Related Research Articles
The Salvesen Mountains or Salvesen Range is a mountain range on the southern tip of South Georgia, rising to a maximum elevation of 2,330 metres (7,644 ft). They were created 127 million years ago and are made mainly from granite. The Cretaceous granite is embedded into the Jurassic basaltic lavas and dolerite dykes. Both of which are black so they create a striking colour contrast in exposures. Both the granite and the basalt were formed from rising magma formed on the divergent plate boundary where the southern Atlantic Ocean opened. The main ranges of South Georgia famously crossed by Ernest Shackleton in 1916, are less rugged and precipitous than the Salvesen Mountains as they are formed from folded sandstone. These were formed from sand deposition, the sediment for which was derived from erosion of the igneous rocks and rifting continental blocks.
Queen Maud Bay is a V-shaped bay 2.5 miles (4.0 km) wide at the entrance, lying immediately north of Nuñez Peninsula along the south coast of South Georgia. Roughly charted in 1819 by a Russian expedition under Bellingshausen, it was named prior to 1922 for Queen Maud, wife of King Haakon VII of Norway, probably by Norwegian whalers who frequented this coast.
Mount Normann is a mountain, 1,240 m (4061 ft), standing 1 mile (1.6 km) north of Smaaland Cove at the south end of South Georgia. The feature has appeared on charts since the 1930s. It was surveyed by the SGS in the period 1951–57, and named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for Wilhelm Normann (1870-1939), German chemist, whose work led to the introduction in about 1907 of the hydrogenation process for hardening whale oil.
Hound Bay is a bay at the base of Barff Peninsula. It is 2.5 miles (4 km) wide at its mouth and recedes 3 miles (5 km), entered between Tijuca Point and Cape Vakop along the north coast of South Georgia. The names "George Bay" and "Hundebugten" have appeared on charts for this feature. The South Georgia Survey (SGS) of 1951–52 reported that this bay was better known to whalers and sealers as "Bikjebugten". The name Hound Bay, proposed by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) is an English form of this name.
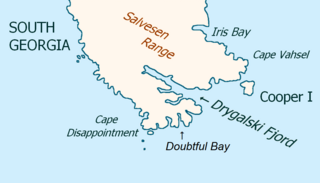
Drygalski Fjord is a bay 1 mile (1.6 km) wide which recedes northwestwards 7 miles (11 km), entered immediately north of Nattriss Head along the southeast coast of South Georgia. It was charted by the Second German Antarctic Expedition, 1911–12, under Wilhelm Filchner, and named for Professor Erich von Drygalski, the leader of the First German Antarctica Expedition, 1901–03.
Mount Paterson is a mountain, 2,195 m, standing 2 miles (3.2 km) north-northwest of Mount Carse in the Salvesen Range of South Georgia. Surveyed by the SGS in the period 1951–57, and named for Stanley B. Paterson, assistant surveyor of the SGS, 1955–56.
Hindle Glacier is a glacier 6 miles (10 km) long, flowing north from the vicinity of Mount Paterson into Royal Bay on the north coast of South Georgia. It was surveyed by the South Georgia Survey (SGS), 1951–52. The name "Bruce Glacier" was used unofficially by the British South Georgia Expedition, 1954–55, but a number of Antarctic features are named for Dr. William S. Bruce. The UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee recommended in 1957 that the glacier be named for Dr. Edward Hindle, a British zoologist who, as Honorary Secretary of the Royal Geographical Society, was of great assistance to the SGS expeditions.
Paget Glacier is a glacier in South Georgia, 4 miles (6 km) long and 1 mile (1.6 km) wide, which flows northeast from the north slopes of Mount Paget into the west side of Nordenskjold Glacier. The glacier was roughly surveyed in 1928–29 by a German expedition under Kohl-Larsen, and resurveyed in 1951–52 by the SGS. The name, which is derived from nearby Mount Paget, was given by the SGS in 1951–52.
Mount Sabatier is a mountain 1,145 m, standing close north of Mount Senderens and 1 mile (1.6 km) northeast of Paradise Beach in the south part of South Georgia. The feature appears on charts dating back to the 1930s. It was surveyed by the SGS in the period 1951–57, and named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for Professor Paul Sabatier (1854-1941), French chemist, whose work with Jean-Baptiste Senderens led to the introduction in about 1907 of the hydrogenation process for hardening whale oil.
