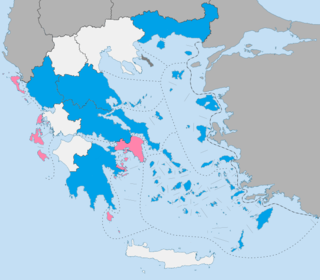
Local elections were held in Greece on 18 May 2014 and 25 May 2014. Voters elected representatives to the country's local authorities, comprising 13 regions and 325 municipalities.

The River was a centrist and social-liberal political party in Greece. The party was founded in February 2014 by Stavros Theodorakis. The party did not run in the 2019 elections and had no seats in the Hellenic Parliament.

Indirect presidential elections were held in Greece in December 2014 and February 2015 for the succession to Karolos Papoulias as President of the Hellenic Republic. The candidate of the ND–PASOK government, Stavros Dimas, failed to secure the required majority of MPs of the Hellenic Parliament in the first three rounds of voting in December. According to the provisions of the Constitution of Greece, a snap election was held on 25 January 2015, which was won by the left-wing Syriza party. Following the convening of the new Parliament, the presidential election resumed. On 18 February 2015, veteran ND politician Prokopis Pavlopoulos, backed by the Syriza-ANEL coalition government, was elected with 233 votes.

The PASOK – Movement for Change is a political alliance in Greece, which was founded in March 2018, initially as "Movement for Change", mainly affiliated with the centre-left of the political spectrum. It includes the Panhellenic Socialist Movement (PASOK) and Movement of Democratic Socialists (KIDISO).
Following the January 2015 Greek election, the leader of the largest party SYRIZA, Alexis Tsipras, was charged with forming a coalition government.
The First Shadow Cabinet of Alexis Tsipras was formed on 3 July 2012, following the June 2012 Greek legislative election. It consisted of only Syriza MPs, as they were the largest party to refuse to participate in the ND-PASOK-DIMAR coalition. The Shadow Cabinet was dissolved following the January 2015 Greek legislative election, and was replaced by a New Democracy shadow cabinet led by Antonis Samaras. Tsipras subsequently formed his First Cabinet on 27 January 2015, consisting of a coalition of both Syriza and the Independent Greeks.
Thanassis Theocharopoulos is an agricultural economist, Greek politician and chairman of the Democratic Left (DIMAR). In 2019 he served as Tourism Minister for Syriza.
References
- 1 2 "The official English language translation of the Greek Constitution as of 27 May 2008" (PDF). Hellenic Parliament. 27 May 2008. Retrieved 13 May 2012.
- ↑ "Greece exit polls suggest no majority win – Europe". Al Jazeera. 4 October 2011. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- 1 2 "Greece radical Leftist Syriza party to try to build anti-austerity cabinet". The Telegraph. 8 May 2012. Retrieved 8 May 2012.
- ↑ "Greek government talks in final stretch". Ekathimerini. 11 May 2012. Retrieved 11 May 2012.
- 1 2 Kyriakidou, Dina (3 May 2012). "Left gets historic chance to pull Greece out of limbo". Reuters. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ↑ "Exclusive: Greece's Democratic Left Refuses to Join Bailout Alliance". Reuters. 7 May 2012. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- 1 2 "Leading Greek party fails to form government - Europe". Al Jazeera. 4 October 2011. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ↑ "Greek election: Antonis Samaras coalition bid fails". BBC News. 7 May 2012. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ↑ Petrakis, Maria (8 May 2012). "Greek Pro-Bailout Leaders Told by Syriza to Revoke Aid Pledges". Bloomberg. Retrieved 8 May 2012.
- 1 2 Daniel Howden (30 April 2012). "Greece's radical new leader Alexis Tsipras plots course to tear up bailout deal" . The Independent. Archived from the original on 12 May 2022. Retrieved 13 May 2012.
- ↑ "Venizelos to try forming a gov't". ekathimerini.com. 9 May 2012. Retrieved 13 May 2012.
- 1 2 "Greek far-left leader fails in coalition bid". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 13 May 2012.
- ↑ "Greek Syriza leader hands rivals ultimatum to renounce austerity". The Telegraph. 9 May 2012. Retrieved 13 May 2012.
- ↑ "Greece's Venizelos won't accept government mandate, Proto Thema says". FXstreet.com. 9 May 2012. Retrieved 9 May 2012.
- ↑ "What's up". Zougla. 9 May 2012. Retrieved 9 May 2012.
- ↑ "Venizelos Says He'll Continue Efforts to Form Greek Government". Bloomberg. 9 May 2012. Retrieved 9 May 2012.
- 1 2 3 "Greece closer to unity government after Venizelos, Kouvelis talks". Ekathimerini. 10 May 2012. Retrieved 10 May 2012.
- 1 2 "PASOK leader to meet Samaras, Tsipras". Ekathimerini. 11 May 2012. Retrieved 11 May 2012.
- ↑ "Samaras launches all out attack on SYRIZA". Ekathimerini. 11 May 2012. Retrieved 11 May 2012.
- ↑ Mark Lowen (6 April 2012). "Third Greek coalition bid fails". BBC News. Retrieved 13 May 2012.
- ↑ "Greece's Socialists Fail To Reach Deal on Coalition Government". The Wall Street Journal. 11 May 2012. Retrieved 13 May 2012.
- ↑ "Greece bailout crisis: President seeks unity government". BBC News. 12 May 2012. Retrieved 13 May 2012.
- ↑ "No agreement on ecumenical gov't reached, talks to continue Monday". Ekathimerini. 13 May 2012. Retrieved 14 May 2012.
- ↑ Paul Mason (14 May 2012). "Greece's moderate left says no government possible". BBC News.
- 1 2 McManus, Bryan (15 May 2012). "Greek president calls for technocrat government". Athens. Agence France-Presse. Archived from the original on 24 May 2012. Retrieved 17 May 2012.
- ↑ Helena Smith in Athens (25 September 2009). "Greece to hold more coalition talks". The Guardian.
- ↑ Alderman, Liz; Donadio, Rachel (16 May 2012), "Greek President Is Expected to Name Caretaker Government Ahead of Vote", The New York Times, Athens, retrieved 17 May 2012
- ↑ Richard Galpin (10 May 2012). "BBC News Greece to hold new election on 17 June". BBC News.
- ↑ Weeks, Natalie (16 May 2012). "Greek President Told Banks Anxious as Deposits Pulled". Bloomberg.