
Dry rot is wood decay caused by one of several species of fungi that digest parts of wood which give it strength and stiffness. It was previously used to describe any decay of cured wood in ships and buildings by a fungus which resulted in a darkly colored deteriorated and cracked condition.

Serpula lacrymans is a species of fungi known for causing dry rot. It is a basidiomycete in the order Boletales. It has the ability to rapidly colonise sites through unique and highly specialised mycelium which also leads to greater degradation rates of wood cellulose.

Mycelial cords are linear aggregations of parallel-oriented hyphae. The mature cords are composed of wide, empty vessel hyphae surrounded by narrower sheathing hyphae. Cords may look similar to plant roots, and also frequently have similar functions; hence they are also called rhizomorphs. As well as growing underground or on the surface of trees and other plants, some fungi make mycelial cords which hang in the air from vegetation.

Zygaena fausta is a member of the family Zygaenidae, the day-flying burnet moths. Its bright aposematic colours of red, white and black on the wings indicate to possible predators such as birds that it is foul tasting or poisonous. In flight, the bright red abdomen is revealed, contrasting with the white legs and black head and antennae; the thorax is black and white with an eye spot on each side. There appears to be a considerable variation in pattern among specimens from different parts of Europe.

Serpula is a genus of fungi in the family Serpulaceae.
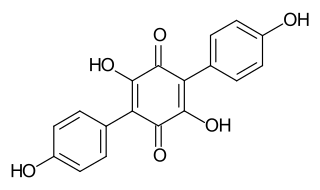
Atromentin is a natural chemical compound found in Agaricomycetes fungi in the orders Agaricales and Thelephorales. It can also be prepared by laboratory synthesis. Chemically, it is a polyphenol and a benzoquinone.

Xenocerus lacrymans is a species of beetles from the family Anthribidae, also known as fungus weevils.

Pulvinic acids are natural chemical pigments found in some lichens, derived biosynthetically from the aromatic amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine, via dimerization and oxidative ring-cleavage of arylpyruvic acids, a process that also produces the related pulvinones.

Serpula himantioides is a species of fungus that causes damage to timber referred to as dry rot. It is a basidiomycete in the order Boletales. It has been found on all continents except for Antarctica. Recent molecular work demonstrates that S. himantioides is a species complex including multiple cryptic lineages.
Scythropopsis is a genus of beetles in the family Cerambycidae, containing the following species, most of which were formerly classified under the genus name Psapharochrus:

Scythropopsis lacrymans is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae.
Morimopsini is a tribe of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae. It was described by Lacordaire in 1869.
Morimopsis is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae, containing the following species:

Trenetica lacrymans is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae, and the only species in the genus Trenetica. It was described by Thomson in 1864.
Morimopsis glabripennis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Holzschuh in 2003.
Morimopsis mussardi is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1965.
Morimopsis unicolor is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1975.

Atromentic acid is a red-organge pigment found in fungi within the Boletales group. It is the precursor to variegatic acid and xerocomic acid, and is preceded by atromentin. As an example, it is isolated from Serpula lacrymans. It is soluble in methanol. Variants include homoatromentic acid. This pigment has been studied and elucidated by Wolfgang Steglich and colleagues over decades. When atromentin is oxidised with hydrogen peroxide a yellow product is produced. A sodium hydroxide solution is also yellow, but when this is neutralized with acid the red atromentic acid crystallises. Concentrated potassium hydroxide breaks up the compound to p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid and oxalic acid.
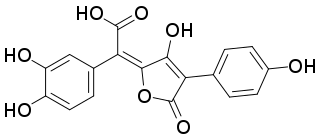
Isoxerocomic acid is a red-orange pigment found in Boletales. It is the precursor to variegatic acid, and is preceded by atromentic acid and atromentin. As an example, it is isolated from Serpula lacrymans. It is soluble in methanol. It is the isomer of xerocomic acid and precursor to xerocomorubin.

Leucoagaricus lacrymans is a species of mushroom producing fungus in the family Agaricaceae.













