
Acadia was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River.

Penobscot Indian Island Reservation is an Indian reservation for the Penobscot Tribe of Maine, a federally recognized tribe of the Penobscot in Penobscot County, Maine, United States, near Old Town. The population was 758 at the 2020 census. The reservation extends for many miles alongside 15 towns and two unorganized territories in a thin string along the Penobscot River, from its base at Indian Island, near Old Town and Milford, northward to the vicinity of East Millinocket, almost entirely in Penobscot County. A small, uninhabited part of the reservation used as a game preserve and hunting and gathering ground is in South Aroostook, Aroostook County, by which it passes along its way northward.

King William's War was the North American theater of the Nine Years' War (1688–1697), also known as the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg. It was the first of six colonial wars fought between New France and New England along with their respective Native allies before France ceded its remaining mainland territories in North America east of the Mississippi River in 1763.

The Kennebec River is a 170-mile-long (270 km) river within the U.S. state of Maine. It rises in Moosehead Lake in west-central Maine. The East and West Outlets join at Indian Pond and the river flows southward. Harris Station Dam, the largest hydroelectric dam in the state, was constructed near that confluence. The river is joined at The Forks by its tributary the Dead River, also called the West Branch.

The Wolastoqiyik, also Wəlastəkwewiyik, Malecite or Maliseet are an Algonquian-speaking First Nation of the Wabanaki Confederacy. They are the Indigenous people of the Wolastoq valley and its tributaries. Their territory extends across the current borders of New Brunswick and Quebec in Canada, and parts of Maine in the United States.

Norridgewock was the name of both an Indigenous village and a band of the Abenaki Native Americans/First Nations, an Eastern Algonquian tribe of the United States and Canada. The French of New France called the village Kennebec. The tribe occupied an area in the interior of Maine. During colonial times, this area was territory disputed between British and French colonists, and was set along the claimed western border of Acadia, the western bank of the Kennebec River.

Dummer's War (1722–1725) was a series of battles between the New England Colonies and the Wabanaki Confederacy, who were allied with New France. The eastern theater of the war was located primarily along the border between New England and Acadia in Maine, as well as in Nova Scotia; the western theater was located in northern Massachusetts and Vermont in the frontier areas between Canada and New England.
Meductic is a community and former municipality along the Saint John River in southern New Brunswick, Canada. It held village status prior to 2023 and is now part of the village of Lakeland Ridges. It is approximately 33 kilometres southeast of Woodstock.

The Wabanaki Confederacy is a North American First Nations and Native American confederation of five principal Eastern Algonquian nations: the Abenaki, Mi'kmaq, Wolastoqiyik, Passamaquoddy (Peskotomahkati) and Penobscot.
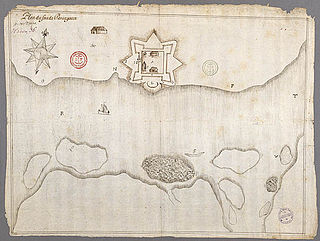
Fort Pentagouët was a French fort established in present-day Castine, Maine, which was the capital of Acadia (1670–1674). It is the oldest permanent settlement in New England.

Fort William Henry is located in the village of New Harbor in the town of Bristol, Maine. The fort was, in its time, the largest in New England. The fort was originally built in 1692 but destroyed four years later by New France in the Siege of Pemaquid (1696). A reconstruction was built in 1908. The fort was added to the National Register of Historic Places on December 1, 1969. Fort William Henry is now operated as a museum about the fort's history.

The siege of Pemaquid was a successful attack by a large band of Abenaki Indians on the English fort at Pemaquid, Fort Charles, then the easternmost outpost of colonial Massachusetts. The French-Abenaki attack was led by Jean-Vincent d'Abbadie de Saint-Castin and Father Louis-Pierre Thury and Chief Moxus. The fall of Pemaquid was a significant setback to the English. It pushed the frontier back to Casco (Falmouth), Maine.

The siege of Fort Nashwaak occurred during King William's War when New England forces from Boston attacked the capital of Acadia, Fort Nashwaak, at present-day Fredericton, New Brunswick. The siege was in retaliation for the French and Indian Siege of Pemaquid (1696) at present day Bristol, Maine. In the English Province of Massachusetts Bay. Colonel John Hathorne and Major Benjamin Church were the leaders of the New England force of 400 men. The siege lasted two days, between October 18–20, 1696, and formed part of a larger expedition by Church against a number of other Acadian communities.
The Northeast Coast campaign was the first major campaign by the French of Queen Anne's War in New England. Alexandre Leneuf de La Vallière de Beaubassin led 500 troops made up of French colonial forces and the Wabanaki Confederacy of Acadia. They attacked English settlements on the coast of present-day Maine between Wells and Casco Bay, burning more than 15 leagues of New England country and killing or capturing more than 150 people. The English colonists protected some of their settlements, but a number of others were destroyed and abandoned. Historian Samuel Drake reported that, "Maine had nearly received her death-blow" as a result of the campaign.
The Northeast Coast campaign (1723) occurred during Father Rale's War from April 19, 1723 – January 28, 1724. In response to the previous year, in which New England attacked the Wabanaki Confederacy at Norridgewock and Penobscot, the Wabanaki Confederacy retaliated by attacking the coast of present-day Maine that was below the Kennebec River, the border of Acadia. They attacked English settlements on the coast of present-day Maine between Berwick and Mount Desert Island. Casco was the principal settlement. The 1723 campaign was so successful along the Maine frontier that Dummer ordered its evacuation to the blockhouses in the spring of 1724.

The siege of Annapolis Royal in 1745 involved the third of four attempts by the French, along with their Acadian and native allies, to regain the capital of Nova Scotia/Acadia, Annapolis Royal, during King George's War. During the siege William Pote was taken prisoner and wrote one of the rare captivity narratives that exist from Nova Scotia and Acadia.
William Pote was a British surveyor and ship captain who wrote one of the few captivity narratives from Acadia/Nova Scotia when he was captured by the Wabanaki Confederacy during King George's War.

The Maliseet militia was made up of warriors from the Maliseet of northeastern North America. Along with the Wabanaki Confederacy, the French and Acadian militia, the Maliseet fought the British through six wars over a period of 75 years. They also mobilized against the British in the American Revolution. After confederation, Maliseet warriors eventually joined Canada's war efforts in World War I and World War II.
The Battle of Falmouth was fought at Falmouth, Maine when the Canadiens and Wabanaki Confederacy attacked the English New Casco Fort. The battle was part of the Northeast Coast Campaign (1703) during Queen Anne's War.
Simon-Gérard de La Place was a 17th-century French priest and missionary who served in Acadia, the French province in what is modern north-eastern Canada. He participated in King William's War against English-led forces in Acadia.















