
Khabarovsk is the largest city and the administrative centre of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia, located 30 kilometers (19 mi) from the China–Russia border, at the confluence of the Amur and Ussuri Rivers, about 800 kilometers (500 mi) north of Vladivostok. As of the 2021 Russian census, it had a population of 617,441. The city was the administrative center of the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia from 2002 until December 2018, when the status was given to Vladivostok. It is the largest city in the Russian Far East, having overtaken Vladivostok in 2015. It was known as Khabarovka until 1893. As is typical of the interior of the Russian Far East, Khabarovsk has an extreme climate with strong seasonal swings resulting in strong, cold winters and relatively hot and humid summers.
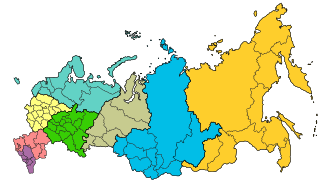
The federal districts are groupings of the federal subjects of Russia. Federal districts consist of a group of regions with various autonomy levels as per constitution, but the districts themselves are not mentioned by the constitution and are not autonomous, do not have administrative competences of their own, and do not manage regional affairs. They exist solely to monitor consistency between the federal and regional bodies of law, and ensure federal management of the civil service, judiciary, and federal agencies operating in the regions. The federal district system was established on 13 May 2000.

The Far Eastern Federal District is the largest of the eight federal districts of Russia, but the least populated, with a population of around 8 million according to the 2021 Census. The federal district lies entirely within the easternmost part of Asia and is coextensive with the Russian Far East.

The Battle of Lake Khasan, also known as the Changkufeng Incident in China and Japan, was an attempted military incursion by Manchukuo, a Japanese puppet state, into the territory claimed and controlled by the Soviet Union. That incursion was founded in the Japanese belief that the Soviet Union had misinterpreted the demarcation of the boundary based on the Treaty of Peking between Imperial Russia and Qing China and the subsequent supplementary agreements on demarcation and tampered with the demarcation markers. Japanese forces occupied the disputed area but withdrew after heavy fighting and a diplomatic settlement.

The North Caucasus Military District was a military district of the Russian Armed Forces from 1992-2010. Before 1992 it had been part of the Soviet Armed Forces since 1918. In 2010 it became the Southern Military District and lately also included the Black Sea Fleet and Caspian Flotilla.

The Military Historical Museum of Artillery, Engineers and Signal Corps, also known simply as the Artillery Museum, is a state-owned military museum in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Its collections – consisting of Russian military equipment, uniforms and decorations – are hosted in the Kronverk situated on the right bank of the Neva near Alexander Park. The museum is managed by the Russian Ministry of Defence.
Ivan Vasilievich Timokhovich was a Russian military historian, Doctor of Historical Sciences, professor, Honored Scientist of Russia, Associate Member of the Russian Academy of Natural Sciences, Major General, Russian Air Force.

The Order of the Red Banner Eastern Military District is a military district of Russia.

The military districts in Russia serve as administrative divisions for the Russian Armed Forces. Each has a headquarters administering the military formations within the Russian federal subjects that it includes.

Nikolai Dmitrievich Kashirin was a Soviet Komandarm 2nd rank. He fought for the Imperial Russian Army in World War I, receiving the Order of Saint Vladimir and the Order of Saint Anna. He was a recipient of the Order of the Red Banner. He was one of the judges at the trial of Marshal of the Soviet Union Mikhail Tukhachevsky in the Case of Trotskyist Anti-Soviet Military Organization in June 1937. Kashirin was himself arrested on 19 August 1937 and later executed. His younger brother, Ivan, was arrested on 20/21 June 1937 and executed on 20 September 1937.
The 26th Air Army was an Air army of the Soviet Air Forces active from 1949 to 1980, and then 1988-1992.

The Military Band of the Eastern Military District is a military band unit of the Russian Armed Forces. It is a branch of the Military Band Service of the Armed Forces of Russia. The band mainly performs in Khabarovsk and in cities in the Eastern Military District. It is the oldest creative collective in the Russian Far East.

Khabarovsk Tsentralny, is the primary Russian military airfield in Khabarovsk. It is located on the east side of the city, about 8 km southwest of Khabarovsk Novy Airport. The aerodrome operator is the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation, along with the 573rd Aviation Base of Army Aviation, and 12th Aircraft Repair Factory.
The National Military-Patriotic Center of the Armed Forces of Kazakhstan is a museum of the Armed Forces of Kazakhstan. Located on Respublika Avenue in the capital of Astana, it was conceived by Minister of Defense Saken Zhasuzakov and was officially opened by decree of the President of Kazakhstan Nursultan Nazarbayev on 1 December 2016. The center is located at the former building of the Presidential Palace of Culture and the Nazarbayev Center.

Viktor Borisovich Astapov is an officer of the Russian Armed Forces. He currently holds the rank of Lieutenant General, and since 2019 has served as a deputy commander in chief of the Russian Navy.

Protests began on 11 July 2020 in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia, in support of the popular then-Governor, Sergei Furgal, after his arrest that was seen by many as politically motivated. Similar protests in support of Furgal also took place in other mostly eastern cities, including Novosibirsk, Vladivostok and Omsk.

The 88th Separate Rifle Brigade, also known as the Northeast Anti-Japanese Allied Forces Teaching Brigade or the 88th International Brigade, was an international military unit of the Red Army created during World War II. It was unique in that it incorporated the peoples of Korea, China, and Soviet Central Asia in its ranks.

The Kyrgyz State History Museum is a museum located in Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan. The museum contains literally thousands of exhibits about the cultural heritage of the Kyrgyz people, whose sculptures and objects date from antiquity to the end of the 20th century. It is one of the most important museums in Central Asia.

The Nazranians were a historical Ingush ethnoterritorial subethnic group (society) which inhabited modern day Nazranovsky District and Prigorodny District.
Arsiko-Makhamaz-ogly was the Kistin naib of Imam Shamil who served as the governor of the District of Mountainous Chechnya of North Caucasian Imamate during the Caucasian War. Arsiko was also referred as the Kistin Naib. According to historian Yu. U. Dadayev, he was among the brave and faithful naibs of Shamil alongside Muhammad-Mirza Anzorov and a number of others.




















