
Cape Hooker is the south-eastern point of Low Island, in the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. The feature was roughly charted by nineteenth century sealers; it was further charted by Commander Henry Foster in 1829 but shown as the north-eastern point of the island. Following air photography by the Falkland Islands and Dependencies Aerial Survey Expedition in 1956, the charted shape of the island was drastically altered and the name Cape Hooker was applied to its south-eastern point as originally described.
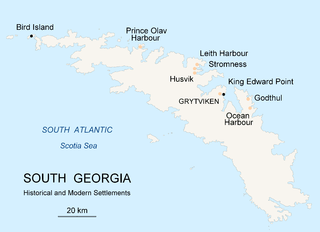
Prince Olav Harbour is a small harbour in the south west portion of Cook Bay, entered between Point Abrahamsen and Sheep Point, along the north coast of South Georgia.
Iris Bay is a small bay immediately south of Muller Point at the east end of South Georgia, lying 6 miles (10 km) northwest of Cape Vahsel, along the embayment between Cape Vahsel and Cape Charlotte. The name "Sandwich Bay", for John Montagu, 4th Earl of Sandwich, was given to the whole embayment between Cape Vahsel and Cape Charlotte in 1775 by a British expedition under James Cook. The name was later restricted on maps to the small bay described, since a name for the large embayment was not considered useful. The South Georgia Survey, 1951–52, reported that the name Iris Bay for the same feature is well established in use among the whalers and sealers in South Georgia, and that the name Sandwich Bay is unknown locally, so Iris Bay was approved to conform with local usage.
Barff Peninsula is a peninsula forming the east margin of Cumberland East Bay, South Georgia Island. It is 8 miles (13 km) long and extends northwest from Sörling Valley to Barff Point, its farthest extremity. It was probably first seen by the British expedition under James Cook in 1775. The peninsula as a whole takes its name from Barff Point, which was named for Royal Navy Lieutenant A.D. Barff of HMS Sappho, who, assisted by Captain C.A. Larsen, sketched a map of Cumberland Bay in 1906. Barff Point is considered the eastern headland of East Cumberland Bay.
Jason Harbour is a bay 1 mile (1.6 km) wide, lying west of Allen Bay in the north side of Cumberland West Bay, South Georgia. It was charted and named by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Otto Nordenskiöld. The bay was previously visited by the Jason, Captain C.A. Larsen, in 1894.
Lyell Glacier is a glacier flowing in a northerly direction to Harpon Bay at the southeast head of Cumberland West Bay, South Georgia. It was mapped by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Otto Nordenskjöld, who named it for Sir Charles Lyell, an eminent British geologist.
Twitcher Glacier is a glacier, 4 miles (6 km) long, which flows east from the Salvesen Range to the east coast of South Georgia, immediately south of Herz Glacier and Iris Bay. The glacier was surveyed in 1951-52 by the SGS. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for John Montagu, 4th Earl of Sandwich, First Lord of the Admiralty, 1771–82, who was popularly known as "Jemmy Twitcher."

Bertrab Glacier is a small glacier at the head of Gold Harbour, at the east end of South Georgia. It was charted by the Second German Antarctic Expedition, 1911–12, under Wilhelm Filchner, and named by him for General von Bertrab, Chief Quartermaster in the German General Staff and Chief of the Land Survey, who was chairman of the expedition.

Larsen Harbour is a narrow 2.6 miles (4.2 km) long inlet of indenting volcanic rocks and sheeted dykes known as the Larsen Harbour Formation. It is a branch of Drygalski Fjord, entered 2.5 miles (4 km) west-northwest of Nattriss Head, at the southeast end of South Georgia Island. It was charted by the Second German Antarctic Expedition, 1911–12, under Filchner, who named it for Captain Carl Anton Larsen a Norwegian explorer, who made significant contributions to the exploration of Antarctica. The most significant of these was the first discovery of fossils on the continent, for which he received the Back Grant from the Royal Geographical Society. Larsen is also considered the founder of the Antarctic whaling industry and the settlement and whaling station of Grytviken, South Georgia.

