In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride is an organic compound with the functional group −C(=O)Cl. Their formula is usually written R−COCl, where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids. A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride, CH3COCl. Acyl chlorides are the most important subset of acyl halides.

In organic chemistry, an acyl halide is a chemical compound derived from an oxoacid by replacing a hydroxyl group with a halide group.

Phosphorus pentachloride is the chemical compound with the formula PCl5. It is one of the most important phosphorus chlorides/oxychlorides, others being PCl3 and POCl3. PCl5 finds use as a chlorinating reagent. It is a colourless, water-sensitive solid, although commercial samples can be yellowish and contaminated with hydrogen chloride.

Phosphorus trichloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula PCl3. A colorless liquid when pure, it is an important industrial chemical, being used for the manufacture of phosphites and other organophosphorus compounds. It is toxic and reacts readily with water to release hydrogen chloride.

Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether.

Phosphorous acid (or phosphonic acid) is the compound described by the formula H3PO3. This acid is diprotic (readily ionizes two protons), not triprotic as might be suggested by this formula. Phosphorous acid is an intermediate in the preparation of other phosphorus compounds. Organic derivatives of phosphorous acid, compounds with the formula RPO3H2, are called phosphonic acids.
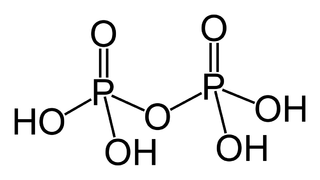
A phosphoric acid, in the general sense, is a phosphorus oxoacid in which each phosphorus (P) atom is in the oxidation state +5, and is bonded to four oxygen (O) atoms, one of them through a double bond, arranged as the corners of a tetrahedron. Two or more of these PO
4 tetrahedra may be connected by shared single-bonded oxygens, forming linear or branched chains, cycles, or more complex structures. The single-bonded oxygen atoms that are not shared are completed with acidic hydrogen atoms. The general formula of a phosphoric acid is H
n+2−2xP
nO
3n+1−x, where n is the number of phosphorus atoms and x is the number of fundamental cycles in the molecule's structure, between 0 and (n+2)/2.
The nitrosonium ion is NO+, in which the nitrogen atom is bonded to an oxygen atom with a bond order of 3, and the overall diatomic species bears a positive charge. It can be viewed as nitric oxide with one electron removed. This ion is usually obtained as the following salts: NOClO4, NOSO4H (nitrosylsulfuric acid, more descriptively written ONSO3OH) and NOBF4. The ClO−4 and BF−4 salts are slightly soluble in acetonitrile CH3CN. NOBF4 can be purified by sublimation at 200–250 °C and 0.01 mmHg (1.3 Pa).

In organic chemistry, phosphonates or phosphonic acids are organophosphorus compounds containing C−PO(OR)2 groups. Phosphonic acids, typically handled as salts, are generally nonvolatile solids that are poorly soluble in organic solvents, but soluble in water and common alcohols.
Organophosphorus chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organophosphorus compounds, which are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents.

Organolead chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organolead compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a chemical bond between carbon and lead. The first organolead compound was hexaethyldilead (Pb2(C2H5)6), first synthesized in 1858. Sharing the same group with carbon, lead is tetravalent.

Triphenylphosphine oxide (often abbreviated TPPO) is the organophosphorus compound with the formula OP(C6H5)3, also written as Ph3PO or PPh3O (Ph = C6H5). This colourless crystalline compound is a common but potentially useful waste product in reactions involving triphenylphosphine. It is a popular reagent to induce the crystallizing of chemical compounds.

Hexamethyldisiloxane (HMDSO or MM) is an organosilicon compound with the formula O[Si(CH3)3]2. This volatile colourless liquid is used as a solvent and as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is prepared by the hydrolysis of trimethylsilyl chloride. The molecule is the protypical disiloxane and resembles a subunit of polydimethylsiloxane.

Hexafluorophosphate is an anion with chemical formula of [PF6]−. It is an octahedral species that imparts no color to its salts. [PF6]− is isoelectronic with sulfur hexafluoride, SF6, and the hexafluorosilicate dianion, [SiF6]2−, and hexafluoroantimonate [SbF6]−. In this anion, phosphorus has a valence of 5. Being poorly nucleophilic, hexafluorophosphate is classified as a non-coordinating anion.

Thioacetic acid is an organosulfur compound with the molecular formula CH3C(O)SH. It is the sulfur analogue of acetic acid, as implied by the thio- prefix. It is a yellow liquid with a strong thiol-like odor. It is used in organic synthesis for the introduction of thiol groups in molecules.

Thiophosphoryl chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula PSCl3. It is a colorless pungent smelling liquid that fumes in air. It is synthesized from phosphorus chloride and used to thiophosphorylate organic compounds, such as to produce insecticides.

Methyltrichlorosilane, also known as trichloromethylsilane, is a monomer and organosilicon compound with the formula CH3SiCl3. It is a colorless liquid with a sharp odor similar to that of hydrochloric acid. As methyltrichlorosilane is a reactive compound, it is mainly used a precursor for forming various cross-linked siloxane polymers.

Tetrakis(hydroxymethyl)phosphonium chloride (THPC) is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula [P(CH2OH)4]Cl. The cation P(CH2OH)4+ is four-coordinate, as is typical for phosphonium salts. THPC has applications as a precursor to fire-retardant materials, as well as a microbiocide in commercial and industrial water systems.

Diethyl phosphite is the organophosphorus compound with the formula (C2H5O)2P(O)H. It is a popular reagent for generating other organophosphorus compounds, exploiting the high reactivity of the P-H bond. Diethyl phosphite is a colorless liquid. The molecule is tetrahedral.
Hydroxymethylation is a chemical reaction that installs the CH2OH group. The transformation can be implemented in many ways and applies to both industrial and biochemical processes.
















