
Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the dominant vegetation type. Temperate grassland regions include the Pampas of Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay, and the steppe of Ukraine, Russia, and Kazakhstan. Lands typically referred to as "prairie" tend to be in North America. The term encompasses the lower and mid-latitude of the area referred to as the Interior Plains of Canada, the United States, and Mexico. It includes all of the Great Plains as well as the wetter, hillier land to the east. From west to east, generally the drier expanse of shortgrass prairie gives way to mixed grass prairie and ultimately the richer soils of the tallgrass prairie.

The National Cooperative Soil Survey Program (NCSS) in the United States is a nationwide partnership of federal, regional, state, and local agencies and institutions. This partnership works together to cooperatively investigate, inventory, document, classify, and interpret soils and to disseminate, publish, and promote the use of information about the soils of the United States and its trust territories. The activities of the NCSS are carried out on national, regional, and state levels.

Downer is the New Jersey state soil. The Downer has four soil horizons:

Bama is the official state soil of Alabama.

Myakka soil is the official state soil of Florida, which has more than 1,500,000 acres (6,100 km2) of land composed partly or entirely of Myakka soils, out of its total acreage of 42,084,928 acres (170,311.66 km2). This soil is primarily located in broad flatwoods in irregularly shaped areas ranging from 5 to 500 acres in size. The organic matter content and fertility of the soil is low. Most areas where this soil occurs are native range or improved pasture, although some is used for citrus or vegetable farming. Some counties in Florida where this soil occurs are Hendry, Collier, Glades, and Lee.

Houdek is a type of soil composed of glacial till and decomposed organic matter. The soil series was established in 1955 in Spink County, South Dakota. It is unique to the United States, but in particular to South Dakota where it is the state soil.

The Kankakee Outwash Plain is a flat plain interspersed with sand dunes in the Kankakee River valley in northwestern Indiana and northeastern Illinois of the United States. It is just south of the Valparaiso Moraine and was formed during the Wisconsin Glaciation. As the glacier stopped at the Valparaiso Moraine, its meltwater was carried away to the outwash plain. On the south side of the moraine, where the elevation drops, the meltwaters eroded away valleys, carrying sand and mud with them. As the muddy meltwater reached the valley where the slope lessened, the water slowed, depositing the sand on the outwash plain. This created a smooth, flat, and sandy plain. Before its draining, the Kankakee Marsh, located on the outwash plain, was one of the largest freshwater marshes in the United States.

Menfro soil is a series of deep, well drained, moderately permeable soils formed in 6-to-20-foot thick loess deposits. It is found in central and eastern Missouri and west-central and southwestern Illinois on upland ridgetops, backslopes, and benches adjacent to the Missouri and Mississippi rivers and their major tributaries. Menfro soils are prime farmland where the slope is less than 6 percent.

A Stagnosol in the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB) is soil with strong mottling of the soil profile due to redox processes caused by stagnating surface water.
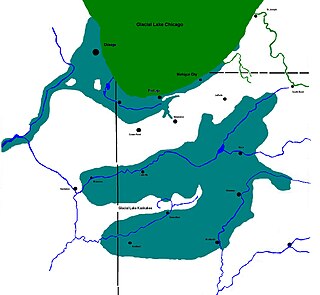
Lake Kankakee formed 14,000 years before present (YBP) in the valley of the Kankakee River. It developed from the outwash of the Michigan Lobe, Saginaw Lobe, and the Huron-Erie Lobe of the Wisconsin glaciation. These three ice sheets formed a basin across Northwestern Indiana. It was a time when the glaciers were receding, but had stopped for a thousand years in these locations. The lake drained about 13,000 YBP, until reaching the level of the Momence Ledge. The outcropping of limestone created an artificial base level, holding water throughout the upper basin, creating the Grand Kankakee Marsh.
The Olympic soil series is a type of deep, dark reddish brown, moderately fine-textured soil that has developed on mafic rock such as basalt. The series covers large areas in southwestern Washington and western Oregon, and usually supports forests of Douglas-fir, red alder, western redcedar, western hemlock, and bigleaf maple.

Agriculture in Alaska faces many challenges, largely due to the climate, the short growing season, and generally poor soils. However, the exceptionally long days of summer enable some vegetables to attain world record sizes.

The soils of the Kilte Awula’ilo woreda (district) in Tigray, Ethiopia reflect its longstanding agricultural history, highly seasonal rainfall regime, relatively low temperatures, the presence of a wide depression at the foot of the Atsbi horst and steep slopes. Outstanding features in the soilscape are the wide ancient fluvial deposits, the soils of the granite batholith, cuestas and fertile lands behind tufa dams.

The soils of the Atsbi Wenberta woreda (district) in Tigray (Ethiopia) reflect its longstanding agricultural history, highly seasonal rainfall regime and relatively low temperatures. The northern part of the district is on the high uplifted Atsbi Horst, whereas the southern part is dominated by the Des’a forest on Antalo Limestone. In between there is the fluvial landscape of Hayqi Meshal. Particularities in the southern part of the district are soil catenas on intervening plains behind tufa dams and in a polje.

The soils of the Sa'isi Tsa'ida Imba woreda (district) in Tigray (Ethiopia) reflect its longstanding agricultural history, highly seasonal rainfall regime, relatively low temperatures, overall dominance of metamorphic and sandstone lithology and steep slopes.
The soils of the Inderta woreda (district) in Tigray (Ethiopia) reflect its longstanding agricultural history, highly seasonal rainfall regime, relatively low temperatures, overall dominance of limestone and dolerite lithologies and steep slopes. Outstanding features in the soilscape are wide plains with Vertisols.

The soils of the Kola Tembien woreda (district) in Tigray (Ethiopia) reflect its longstanding agricultural history, highly seasonal rainfall regime, relatively high temperatures, overall dominance of sandstone and metamorphic lithology and steep slopes.

The soils of the Dogu’a Tembien woreda (district) in Tigray (Ethiopia) reflect its longstanding agricultural history, highly seasonal rainfall regime, relatively low temperatures, an extremely great variety in lithology and steep slopes. Outstanding features in the soilscape are the fertile highland Vertisols and Phaeozems in forests.

Crider is a soil series and the state soil of Kentucky.
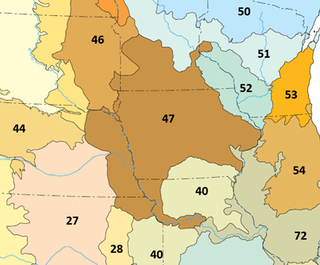
The Western Corn Belt Plains is a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in seven U.S. states, though predominantly in Iowa.


















