Related Research Articles
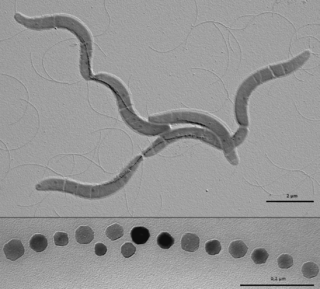
The Rhodospirillales are an order of Proteobacteria.

Bacilli is a taxonomic class of bacteria that includes two orders, Bacillales and Lactobacillales, which contain several well-known pathogens such as Bacillus anthracis. Bacilli are almost exclusively gram-positive bacteria.

The Clostridia are a highly polyphyletic class of Firmicutes, including Clostridium and other similar genera. They are distinguished from the Bacilli by lacking aerobic respiration. They are obligate anaerobes and oxygen is toxic to them. Species of the class Clostridia are often but not always Gram-positive and have the ability to form spores. Studies show they are not a monophyletic group, and their relationships are not entirely certain. Currently, most are placed in a single order called Clostridiales, but this is not a natural group and is likely to be redefined in the future.
The Xanthomonadaceae are a family of Proteobacteria, within the Xanthomonadales order.
Oceanospirillaceae is a family of Proteobacteria. Most genera in this family live in environments with high concentrations of salt; they are halotolerant or halophilic. They are marine, except Balneatrix which is found in fresh water.

Archaeoglobaceae are a family of the Archaeoglobales. All known genera within the Archaeoglobaceae are hyperthermophilic and can be found near undersea hydrothermal vents. Archaeoglobaceae are the only family in the order Archaeoglobales, which is the only order in the class Archaeoglobi.

Haemophilus is a genus of Gram-negative, pleomorphic, coccobacilli bacteria belonging to the family Pasteurellaceae. While Haemophilus bacteria are typically small coccobacilli, they are categorized as pleomorphic bacteria because of the wide range of shapes they occasionally assume. These organisms inhabit the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, mouth, vagina, and intestinal tract. The genus includes commensal organisms along with some significant pathogenic species such as H. influenzae—a cause of sepsis and bacterial meningitis in young children—and H. ducreyi, the causative agent of chancroid. All members are either aerobic or facultatively anaerobic. This genus has been found to be part of the salivary microbiome.
In taxonomy, the Thermoplasmata are a class of the Euryarchaeota.
In taxonomy, the Thermoplasmatales are an order of the Thermoplasmata. All are acidophiles, growing optimally at pH below 2. Picrophilus is currently the most acidophilic of all known organisms, being capable of growing at a pH of -0.06. Many of these organisms do not contain a cell wall, although this is not true in the case of Picrophilus. Most members of the Thermotoplasmata are thermophilic.

In the taxonomy of microorganisms, the Methanomicrobia are a class of the Euryarchaeota.

Methylomonas methanica is a Gram-negative bacterium that obtains its carbon and energy from methane, a metabolic process called methanotrophy. It is found in lakes, ponds, freshwater sediment and marshy ground. They are motile, the cells are rod-shaped.
Scandinavica may refer to:
The phylum Elusimicrobiota, previously known as "Termite Group 1", has been shown to be widespread in different ecosystems like marine environment, sewage sludge, contaminated sites and soils, and toxic wastes. The high abundance of Elusimicrobiota representatives is only evidenced for the lineage of symbionts found in termites and ants.
Armatimonadota is a phylum of gram-negative bacteria.

The Thermoanaerobacteraceae is a highly polyphyletic family of bacteria placed within the class clostridia. Originally placed within the highly polyphyletic class Clostridia and order Thermoanaerobacterales, according to the NCBI and LPSN, it is now thought to be a basal clade of the phylum Firmicutes.
3-hexulose-6-phosphate synthase is an enzyme with systematic name D-arabino-hex-3-ulose-6-phosphate formaldehyde-lyase (D-ribulose-5-phosphate-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Methylomonas scandinavica is a species of Gram-negative gammaproteobacteria found in deep igneous rock ground water in Sweden. As a member of the Methylomonas genus, M. scandinavica has the ability to use methane as a carbon source.
The Mycobacteriales are an order of bacteria.
The Propionibacteriales are an order of bacteria.