
HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It defines the content and structure of web content. It is often assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript.

Synchronized Multimedia Integration Language ) is a World Wide Web Consortium recommended Extensible Markup Language (XML) markup language to describe multimedia presentations. It defines markup for timing, layout, animations, visual transitions, and media embedding, among other things. SMIL allows presenting media items such as text, images, video, audio, links to other SMIL presentations, and files from multiple web servers. SMIL markup is written in XML, and has similarities to HTML.

Wireless Markup Language (WML), based on XML, is an obsolete markup language intended for devices that implement the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) specification, such as mobile phones. It provides navigational support, data input, hyperlinks, text and image presentation, and forms, much like HTML. It preceded the use of other markup languages used with WAP, such as XHTML and HTML itself, which achieved dominance as processing power in mobile devices increased.
A HTML editor is a program used for editing HTML, the markup of a web page. Although the HTML markup in a web page can be controlled with any text editor, specialized HTML editors can offer convenience, added functionality, and organisation. For example, many HTML editors handle not only HTML, but also related technologies such as CSS, XML and JavaScript or ECMAScript. In some cases they also manage communication with remote web servers via FTP and WebDAV, and version control systems such as Subversion or Git. Many word processing, graphic design and page layout programs that are not dedicated to web design, such as Microsoft Word or Quark XPress, also have the ability to function as HTML editors.
An HTML element is a type of HTML document component, one of several types of HTML nodes. The first used version of HTML was written by Tim Berners-Lee in 1993 and there have since been many versions of HTML. The current de facto standard is governed by the industry group WHATWG and is known as the HTML Living Standard.

NTT DoCoMo's i-mode is a mobile internet service popular in Japan. Unlike Wireless Application Protocols, i-mode encompasses a wider variety of internet standards, including web access, e-mail, and the packet-switched network that delivers the data. i-mode users also have access to other various services such as: sports results, weather forecasts, games, financial services, and ticket booking. Content is provided by specialised services, typically from the mobile carrier, which allows them to have tighter control over billing.
XHTML Basic is an XML-based structured markup language primarily designed for simple user agents, often found in mobile devices such as mobile phones, PDAs, pagers, and set-top boxes..
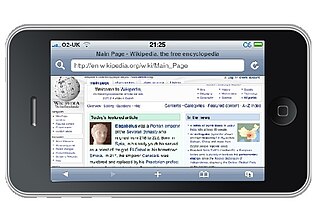
A mobile browser is a web browser designed for use on a mobile device such as a mobile phone, PDA, smartphone, or tablet. Mobile browsers are optimized to display Web content most effectively on small screens on portable devices. Mobile browser software must be small and efficient to accommodate the low memory capacity and low-bandwidth of wireless handheld devices. Traditional smaller feature phones use stripped-down mobile web browsers; however, most current smartphones have full-fledged browsers that can handle the latest web technologies, such as CSS 3, JavaScript, and Ajax.
Web standards are the formal, non-proprietary standards and other technical specifications that define and describe aspects of the World Wide Web. In recent years, the term has been more frequently associated with the trend of endorsing a set of standardized best practices for building web sites, and a philosophy of web design and development that includes those methods.
WapTV now Miniweb was the name given to the company which originated the WTVML as a content format for the delivery of Interactive TV applications using Internet Servers. The system is an Interactive television technology platform comprising a mobile browser, a markup language, and a significant collection of associated software tools and services.

William "Bill" Yeager is an American engineer. He is an inventor of a packet-switched, "Ships in the Night", multiple-protocol router in 1981.

The mobile web comprises mobile browser-based World Wide Web services accessed from handheld mobile devices, such as smartphones or feature phones, through a mobile or other wireless network.
Content adaptation is the action of transforming content to adapt to device capabilities. Content adaptation is usually related to mobile devices, which require special handling because of their limited computational power, small screen size, and constrained keyboard functionality.
A WAP gateway sits between mobile devices using the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) and the World Wide Web, passing pages from one to the other much like a proxy. This translates pages into a form suitable for the mobiles, for instance using the Wireless Markup Language (WML). This process is hidden from the phone, so it may access the page in the same way as a browser accesses HTML, using a URL, provided the mobile phone operator has not specifically prevented this. WAP gateway software encodes and decodes requests and responses between the smartphones, microbrowser and internet. It decodes the encoded WAP requests from the microbrowser and send the HTTP requests to the internet or to a local application server. It also encodes the WML and HDML data returning from the web for transmission to the microbrowser in the handset.
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) is a technical standard for accessing information over a mobile wireless network. A WAP browser is a web browser for mobile devices such as mobile phones that use the protocol. Introduced in 1999, WAP achieved some popularity in the early 2000s, but by the 2010s it had been largely superseded by more modern standards. Almost all modern handset internet browsers now fully support HTML, so they do not need to use WAP markup for web page compatibility, and therefore, most are no longer able to render and display pages written in WML, WAP's markup language.
Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) is part of the family of XML markup languages which mirrors or extends versions of the widely used HyperText Markup Language (HTML), the language in which Web pages are formulated.

Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a style sheet language used for specifying the presentation and styling of a document written in a markup language such as HTML or XML. CSS is a cornerstone technology of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and JavaScript.
The Web platform is a collection of technologies developed as open standards by the World Wide Web Consortium and other standardization bodies such as the Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group, the Unicode Consortium, the Internet Engineering Task Force, and Ecma International. It is the umbrella term introduced by the World Wide Web Consortium, and in 2011 it was defined as "a platform for innovation, consolidation and cost efficiencies" by W3C CEO Jeff Jaffe. Being built on The evergreen Web has allowed for the addition of new capabilities while addressing security and privacy risks. Additionally, developers are enabled to build interoperable content on a cohesive platform.