Neko Harbour is an inlet of the Antarctic Peninsula on Andvord Bay, situated on the west coast of Graham Land.

Port Foster is one of the safest harbours in Antarctica, located in Deception Island in the South Shetland Islands.
Bogen Glacier is a small glacier on the north side of Drygalski Fjord between Trendall Crag and Hamilton Bay, at the southeast end of South Georgia. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1979 after Arne Bogen, Norwegian sealer working in South Georgia after 1950; Master of the sealing vessel Albatross and Station Foreman, Grytviken.
Dead End Glacier is a glacier flowing east from the south end of the Salvesen Range of South Georgia into the west side of Salomon Glacier. It was surveyed by the South Georgia Survey in the period 1951–57, and so named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee because there is no route for sledging parties from the head of this glacier to the north shore of Drygalski Fjord.
Lancing Glacier is a glacier 3 nautical miles (6 km) long, flowing south from Mount Corneliussen and Smillie Peak to Newark Bay on the south side of South Georgia. It was surveyed by the South Georgia Survey in the period 1951–57, and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for the Lancing, built in 1898, and converted to a whale factory ship in 1923. It was the first factory ship to be fitted with a slipway.
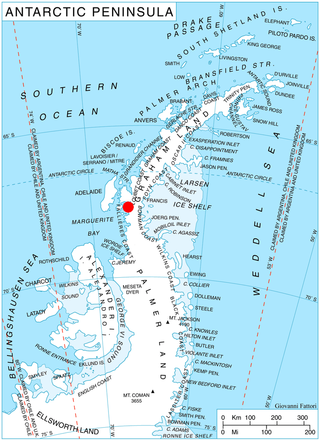
Bagshawe Glacier is a glacier which drains the northeast slopes of Mount Theodore and discharges into Lester Cove, Andvord Bay west of Mount Tsotsorkov, on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica.
Bolinder Bluff is a prominent bluff crowned by three buttresses of dark grey and light brown rock, overlooking Venus Bay 3 nautical miles (6 km) southeast of False Round Point on the north coast of King George Island, in the South Shetland Islands. The feature was known to sealers using the anchorage at nearby Esther Harbor in the 1820s. It was charted and named by Discovery Investigations personnel on the Discovery II in 1937 when the breakdown of the Bolinder boat engine caused 6 men to be marooned for 9 days on the beach at the foot of the bluff.
Frida Hole is a small bay lying 0.5 nautical miles (1 km) southeast of Coal Harbour, along the south coast and near the west end of South Georgia. It was probably named by early whalers or sealers who used the bay as an anchorage.
Morse Point is a point marking the east side of the entrance of Antarctic Bay on the north coast of South Georgia. The point appears roughly charted on maps dating back to about 1900; it was roughly surveyed by Discovery Investigations personnel in the period 1925–31, and resurveyed by the South Georgia Survey in 1951–52. The point was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee after the British sealing vessel Morse, which was working in South Georgia in 1799–1800, probably the first British sealer to do so. She was based at Antarctic Bay when encountered by Edmund Fanning, who published an account of the meeting.

Lucchitta Glacier is a glacier about 20 nautical miles (37 km) long flowing south from the Hudson Mountains of Antarctica into Pine Island Bay. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names after geologist Baerbel K. Lucchitta of the United States Geological Survey, Flagstaff, Arizona, a specialist in the use of satellite imagery for geological and glaciological studies from the early 1980s to the early 2000s (decade), and one of the pioneers in the use of imagery for glacier velocity measurements in Antarctica.
Coal Harbour is a small bay 0.5 nautical miles (0.9 km) east of Undine Harbor along the south coast and near the west end of South Georgia. The name Coaling Harbour, given in about 1912, suggests a possible early use of the bay by sealers and whalers. The name was shortened to 'Coal Harbour' by DI personnel who charted the area during the period 1926–30.









