Examples
Distinguishing multiple and single dispatch may be made clearer by an example. Imagine a game that has, among its (user-visible) objects, spaceships and asteroids. When two objects collide, the program may need to do different things according to what has just hit what.
Languages with built-in multiple dispatch
C#
C# introduced support for dynamic multimethods in version 4 [8] (April 2010) using the 'dynamic' keyword. The following example demonstrates multimethods. Like many other statically-typed languages, C# also supports static method overloading. [9] Microsoft expects that developers will choose static typing over dynamic typing in most scenarios. [10] The 'dynamic' keyword supports interoperability with COM objects and dynamically-typed .NET languages.
The example below uses features introduced in C# 9 and C# 10.
usingstaticColliderLibrary;Console.WriteLine(Collide(newAsteroid(101),newSpaceship(300)));Console.WriteLine(Collide(newAsteroid(10),newSpaceship(10)));Console.WriteLine(Collide(newSpaceship(101),newSpaceship(10)));stringCollide(SpaceObjectx,SpaceObjecty)=>x.Size>100&&y.Size>100?"Big boom!":CollideWith(xasdynamic,yasdynamic);// Dynamic dispatch to CollideWith methodclassColliderLibrary{publicstaticstringCollideWith(Asteroidx,Asteroidy)=>"a/a";publicstaticstringCollideWith(Asteroidx,Spaceshipy)=>"a/s";publicstaticstringCollideWith(Spaceshipx,Asteroidy)=>"s/a";publicstaticstringCollideWith(Spaceshipx,Spaceshipy)=>"s/s";}abstractrecordSpaceObject(intSize);recordAsteroid(intSize):SpaceObject(Size);recordSpaceship(intSize):SpaceObject(Size);Output:
Big boom!a/ss/sGroovy
Groovy is a general purpose Java compatible/interusable JVM language, which, contrary to Java, uses late binding / multiple dispatch. [11]
/* Groovy implementation of C# example above Late binding works the same when using non-static methods or compiling class/methods statically (@CompileStatic annotation)*/classProgram{staticvoidmain(String[]args){printlnCollider.collide(newAsteroid(101),newSpaceship(300))printlnCollider.collide(newAsteroid(10),newSpaceship(10))printlnCollider.collide(newSpaceship(101),newSpaceship(10))}}classCollider{staticStringcollide(SpaceObjectx,SpaceObjecty){(x.size>100&&y.size>100)?"big-boom":collideWith(x,y)// Dynamic dispatch to collideWith method}privatestaticStringcollideWith(Asteroidx,Asteroidy){"a/a"}privatestaticStringcollideWith(Asteroidx,Spaceshipy){"a/s"}privatestaticStringcollideWith(Spaceshipx,Asteroidy){"s/a"}privatestaticStringcollideWith(Spaceshipx,Spaceshipy){"s/s"}}classSpaceObject{intsizeSpaceObject(intsize){this.size=size}}@InheritConstructorsclassAsteroidextendsSpaceObject{}@InheritConstructorsclassSpaceshipextendsSpaceObject{}Common Lisp
In a language with multiple dispatch, such as Common Lisp, it might look more like this (Common Lisp example shown):
(defclassasteroid()((size:readersize:initarg:size)))(defclassspaceship()((size:readersize:initarg:size)))(defunspace-object(classsize)(make-instanceclass:sizesize)); collide-with is a generic function with multiple dispatch(defmethodcollide-with((xasteroid)(yasteroid))"a/a")(defmethodcollide-with((xasteroid)(yspaceship))"a/s")(defmethodcollide-with((xspaceship)(yasteroid))"s/a")(defmethodcollide-with((xspaceship)(yspaceship))"s/s")(defuncollide(xy)(if(and(>(sizex)100)(>(sizey)100))"big-boom"(collide-withxy)))(print(collide(space-object'asteroid101)(space-object'spaceship300)))(print(collide(space-object'asteroid10)(space-object'spaceship10)))(print(collide(space-object'spaceship101)(space-object'spaceship10)))and similarly for the other methods. Explicit testing and "dynamic casting" are not used.
In the presence of multiple dispatch, the traditional idea of methods as being defined in classes and contained in objects becomes less appealing—each collide-with method above is attached to two different classes, not one. Hence, the special syntax for method invocation generally disappears, so that method invocation looks exactly like ordinary function invocation, and methods are grouped not in classes but in generic functions.
