
A phosphodiesterase inhibitor is a drug that blocks one or more of the five subtypes of the enzyme phosphodiesterase (PDE), thereby preventing the inactivation of the intracellular second messengers, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) by the respective PDE subtype(s). The ubiquitous presence of this enzyme means that non-specific inhibitors have a wide range of actions, the actions in the heart, and lungs being some of the first to find a therapeutic use.

Morus, a genus of flowering plants in the family Moraceae, consists of diverse species of deciduous trees commonly known as mulberries, growing wild and under cultivation in many temperate world regions. Generally, the genus has 64 subordinate taxa, three of which are well-known and are ostensibly named for the fruit color of the best-known cultivar: white, red, and black mulberry, with numerous cultivars and some taxa currently unchecked and awaiting taxonomic scrutiny. M. alba is native to South Asia, but is widely distributed across Europe, Southern Africa, South America, and North America. M. alba is also the species most preferred by the silkworm, and is regarded as an invasive species in Brazil and the United States.
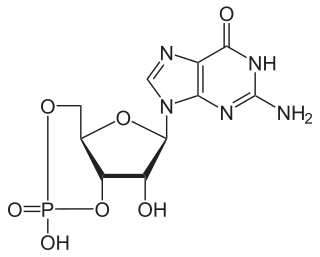
A phosphodiesterase (PDE) is an enzyme that breaks a phosphodiester bond. Usually, phosphodiesterase refers to cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases, which have great clinical significance and are described below. However, there are many other families of phosphodiesterases, including phospholipases C and D, autotaxin, sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase, DNases, RNases, and restriction endonucleases, as well as numerous less-well-characterized small-molecule phosphodiesterases.

Morus alba, known as white mulberry, common mulberry and silkworm mulberry, is a fast-growing, small to medium-sized mulberry tree which grows to 10–20 m (33–66 ft) tall. It is generally a short-lived tree with a lifespan comparable to that of humans, although there are some specimens known to be more than 250 years old. The species is native to China and India and is widely cultivated and naturalized elsewhere.

A phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor is a vasodilating drug that works by blocking the degradative action of cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) on cyclic GMP in the smooth muscle cells lining the blood vessels supplying various tissues. These drugs dilate the corpora cavernosa of the penis, facilitating erection with sexual stimulation, and are used in the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED). Sildenafil was the first effective oral treatment available for ED. Because PDE5 is also present in the smooth muscle of the walls of the arterioles within the lungs, two PDE5 inhibitors, sildenafil and tadalafil, are FDA-approved for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension. As of 2019, the wider cardiovascular benefits of PDE5 inhibitors are being appreciated.

Cyclic guanosine monophosphate-specific phosphodiesterase type 5 is an enzyme from the phosphodiesterase class. It is found in various tissues, most prominently the corpus cavernosum and the retina. It has also been recently discovered to play a vital role in the cardiovascular system.
Phosphodiesterase 1, PDE1, EC 3.1.4.1, systematic name oligonucleotide 5′-nucleotidohydrolase) is a phosphodiesterase enzyme also known as calcium- and calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase. It is one of the 11 families of phosphodiesterase (PDE1-PDE11). Phosphodiesterase 1 has three subtypes, PDE1A, PDE1B and PDE1C which divide further into various isoforms. The various isoforms exhibit different affinities for cAMP and cGMP.

The PDE2 enzyme is one of 21 different phosphodiesterases (PDE) found in mammals. These different PDEs can be subdivided to 11 families. The different PDEs of the same family are functionally related despite the fact that their amino acid sequences show considerable divergence. The PDEs have different substrate specificities. Some are cAMP selective hydrolases, others are cGMP selective hydrolases and the rest can hydrolyse both cAMP and cGMP.
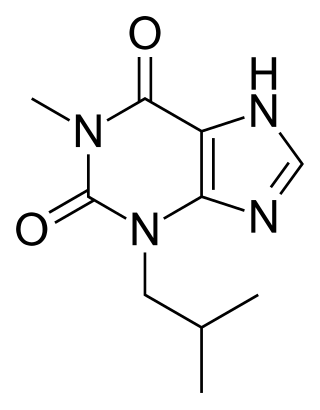
IBMX (3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine), like other methylated xanthine derivatives, is both a:
- competitive non-selective phosphodiesterase inhibitor which raises intracellular cAMP, activates PKA, inhibits TNFα and leukotriene synthesis, and reduces inflammation and innate immunity, and
- nonselective adenosine receptor antagonist.

