
Aromatic compounds or arenes usually refers to organic compounds "with a chemistry typified by benzene" and "cyclically conjugated." The word "aromatic" originates from the past grouping of molecules based on odor, before their general chemical properties were understood. The current definition of aromatic compounds does not have any relation to their odor. Aromatic compounds are now defined as cyclic compounds satisfying Hückel's Rule. Aromatic compounds have the following general properties:

Trinitrotoluene, more commonly known as TNT (and more specifically 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, and by its preferred IUPAC name 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene), is a chemical compound with the formula C6H2(NO2)3CH3. TNT is occasionally used as a reagent in chemical synthesis, but it is best known as an explosive material with convenient handling properties. The explosive yield of TNT is considered to be the standard comparative convention of bombs and asteroid impacts. In chemistry, TNT is used to generate charge transfer salts.

Toluene, also known as toluol, is a substituted aromatic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C6H5CH3, often abbreviated as PhCH3, where Ph stands for phenyl group. It is a colorless, water-insoluble liquid with the odor associated with paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, consisting of a methyl group (CH3) attached to a phenyl group by a single bond. As such, its systematic IUPAC name is methylbenzene. Toluene is predominantly used as an industrial feedstock and a solvent.

Acetophenone is the organic compound with the formula C6H5C(O)CH3. It is the simplest aromatic ketone. This colorless, viscous liquid is a precursor to useful resins and fragrances.
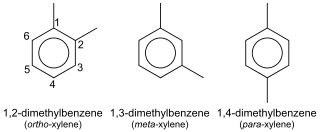
In organic chemistry, xylene or xylol are any of three organic compounds with the formula (CH3)2C6H4. They are derived from the substitution of two hydrogen atoms with methyl groups in a benzene ring; which hydrogens are substituted determines which of three structural isomers results. It is a colorless, flammable, slightly greasy liquid of great industrial value.
Demeton-S-methyl is an organic compound with the molecular formula C6H15O3PS2. It was used as an organothiophosphate acaricide and organothiophosphate insecticide. It is flammable. With prolonged storage, Demeton-S-methyl becomes more toxic due to formation of a sulfonium derivative which has greater affinity to the human form of the acetylcholinesterase enzyme, and this may present a hazard in agricultural use.

Toluene diisocyanate (TDI) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H3(NCO)2. Two of the six possible isomers are commercially important: 2,4-TDI (CAS: 584-84-9) and 2,6-TDI (CAS: 91-08-7). 2,4-TDI is produced in the pure state, but TDI is often marketed as 80/20 and 65/35 mixtures of the 2,4 and 2,6 isomers respectively. It is produced on a large scale, accounting for 34.1% of the global isocyanate market in 2000, second only to MDI. Approximately 1.4 billion kilograms were produced in 2000. All isomers of TDI are colorless, although commercial samples can appear yellow.

Ethylbenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2CH3. It is a highly flammable, colorless liquid with an odor similar to that of gasoline. This monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is important in the petrochemical industry as a reaction intermediate in the production of styrene, the precursor to polystyrene, a common plastic material. In 2012, more than 99% of ethylbenzene produced was consumed in the production of styrene.

p-Xylene (para-xylene) is an aromatic hydrocarbon. It is one of the three isomers of dimethylbenzene known collectively as xylenes. The p- stands for para-, indicating that the two methyl groups in p-xylene occupy the diametrically opposite substituent positions 1 and 4. It is in the positions of the two methyl groups, their arene substitution pattern, that it differs from the other isomers, o-xylene and m-xylene. All have the same chemical formula C6H4(CH3)2. All xylene isomers are colorless and highly flammable. The odor threshold of p-xylene is 0.62 parts per million (ppm).

Hippuric acid is a carboxylic acid and organic compound. It is found in urine and is formed from the combination of benzoic acid and glycine. Levels of hippuric acid rise with the consumption of phenolic compounds. The phenols are first converted to benzoic acid, and then to hippuric acid and excreted in urine.
para-Cresol, also 4-methylphenol, is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4(OH). It is a colourless solid that is widely used intermediate in the production of other chemicals. It is a derivative of phenol and is an isomer of o-cresol and m-cresol.

m-Xylene (meta-xylene) is an aromatic hydrocarbon. It is one of the three isomers of dimethylbenzene known collectively as xylenes. The m- stands for meta-, indicating that the two methyl groups in m-xylene occupy positions 1 and 3 on a benzene ring. It is in the positions of the two methyl groups, their arene substitution pattern, that it differs from the other isomers, o-xylene and p-xylene. All have the same chemical formula C6H4(CH3)2. All xylene isomers are colorless and highly flammable.
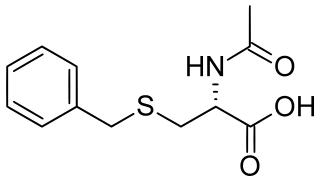
Benzylmercapturic acid is a minor metabolite of toluene in humans and is used in the diagnosis of toluene exposure. As its name indicates, is a benzyl derivative of mercapturic acid (acetylcysteine).
Toluene toxicity refers to the harmful effects caused by toluene on the body.
1,2,4-Trimethylbenzene, also known as pseudocumene, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H3(CH3)3. Classified as an aromatic hydrocarbon, it is a flammable colorless liquid with a strong odor. It is nearly insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. It occurs naturally in coal tar and petroleum (about 3%). It is one of the three isomers of trimethylbenzene.

Tricresyl phosphate (TCP), is a mixture of three isomeric organophosphate compounds most notably used as a flame retardant. Other uses include as a plasticizer in manufacturing for lacquers and varnishes and vinyl plastics and as an antiwear additive in lubricants. Pure tricresyl phosphate is a colourless, viscous liquid, although commercial samples are typically yellow. It is virtually insoluble in water, but easily soluble in organic solvents like toluene, hexane, and diethyl ether among others. It was synthesized by Alexander Williamson in 1854 upon reacting phosphorus pentachloride with cresol, though today's manufacturers can prepare TCP by mixing cresol with phosphorus oxychloride or phosphoric acid as well. TCP, especially the all-ortho isomer, is the causative agent in a number of acute poisonings. Its chronic toxicity is also of concern. The ortho-isomer is rarely used on its own outside of laboratory studies that require isomeric purity, due to its extremely toxic nature, and is generally excluded from commercial products where TCP is involved.

Benzotrichloride (BTC), also known as α,α,α-trichlorotoluene, phenyl chloroform or (trichloromethyl)benzene, is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CCl3. Benzotrichloride is an unstable, colorless or somewhat yellowish, viscous, chlorinated hydrocarbon with a penetrating odor. Benzotrichloride is used extensively as a chemical intermediate for products of various classes, i.e. dyes and antimicrobial agents.
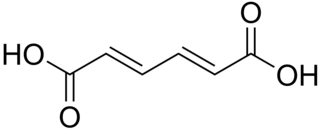
Muconic acid is a dicarboxylic acid. There are three isomeric forms designated trans,trans-muconic acid, cis,trans-muconic acid, and cis,cis-muconic acid which differ by the geometry around the double bonds. Its name is derived from mucic acid.

Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon.
In analytical chemistry, biomonitoring is the measurement of the body burden of toxic chemical compounds, elements, or their metabolites, in biological substances. Often, these measurements are done in blood and urine. Biomonitoring is performed in both environmental health, and in occupational safety and health as a means of exposure assessment and workplace health surveillance.
