Julia
Julia has built-in multiple dispatch, and it is central to the language design. [3] The Julia version of the example above might look like:
abstracttypeSpaceObjectendstructAsteroid<:SpaceObjectsize::IntendstructSpaceship<:SpaceObjectsize::Intendcollide_with(::Asteroid,::Spaceship)="a/s"collide_with(::Spaceship,::Asteroid)="s/a"collide_with(::Spaceship,::Spaceship)="s/s"collide_with(::Asteroid,::Asteroid)="a/a"collide(x::SpaceObject,y::SpaceObject)=(x.size>100&&y.size>100)?"Big boom!":collide_with(x,y)Output:
julia>collide(Asteroid(101),Spaceship(300))"Big boom!"julia>collide(Asteroid(10),Spaceship(10))"a/s"julia>collide(Spaceship(101),Spaceship(10))"s/s"Raku
Raku, like Perl, uses proven ideas from other languages, and type systems have shown themselves to offer compelling advantages in compiler-side code analysis and powerful user-side semantics via multiple dispatch.
It has both multimethods, and multisubs. Since most operators are subroutines, it also has multiple dispatched operators.
Along with the usual type constraints, it also has where constraints that allow making very specialized subroutines.
subsetMassofRealwhere0 ^..^ Inf; roleStellar-Object { hasMass$.massisrequired; methodname () returnsStr {...}; } classAsteroiddoesStellar-Object { methodname () { 'an asteroid' } } classSpaceshipdoesStellar-Object { hasStr$.name = 'some unnamed spaceship'; } myStr@destroyed = < obliterateddestroyedmangled >; myStr@damaged = « damaged'collided with''was damaged by' »; # We add multi candidates to the numeric comparison operators because we are comparing them numerically,# but makes no sense to have the objects coerce to a Numeric type.# ( If they did coerce we wouldn't necessarily need to add these operators. )# We could have also defined entirely new operators this same way.multisubinfix:« <=> » ( Stellar-Object:D$a, Stellar-Object:D$b ) { $a.mass <=> $b.mass } multisubinfix:« < » ( Stellar-Object:D$a, Stellar-Object:D$b ) { $a.mass < $b.mass } multisubinfix:« > » ( Stellar-Object:D$a, Stellar-Object:D$b ) { $a.mass > $b.mass } multisubinfix:« == » ( Stellar-Object:D$a, Stellar-Object:D$b ) { $a.mass == $b.mass } # Define a new multi dispatcher, and add some type constraints to the parameters.# If we didn't define it we would have gotten a generic one that didn't have constraints.protosubcollide ( Stellar-Object:D $, Stellar-Object:D $ ) {*} # No need to repeat the types here since they are the same as the prototype.# The 'where' constraint technically only applies to $b not the whole signature.# Note that the 'where' constraint uses the `<` operator candidate we added earlier.multisubcollide ( $a, $bwhere$a < $b ) { say"$a.name() was @destroyed.pick() by $b.name()"; } multisubcollide ( $a, $bwhere$a > $b ) { # redispatch to the previous candidate with the arguments swappedsamewith$b, $a; } # This has to be after the first two because the other ones# have 'where' constraints, which get checked in the# order the subs were written. ( This one would always match. )multisubcollide ( $a, $b ) { # randomize the ordermy ($n1, $n2) = ( $a.name, $b.name ).pick(*); say"$n1 @damaged.pick() $n2"; } # The following two candidates can be anywhere after the proto,# because they have more specialized types than the preceding three.# If the ships have unequal mass one of the first two candidates gets called instead.multisubcollide ( Spaceship$a, Spaceship$bwhere$a == $b ){ my ($n1, $n2) = ( $a.name, $b.name ).pick(*); say"$n1 collided with $n2, and both ships were ", ( @destroyed.pick, 'left damaged' ).pick; } # You can unpack the attributes into variables within the signature.# You could even have a constraint on them `(:mass($a) where 10)`.multisubcollide ( Asteroid $ (:mass($a)), Asteroid $ (:mass($b)) ){ say"two asteroids collided and combined into one larger asteroid of mass { $a + $b }"; } mySpaceship$Enterprise .= new(:mass(1),:name('The Enterprise')); collideAsteroid.new(:mass(.1)), $Enterprise; collide$Enterprise, Spaceship.new(:mass(.1)); collide$Enterprise, Asteroid.new(:mass(1)); collide$Enterprise, Spaceship.new(:mass(1)); collideAsteroid.new(:mass(10)), Asteroid.new(:mass(5)); Extending languages with multiple-dispatch libraries
JavaScript
In languages that do not support multiple dispatch at the language definition or syntactic level, it is often possible to add multiple dispatch using a library extension. JavaScript and TypeScript do not support multimethods at the syntax level, but it is possible to add multiple dispatch via a library. For example, the multimethod package [12] provides an implementation of multiple dispatch, generic functions.
