
Konqueror, a free and open-source web browser and file manager, provides web access and file-viewer functionality for file systems. It forms a core part of the KDE Software Compilation. Developed by volunteers, Konqueror can run on most Unix-like operating systems. The KDE community licenses and distributes Konqueror under the GNU General Public License version 2.
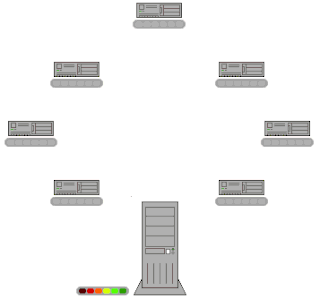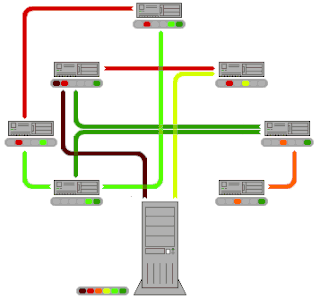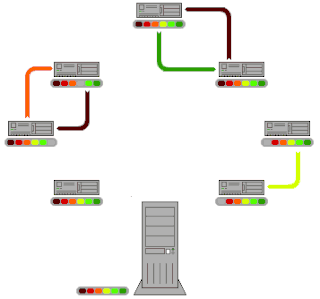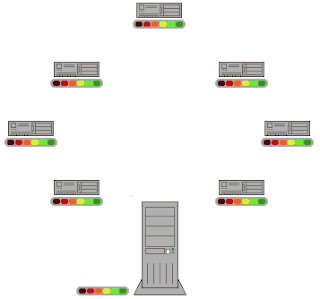
BitTorrent is a communication protocol for peer-to-peer file sharing (P2P) which is used to distribute data and electronic files over the Internet.

GNU Wget is a computer program that retrieves content from web servers. It is part of the GNU Project. Its name derives from World Wide Web and get. It supports downloading via HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP.

HEAnet is the national education and research network of Ireland.

FileZilla is a free software, cross-platform FTP application, consisting of FileZilla Client and FileZilla Server. Client binaries are available for Windows, Linux, and macOS, server binaries are available for Windows only. Both server and client support FTP and FTPS, while the client can in addition connect to SFTP servers.

The Pirate Bay is an online index of digital content of entertainment media and software. Founded in 2003 by Swedish think tank Piratbyrån, The Pirate Bay allows visitors to search, download, and contribute magnet links and torrent files, which facilitate peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing among users of the BitTorrent protocol.

Free Download Manager is a download manager for Windows and macOS.
GNUPanel is a hosting control panel for Debian. It is written in PHP and it is tailored to run on 32 and 64-bit Debian GNU/Linux web hosting servers. The administrator can create public and private hosting plans, accept PayPal, Cuentadigital and Dineromail payments, send messages to users, create redirections, use an integrated support ticket system, control bandwidth, disk space and define policies for account suspension. It provides the usual functions to create mail and FTP accounts, databases, directory security, etc. Additional functionality is included for domain parking and subdomain control over PHP directives including safe_mode and register_globals. GNUPanel stores its configuration in a PostgreSQL 9.1 database and provides three web interfaces with SSL access. User, reseller and administrator accounts may be created.

The GNU Affero General Public License is a free, copyleft license published by the Free Software Foundation in November 2007, and based on the GNU General Public License, version 3 and the Affero General Public License.

Torrentz was a Finland-based metasearch engine for BitTorrent, run by an individual known as Flippy. Founded in July 24, 2003. It indexed torrents from various major torrent websites, and offered compilations of various trackers per torrent that were not necessarily present in the default .torrent file, so that when a tracker was down, other trackers could do the work. It was the second most popular torrent website in 2012.

Belnet is a Belgian internet provider for educational institutions, research centres, scientific institutes and government services. Since 1993, BELNET provides web services to higher education, federal departments and ministries, and international organisations.

EZTV was a TV torrent distribution group founded in May 2005 and dissolved in April 2015, after a hostile takeover of their domains and brand by "EZCLOUD LIMITED".

OpenMediaVault (OMV) is a free Linux distribution designed for network-attached storage (NAS). The project's lead developer is Volker Theile, who instituted it in 2009. OMV is based on the Debian operating system, and is licensed through the GNU General Public License v3.

KickassTorrents was a website that provided a directory for torrent files and magnet links to facilitate peer-to-peer file sharing using the BitTorrent protocol. It was founded in 2008 and by November 2014, KAT became the most visited BitTorrent directory in the world, overtaking The Pirate Bay, according to the site's Alexa ranking. KAT went offline on 20 July 2016 when the domain was seized by the U.S. government. The site's proxy servers were shut down by its staff at the same time.

This is a list of countries where at least one internet service provider (ISP) formerly or currently censors the popular file sharing website The Pirate Bay (TPB).

The InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) is a protocol and peer-to-peer network for storing and sharing data in a distributed file system. IPFS uses content-addressing to uniquely identify each file in a global namespace connecting all computing devices.

1337x is a website that provides a directory of torrent files and magnet links used for peer-to-peer file sharing through the BitTorrent protocol. According to the TorrentFreak news blog, 1337x is the third most popular torrent website as of 2018.

The Torrent Project or Torrent Search Project was a metasearch engine for torrent files, which consolidates links from other popular torrent hosting pages such as ExtraTorrent. It has been suggested as an alternative for the now closed Torrentz.eu site and KickassTorrents, and its index includes over 8 million torrent files, and has been said to have a very clean, simple interface. Beyond allowing torrent files of popular films it also carries self-produced content. The torrentproject.com URL was part of a 2014 United Kingdom High Court decision, which ordered it to be blocked. It has an API that allows the search function to be integrated into applications, and the news-site TorrentFreak has suggested that allow streaming in the future, and it has adopted the Torrents Time plugin.

YIFY Torrents or YTS is a peer-to-peer release group known for distributing large numbers of movies as free downloads through BitTorrent. YIFY releases were characterised through their HD video quality in a small file size, which attracted many downloaders. The original YIFY/YTS website was shut down by the MPAA in 2015; however, a website imitating the YIFY/YTS brand still gains a significant amount of traffic. 'YIFY' is derived from the name of the website's founder, Yiftach Swery.

















