
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and may require a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber.

A mordant or dye fixative is a substance used to set dyes on fabrics. It does this by forming a coordination complex with the dye, which then attaches to the fabric. It may be used for dyeing fabrics or for intensifying stains in cell or tissue preparations. Although mordants are still used, especially by small batch dyers, it has been largely displaced in industry by directs.

Morinda citrifolia is a fruit-bearing tree in the coffee family, Rubiaceae, native to Southeast Asia and Australasia, and was spread across the Pacific by Polynesian sailors. The species is now cultivated throughout the tropics and widely naturalized. There are over 100 names for this fruit across different regions. Common English names include great morinda, Indian mulberry, noni, beach mulberry, vomit fruit, awl tree, and cheese fruit.

Cotinus coggygria, syn. Rhus cotinus, the European smoketree, Eurasian smoketree, smoke tree, smoke bush, Venetian sumach, or dyer's sumach, is a Eurasian species of flowering plant in the family Anacardiaceae.

Lawsonia inermis, also known as hina, the henna tree, the mignonette tree, and the Egyptian privet, is a flowering plant and one of the only two species of the genus Lawsonia, with the other being Lawsonia odorata. The species is named after the Scottish physician Isaac Lawson, a good friend of Linnaeus.

Euonymus europaeus, the spindle, European spindle, or common spindle, is a species of flowering plant in the family Celastraceae, native to much of Europe, where it inhabits the edges of forest, hedges and gentle slopes, tending to thrive on nutrient-rich, chalky and salt-poor soils. It is a deciduous shrub or small tree.

Picea smithiana is a species of evergreen tree in the family Pinaceae family It is referred to by the common names morinda spruce and West Himalayan spruce, and is a spruce native to the western Himalaya and adjacent mountains, from northeast Afghanistan, northern Pakistan, India to central Nepal. It grows at altitudes of 2,400-3,600 m in forests together with deodar cedar, blue pine and pindrow fir.

Textile printing is the process of applying color to fabric in definite patterns or designs. In properly printed fabrics the colour is bonded with the fibre, so as to resist washing and friction. Textile printing is related to dyeing but in dyeing properly the whole fabric is uniformly covered with one colour, whereas in printing one or more colours are applied to it in certain parts only, and in sharply defined patterns.

Fuchsia excorticata, commonly known as tree fuchsia, New Zealand fuchsia and by its Māori name kōtukutuku, is a New Zealand native tree belonging to the family Onagraceae. It is commonly found throughout New Zealand and as far south as the Auckland Islands. It grows from sea level up to about 1,000 m (3,300 ft), particularly alongside creeks and rivers. It is easily recognised in its native environment by the characteristic appearance of its bark, which peels spontaneously, hanging in red papery strips to show a pale bark underneath. Its scientific name, excorticata, reflects this distinctive property.

Syzygium paniculatum, the magenta lilly pilly or magenta cherry, is a species of flowering plant in the myrtle family Myrtaceae, native to New South Wales, Australia. A broad dense bushy rainforest tree, in cultivation it grows to a height of 15 m (49 ft) with a trunk diameter up to 35 cm (14 in). The largest known example is at Ourimbah Creek, 35 m (115 ft) metres tall. The leaves are 3–9 cm (1.2–3.5 in) long, opposite, simple and slightly obovate, tapering at the leaf base. They are dark glossy green above, and paler below. White flowers are produced in clusters. The edible fruit is usually magenta, but can be white, pink or purple. The seeds are polyembryonic.

Kermes is a red dye derived from the dried bodies of the females of a scale insect in the genus Kermes, primarily Kermes vermilio. The Kermes insects are native in the Mediterranean region and are parasites living on the sap of the host plant, the Kermes oak and the Palestine oak.

Bombax buonopozense, commonly known as the Gold Coast bombax or red-flowered silk cotton tree, is a tree in the mallow family. It is also known in the Dagbani language as Vabga.

Rhaphiolepis indica, the Indian hawthorn, India hawthorn or Hong Kong hawthorn is an evergreen shrub in the family Rosaceae.
Turkey red is a dyeing methods that was widely used to give cotton a distinctive bright red colour in the 18th and 19th centuries. It was made using the root of the rubia (madder) plant, through a long and laborious process which originated in the historical Levant region, namely being developed in India and China. Turkey red was brought to Europe in the 1740s and in France was known as rouge d'Andrinople.
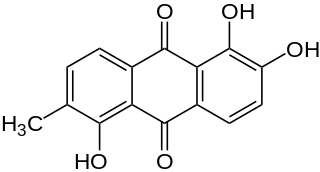
Morindone is an anthraquinone compound obtained from various Morinda species, especially M. tinctoria, but also M. citrifolia. Its principal use is as a dye, but it has also been investigated for anticancer and microbial uses.

Mallotus philippensis is a plant in the spurge family. It is known as the kamala tree or red kamala or kumkum tree, due to the fruit covering, which produces a red dye. However, it must be distinguished from kamala meaning "lotus" in many Indian languages, an unrelated plant, flower, and sometimes metonymic spiritual or artistic concept. Mallotus philippensis has many other local names. This kamala often appears in rainforest margins. Or in disturbed areas free from fire, in moderate to high rainfall areas.

Rubia tinctorum, the rose madder or common madder or dyer's madder, is a herbaceous perennial plant species belonging to the bedstraw and coffee family Rubiaceae.

Natural dyes are dyes or colorants derived from plants, invertebrates, or minerals. The majority of natural dyes are vegetable dyes from plant sources—roots, berries, bark, leaves, and wood—and other biological sources such as fungi.

Dyeing is the craft of imparting colors to textiles in loose fiber, yarn, cloth or garment form by treatment with a dye. Archaeologists have found evidence of textile dyeing with natural dyes dating back to the Neolithic period. In China, dyeing with plants, barks and insects has been traced back more than 5,000 years. Natural insect dyes such as Tyrian purple and kermes and plant-based dyes such as woad, indigo and madder were important elements of the economies of Asia and Europe until the discovery of man-made synthetic dyes in the mid-19th century. Synthetic dyes quickly superseded natural dyes for the large-scale commercial textile production enabled by the industrial revolution, but natural dyes remained in use by traditional cultures around the world.

Cola nitida is a species of plant belonging to the family Malvaceae.




















