
SOAP is a messaging protocol specification for exchanging structured information in the implementation of web services in computer networks. It uses XML Information Set for its message format, and relies on application layer protocols, most often Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), although some legacy systems communicate over Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), for message negotiation and transmission.
Web annotation can refer to online annotations of web resources such as web pages or parts of them, or a set of W3C standards developed for this purpose. The term can also refer to the creations of annotations on the World Wide Web and it has been used in this sense for the annotation tool INCEpTION, formerly WebAnno. This is a general feature of several tools for annotation in natural language processing or in the philologies.
The MetaWeblog API is an application programming interface created by software developer Dave Winer that enables weblog entries to be written, edited, and deleted using web services.
Web Accessibility Initiative – Accessible Rich Internet Applications (WAI-ARIA) is a technical specification published by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) that specifies how to increase the accessibility of web pages, in particular, dynamic content, and user interface components developed with Ajax, HTML, JavaScript, and related technologies.
The Web Open Font Format (WOFF) is a font format for use in web pages. WOFF files are OpenType or TrueType fonts, with format-specific compression applied and additional XML metadata added. The two primary goals are first to distinguish font files intended for use as web fonts from fonts files intended for use in desktop applications via local installation, and second to reduce web font latency when fonts are transferred from a server to a client over a network connection.
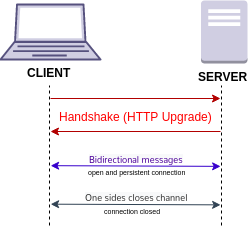
WebSocket is a computer communications protocol, providing simultaneous two-way communication channels over a single Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) connection. The WebSocket protocol was standardized by the IETF as RFC 6455 in 2011. The current specification allowing web applications to use this protocol is known as WebSockets. It is a living standard maintained by the WHATWG and a successor to The WebSocket API from the W3C.
Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) is a mechanism that allows restricted resources on a web page to be accessed from another domain outside the domain from which the first resource was served.
WebRTC is a free and open-source project providing web browsers and mobile applications with real-time communication (RTC) via application programming interfaces (APIs). It allows audio and video communication to work inside web pages by allowing direct peer-to-peer communication, eliminating the need to install plugins or download native apps.
WebSub is an open protocol for distributed publish–subscribe communication on the Internet. Initially designed to extend the Atom protocols for data feeds, the protocol can be applied to any data type as long as it is accessible via HTTP. Its main purpose is to provide real-time notifications of changes, which improves upon the typical situation where a client periodically polls the feed server at some arbitrary interval. In this way, WebSub provides pushed HTTP notifications without requiring clients to spend resources on polling for changes.

The FIDOAlliance is an open industry association launched in February 2013 whose stated mission is to develop and promote authentication standards that "help reduce the world’s over-reliance on passwords". FIDO addresses the lack of interoperability among devices that use strong authentication and reduces the problems users face creating and remembering multiple usernames and passwords.

Pump.io is a general-purpose activity streams engine that can be used as a federated social networking protocol which "does most of what people really want from a social network". Started by Evan Prodromou, it is a follow-up to StatusNet; Identi.ca, which was the largest StatusNet service, switched to pump.io in June 2013.
NATS is an open-source messaging system. The NATS server is written in the Go programming language. Client libraries to interface with the server are available for dozens of major programming languages. The core design principles of NATS are performance, scalability, and ease of use. The acronym NATS stands for Neural Autonomic Transport System.

A well-known URI is a Uniform Resource Identifier for URL path prefixes that start with /.well-known/. They are implemented in webservers so that requests to the servers for well-known services or information are available at URLs consistent well-known locations across servers.
Token Binding is a proposed standard for a Transport Layer Security (TLS) extension that aims to increase TLS security by using cryptographic certificates on both ends of the TLS connection. Current practice often depends on bearer tokens, which may be lost or stolen. Bearer tokens are also vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks or replay attacks. In contrast, bound tokens are established by a user agent that generates a private-public key pair per target server, providing the public key to the server, and thereafter proving possession of the corresponding private key on every TLS connection to the server.
Micro.blog is a microblogging and social networking service created by Manton Reece. It is the first large multi-user social media service to support the Webmention and Micropub standards published by the World Wide Web Consortium, and is part of the Fediverse, supporting ActivityPub.
uWSGI is an open source software application that "aims at developing a full stack for building hosting services". It is named after the Web Server Gateway Interface (WSGI), which was the first plugin supported by the project. uWSGI is maintained by Italian based software company unbit.

ActivityPub is an open, decentralized social networking protocol based on Pump.io's ActivityPump protocol. It provides a client/server API for creating, updating, and deleting content, as well as a federated server-to-server API for delivering notifications and content.
IndieAuth is an open standard decentralized authentication protocol that uses OAuth 2.0 and enables services to verify the identity of a user represented by a URL, as well as to obtain an access token, that can be used to access resources under the control of the user.
The Thing Description (TD) (or W3C WoT Thing Description (TD)) is a royalty-free, open information model with a JSON based representation format for the Internet of Things (IoT). A TD provides a unified way to describe the capabilities of an IoT device or service with its offered data model and functions, protocol usage, and further metadata. Using Thing Descriptions help reduce the complexity of integrating IoT devices and their capabilities into IoT applications.