Ibudilast is an anti-inflammatory drug used mainly in Japan, which acts as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, inhibiting the PDE4 subtype to the greatest extent, but also showing significant inhibition of other PDE subtypes.

cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDE4A gene.

cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4B is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDE4B gene.
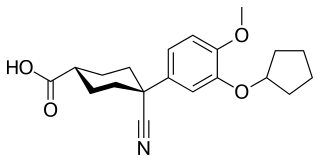
Cilomilast is a drug which was developed for the treatment of respiratory disorders such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is orally active and acts as a selective phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor.

Etazolate (SQ-20,009, EHT-0202) is an anxiolytic drug which is a pyrazolopyridine derivative and has unique pharmacological properties. It acts as a positive allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor at the barbiturate binding site, as an adenosine antagonist of the A1 and A2 subtypes, and as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor selective for the PDE4 isoform. It is currently in clinical trials for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
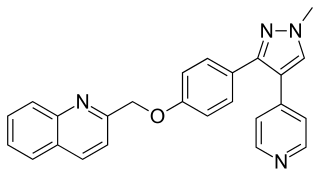
Mardepodect is a drug which was developed by Pfizer for the treatment of schizophrenia. It acts as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor selective for the PDE10A subtype. The PDE10A enzyme is expressed primarily in the brain, mostly in the striatum, nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle, and is thought to be particularly important in regulating the activity of dopamine-sensitive medium spiny neurons in the striatum which are known to be targets of conventional antipsychotic drugs. Older PDE10A inhibitors such as papaverine have been shown to produce antipsychotic effects in animal models, and more potent and selective PDE10A inhibitors are a current area of research for novel antipsychotic drugs which act through a different pathway to conventional dopamine or 5-HT2A antagonist drugs and may have a more favourable side effects profile. Mardepodect is currently one of the furthest advanced PDE10A inhibitors in development and has progressed through to Phase II clinical trials in humans. In 2017, development of mardepodect for the treatment of schizophrenia and Huntington's disease was discontinued.

Dihydromorin is a flavanonol, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in plants of the family Moraceae including Morus nigra, in Morus alba, Maclura pomifera, in the jackfruit and in Artocarpus dadah.

A phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, commonly referred to as a PDE4 inhibitor, is a drug used to block the degradative action of phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) on cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). It is a member of the larger family of PDE inhibitors. The PDE4 family of enzymes are the most prevalent PDE in immune cells. They are predominantly responsible for hydrolyzing cAMP within both immune cells and cells in the central nervous system.
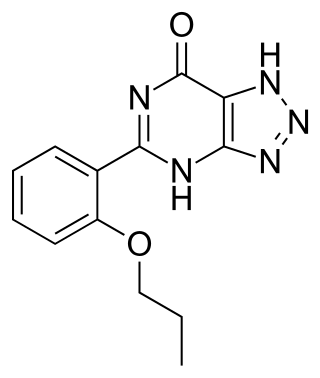
Zaprinast was an unsuccessful clinical drug candidate that was a precursor to the chemically related PDE5 inhibitors, such as sildenafil (Viagra), which successfully reached the market. It is a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, selective for the subtypes PDE5, PDE6, PDE9 and PDE11. IC50 values are 0.76, 0.15, 29.0, and 12.0 μM, respectively.

Oxyresveratrol is a stilbenoid. It is found in the heartwood of Artocarpus lakoocha and in the traditional drug 'Puag-Haad' made from it. It is also the aglycone of mulberroside A, a compound found in Morus alba, the white mulberry.
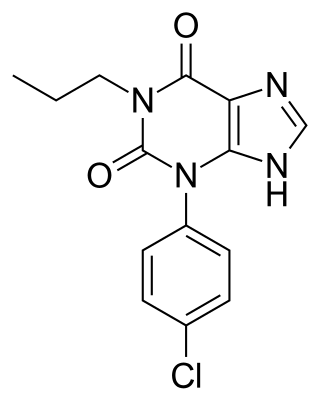
Arofylline is a phosphodiesterase inhibitor.


















