
In Greco-Roman mythology, Aeneas was a Trojan hero, the son of the Dardanian prince Anchises and the Greek goddess Aphrodite. His father was a first cousin of King Priam of Troy, making Aeneas a second cousin to Priam's children. He is a minor character in Greek mythology and is mentioned in Homer's Iliad. Aeneas receives full treatment in Roman mythology, most extensively in Virgil's Aeneid, where he is cast as an ancestor of Romulus and Remus. He became the first true hero of Rome. Snorri Sturluson identifies him with the Norse god Víðarr of the Æsir.

Cassandra or Kassandra in Greek mythology was a Trojan priestess dedicated to the god Apollo and fated by him to utter true prophecies but never to be believed. In modern usage her name is employed as a rhetorical device to indicate a person whose accurate prophecies, generally of impending disaster, are not believed.

Publius Vergilius Maro, usually called Virgil or Vergil in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: the Eclogues, the Georgics, and the epic Aeneid. A number of minor poems, collected in the Appendix Vergiliana, were attributed to him in ancient times, but modern scholars consider his authorship of these poems to be dubious.

The Aeneid is a Latin epic poem that tells the legendary story of Aeneas, a Trojan who fled the fall of Troy and travelled to Italy, where he became the ancestor of the Romans. Written by the Roman poet Virgil between 29 and 19 BC, the Aeneid comprises 9,896 lines in dactylic hexameter. The first six of the poem's twelve books tell the story of Aeneas' wanderings from Troy to Italy, and the poem's second half tells of the Trojans' ultimately victorious war upon the Latins, under whose name Aeneas and his Trojan followers are destined to be subsumed.

In Greek mythology, Sinon or Sinopos was a fictional character who was a Greek warrior during the Trojan War.
In Greek mythology, the name Butes referred to several different people.

Turnus was the legendary King of the Rutuli in Roman history, and the chief antagonist of the hero Aeneas in Virgil's Aeneid.

In Roman mythology, Lavinia is the daughter of Latinus and Amata, and the last wife of Aeneas.
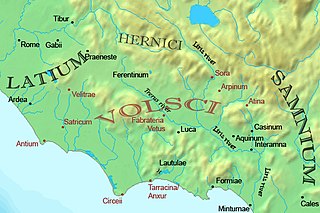
The Volsci were an Italic tribe, well known in the history of the first century of the Roman Republic. At the time they inhabited the partly hilly, partly marshy district of the south of Latium, bounded by the Aurunci and Samnites on the south, the Hernici on the east, and stretching roughly from Norba and Cora in the north to Antium in the south. Rivals of Rome for several hundred years, their territories were taken over by and assimilated into the growing republic by 300 BC. Rome's first emperor Augustus was of Volscian descent.

In Virgil's Aeneid, Camilla of the Volsci is the daughter of King Metabus and Casmilla.

Pallas and the Centaur is a painting by the Italian Renaissance painter Sandro Botticelli, c. 1482. It is now in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence. It has been proposed as a companion piece to his Primavera, though it is a different shape. The medium used is tempera paints on canvas and its size is 207 x 148 cm. The painting has been retouched in many places, and these retouchings have faded.

Tiberinus is a figure in Roman mythology. He was the god of the Tiber River. He was added to the 3,000 rivers, as the genius of the Tiber.

Messapus, a character in Virgil's Aeneid, appears in Books VII to XII of the Latin epic poem. He was a son of Neptune, a famous tamer of horses, and king of Etruria, known for being one "whom no one can fell by fire or steel".
Iarbas was a Roman mythological character, who has appeared in works by various authors including Ovid and Virgil. The character is possibly based on a historical king of Numidia.

The Avenger is a 1962 film directed by Giorgio Venturini.
Camilla and Camila are feminine given names. They originate as the feminine of camillus, a term for a youth serving as acolyte in the ritual of ancient Roman religion, which may be of Etruscan origin. Kamilla/Kamila are similar names.
Camille, reine des Volsques is an opera by the French composer André Campra, first performed at the Académie Royale de Musique on 9 November 1717. It takes the form of a tragédie en musique in a prologue and five acts. The libretto, by Antoine Danchet, is based on Virgil's Aeneid and concerns the Volscian queen Camilla.

The Girl in the Spider's Web is a 2018 action-thriller film directed by Fede Álvarez and written by Jay Basu, Álvarez, and Steven Knight, and based on the 2015 novel of the same name by David Lagercrantz, which in turn is based on characters in the Millennium book series by Stieg Larsson. The film acts as a soft-reboot/sequel to David Fincher's The Girl with the Dragon Tattoo. It stars Claire Foy in the role of Lisbeth Salander and follows Salander as she battles against a mysterious notorious organization, the Spiders, who seek world dominance. Sverrir Gudnason, Lakeith Stanfield, Sylvia Hoeks, and Stephen Merchant also appear in the film.
When writing the Aeneid, Virgil drew from his studies on the Homeric epics of the Iliad to help him create a national epic poem for the Roman people. Virgil used several characteristics associated with epic poetry, more specifically Homer's epics, including the use of hexameter verse, book division, lists of genealogies and underlying themes to draw parallels between the Romans and their cultural predecessors, the Greeks.
Camilla was an opera first performed at Drury Lane in London on 30 April 1706. The libretto was based on Il Trionfo di Camilla, regina de' Volsci by Silvio Stampiglia, translated into English verse by Owen Swiny, Peter Motteux, or others. Authorship of the music for the original is attributed variously to Giovanni Bononcini and to his brother Marc Antonio. Music for the London version was adapted by Nicola Haym. The opera was the first to be sung in a mixture of English and Italian, and it was one of the first London operas in which the castrato Nicolò Grimaldi performed.














