The history of modern Greece covers the history of Greece from the recognition by the Great Powers — Britain, France and Russia — of its independence from the Ottoman Empire in 1828 to the present day.

George Andreas Papandreou is an American-born Greek politician who served as Prime Minister of Greece from 2009 to 2011. He is currently serving as an MP for Movement for Change.

The Panhellenic Socialist Movement, known mostly by its acronym PASOK, is a social-democratic political party in Greece. Until 2012 it was one of the two major parties in the country, along with New Democracy, its main political rival. After a decade of poor electoral outcomes, PASOK has retained its position as one of the main Greek political parties and is currently the second largest party in the Greek Parliament.

New Democracy is a liberal-conservative political party in Greece. In contemporary Greek politics, New Democracy has been the main centre-right to right wing political party and one of the two major parties along with its historic rival, the Panhellenic Socialist Movement (PASOK). New Democracy and PASOK were created in the wake of the toppling of the military junta in 1974, ruling Greece in succession for the next four decades. Following the electoral decline of PASOK, New Democracy remained one of the two major parties in Greece, the other being the Coalition of the Radical Left (SYRIZA). The party was founded in 1974 by Konstantinos Karamanlis and in the same year it formed the first cabinet of the Third Hellenic Republic. New Democracy is a member of the European People's Party, the largest European political party since 1999, the Centrist Democrat International, and the International Democracy Union.

Konstantinos Mitsotakis was a Greek politician who was Prime Minister of Greece from 1990 to 1993. He graduated in law and economics from the University of Athens. His son, Kyriakos Mitsotakis, was elected as the Prime Minister of Greece following the 2019 Greek legislative election.
Tzannis Tzannetakis was a Greek politician who was briefly Prime Minister of Greece during the political crisis of 1989. He also served as a submarine commander in the Hellenic Navy.

Ioannis Alevras, sometimes spelled Yannis Alevras, was a Greek Panhellenic Socialist Movement politician and Speaker of the Hellenic Parliament, who served as acting President of Greece in March 1985.

The Third Hellenic Republic is the period in modern Greek history that stretches from 1974, with the fall of the Greek military junta and the final confirmation of the abolishment of the Greek monarchy, to the present day.

The 2009 New Democracy leadership election was held on 29 November 2009, following the official announcement of the resignation of Kostas Karamanlis, after more than 12 years as leader of New Democracy, the main centre-right political party and one of the two major parties in Greece.

Democratic Left was a social-democratic political party in Greece. Formed as a split from Synaspismós, DIMAR was a minor party supporting the Samaras cabinet from 21 June 2012 to 21 June 2013. After being a member of the Democratic Alignment (DISI) and the Movement for Change (KINAL), it affiliated to Syriza in 2019. The party was dissolved in 2022.
A referendum to decide whether or not Greece was to accept the conditions under which the European Union (EU), the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the European Central Bank (ECB) would allow a 50% haircut of Greek debt owed to private creditors was planned to be held in 2011. However, Prime Minister George Papandreou decided to cancel the referendum on 3 November, if the opposition parties vote in favour of the EU deal. The proposed referendum was later cancelled.

Parliamentary elections were held in Greece on Sunday, 6 May 2012 to elect all 300 members to the Hellenic Parliament. It was scheduled to be held in late 2013, four years after the previous election; however, an early election was stipulated in the coalition agreement of November 2011 which formed the Papademos Cabinet. The coalition comprised both of Greece's traditional major political parties, PASOK on the left and New Democracy (ND) on the right, as well as the right-wing Popular Orthodox Rally (LAOS). The aim of the coalition was to relieve the Greek government-debt crisis by ratifying and implementing decisions taken with other Eurozone countries and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) a month earlier.

Parliamentary elections were held in Greece on Sunday, 17 June 2012, to elect all 300 members to the Hellenic Parliament in accordance with the constitution, after all attempts to form a new government failed following the May elections. If all attempts to form a new government fail, the constitution directs the president to dissolve a newly elected parliament, and then to call for new parliamentary elections within 30 days of the dissolution. The president announced at 16 May the date for the new election, and signed the formal decree to dissolve the parliament and call for the election at 19 May.

Parliamentary elections were held in Greece on Sunday 25 January 2015 to elect all 300 members of the Hellenic Parliament in accordance with the constitution. The election was held earlier than scheduled due to the failure of the Greek parliament to elect a new president on 29 December 2014.
European Parliament elections were held in Greece on 25 May 2014 to elect the 21 Greek members of the European Parliament. The number of seats allocated to Greece declined from 22 to 21, as a result of the 2013 reapportionment of seats in the European Parliament.

Indirect presidential elections were held in Greece in December 2014 and February 2015 for the succession to Karolos Papoulias as President of the Hellenic Republic. The candidate of the ND–PASOK government, Stavros Dimas, failed to secure the required majority of MPs of the Hellenic Parliament in the first three rounds of voting in December. According to the provisions of the Constitution of Greece, a snap election was held on 25 January 2015, which was won by the left-wing Syriza party. Following the convening of the new Parliament, the presidential election resumed. On 18 February 2015, veteran ND politician Prokopis Pavlopoulos, backed by the Syriza-ANEL coalition government, was elected with 233 votes.

Nikos Androulakis is a Greek politician who serves as president of the PASOK – Movement for Change since 2021. He served also as Member of the European Parliament from 2014 to 2023.
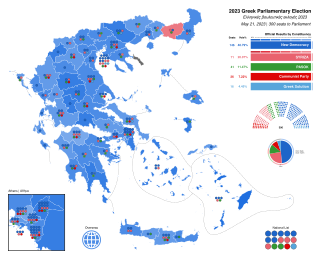
Snap parliamentary elections were held in Greece on 21 May 2023. All 300 seats in the Hellenic Parliament were contested. They were the first elections since 1990 not to be held under a bonus seats system, due to amendments to the electoral law made in 2016. Instead, a purely proportional system was used.

Ioannis Vroutsis, commonly shortened to Giannis (Γιάννης), is a Greek economist, lawyer and politician serving as Alternate Minister for Sport in the Second Cabinet of Kyriakos Mitsotakis from July 2023. He has served as a member of parliament for the Cyclades since 16 September 2007.






