Jason Harbour is a bay 1 mile (1.6 km) wide, lying west of Allen Bay in the north side of Cumberland West Bay, South Georgia. It was charted and named by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Otto Nordenskiöld. The bay was previously visited by the Jason, Captain C.A. Larsen, in 1894.
Graae Glacier is a glacier 2 miles (3 km) long on the north side of Mount Sabatier, flowing west-southwest to Trollhul in the south part of South Georgia. It was surveyed by the South Georgia Survey (SGS) in the period 1951–57, and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Mogens E.W. Graae of Denmark, who developed sledges for the SGS, 1953–54 and 1955–56.
Webb Glacier is a glacier, 2 miles (3.2 km) long, flowing southeast from Mount Brooker into Ross Glacier on the north side of South Georgia. Surveyed by the South Georgia Survey, 1954–55. Named for Edgar Clive Webb, member of the SGS who, with Ian.M. Brooker, climbed Mount Brooker on January 30, 1955. This glacier forms part of the approach route to the mountain.
Wheeler Glacier is a glacier draining the north flank of Mount Fraser, flowing west-northwest for 2 miles (3.2 km) to the south coast of South Georgia. Surveyed by the SGS in the period 1951–57. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for J.F.G. Wheeler, British zoologist and member of the scientific staff of the Discovery Investigations Marine Station, Grytviken, South Georgia, 1925–27 and 1929–30.
Mount Woodward is a mountain, 770 m, standing 1.5 miles (2.4 km) east of the mouth of Antarctic Bay on the north coast of South Georgia. Surveyed by the SGS in the period 1951–57, and named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for Roswall Woodward, of New Haven, Connecticut, who in 1790 commanded one of the first two American sealing vessels to visit South Georgia. Nearby Antarctic Bay was at one time known as "Woodward Harbour", but this name did not survive.
Smillie Peak is a rock peak, 1,765 m, standing 1 mile (1.6 km) east of Mount Corneliussen in the west extremity of the Allardyce Range of South Georgia. Surveyed by the SGS, 1951–52, and named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for Gordon Smillie, SGS surveyor.

Moraine Fjord is an inlet 3.5 nautical miles long with a reef extending across its entrance, forming the west head of Cumberland East Bay, South Georgia. It was charted by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Otto Nordenskjöld, 1901–04, who so named it because of the large glacial moraine at its entrance.
Spenceley Glacier is a glacier 6 nautical miles (11 km) long, flowing northwest along the southwest flank of Salvesen Range to Brøgger Glacier, in the south part of South Georgia. Surveyed by the South Georgia Survey (SGS) under Duncan Carse in the period 1951–57, and named for George Spenceley, photographer, mountaineer on the SGS, 1955–56 and member of the Yorkshire Ramblers' Club and Alpine Club.
Nilsen Island is a small island lying 1.5 nautical miles (2.8 km) west of the north part of Novosilski Bay, off the south coast of South Georgia. The island has appeared on charts since the 1930s. It was recharted by SGS in the period 1951–57, and named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for Nochart Nilsen, gunner of the Compania Argentina de Pesca, Grytviken, 1939–40 and 1946–48, and of the South Georgia Whaling Company, Leith Harbor, for several years beginning in 1949.
Turpie Rock is a rock 1 m high, lying in the entrance to Hercules Bay off the north coast of South Georgia. Positioned by the SGS in the period 1951–57, and named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for the Turpie, which was for many years used by the South Georgia Whaling Co. as a hulk at Leith Harbor and is now sunk there.
Hauge Reef is a chain of islands and rocks extending in an east-northeast direction from the eastern extremity of Annenkov Island to a point about 3 nautical miles (6 km) west-southwest of Cape Darnley, South Georgia. It was first charted in 1819 by a Russian expedition under Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen. The reef was surveyed by the South Georgia Survey (SGS), 1951–52, and named for Captain Ole Hauge, of the sealer Albatros, whose knowledge of the coasts of South Georgia was of great assistance to the SGS.
References
- ↑ "Mount Baume". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior . Retrieved 11 November 2013.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Mount Baume". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Mount Baume". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.