Dynamically-typed version in JavaScript:
import{multi,method}from'@arrows/multimethod'classAsteroid{}classSpaceship{}constcollideWith=multi(method([Asteroid,Asteroid],(x,y)=>{// deal with asteroid hitting asteroid}),method([Asteroid,Spaceship],(x,y)=>{// deal with asteroid hitting spaceship}),method([Spaceship,Asteroid],(x,y)=>{// deal with spaceship hitting asteroid}),method([Spaceship,Spaceship],(x,y)=>{// deal with spaceship hitting spaceship}),)Statically-typed version in TypeScript:
import{multi,method,Multi}from'@arrows/multimethod'classAsteroid{}classSpaceship{}typeCollideWith=Multi&{(x:Asteroid,y:Asteroid):void(x:Asteroid,y:Spaceship):void(x:Spaceship,y:Asteroid):void(x:Spaceship,y:Spaceship):void}constcollideWith:CollideWith=multi(method([Asteroid,Asteroid],(x,y)=>{// deal with asteroid hitting asteroid}),method([Asteroid,Spaceship],(x,y)=>{// deal with asteroid hitting spaceship}),method([Spaceship,Asteroid],(x,y)=>{// deal with spaceship hitting asteroid}),method([Spaceship,Spaceship],(x,y)=>{// deal with spaceship hitting spaceship}),)Python
Multiple dispatch can be added to Python using a library extension. For example, using the module multimethod.py [13] and also with the module multimethods.py [14] which provides CLOS-style multimethods for Python without changing the underlying syntax or keywords of the language.
fromtypingimportAnyimportgame_behaviorsfromgame_objectsimportAsteroid,SpaceshipfrommultimethodsimportDispatchcollide:Dispatch=Dispatch()collide.add_rule((Asteroid,Spaceship),game_behaviors.as_func)collide.add_rule((Spaceship,Spaceship),game_behaviors.ss_func)collide.add_rule((Spaceship,Asteroid),game_behaviors.sa_func)defaa_func(a:Any,b:Any)->None:"""Behavior when asteroid hits asteroid."""# ...define new behavior...collide.add_rule((Asteroid,Asteroid),aa_func)# ...later...collide(thing1,thing2)Functionally, this is very similar to the CLOS example, but the syntax is conventional Python.
Using decorators (introduced since Python 2.4), Guido van Rossum produced a sample implementation of multimethods [15] with a simplified syntax:
@multimethod(Asteroid,Asteroid)defcollide(a:Asteroid,b:Asteroid)->None:"""Behavior when asteroid hits a asteroid."""# ...define new behavior...@multimethod(Asteroid,Spaceship)defcollide(a:Asteroid,b:Spaceship)->None:"""Behavior when asteroid hits a spaceship."""# ...define new behavior...# ... define other multimethod rules ...and then it goes on to define the multimethod decorator.
The PEAK-Rules package provides multiple dispatch with a syntax similar to the above example. [16] It was later replaced by PyProtocols. [17]
The Reg library also supports multiple and predicate dispatch. [18]
With the introduction of type hints, multiple dispatch is possible with even simpler syntax. For example, using plum-dispatch,
fromplumimportdispatch@dispatchdefcollide(a:Asteroid,b:Asteroid)->None:"""Behavior when asteroid hits a asteroid."""# ...define new behavior...@dispatchdefcollide(a:Asteroid,b:Spaceship)->None:"""Behavior when asteroid hits a spaceship."""# ...define new behavior...# ...define further rules...Emulating multiple dispatch
C
C does not have dynamic dispatch, so it must be implemented manually in some form. Often an enum is used to identify the subtype of an object. Dynamic dispatch can be done by looking up this value in a function pointer branch table. Here is a simple example in C:
typedefvoid(*CollisionCase)(void);voidcollisionAsteroidAsteroid(void){// handle Asteroid-Asteroid collision...}voidcollisionAsteroidSpaceship(void){// handle Asteroid-Spaceship collision...}voidcollisionSpaceshipAsteroid(void){// handle Spaceship-Asteroid collision...}voidcollisionSpaceshipSpaceship(void){// handle Spaceship-Spaceship collision...}typedefenum{COLLIDEABLE_ASTEROID=0,COLLIDEABLE_SPACESHIP,COLLIDEABLE_COUNT// not a type of Collideable itself, instead used to find number of space objects defined}Collideable;CollisionCasecollisionCases[COLLIDEABLE_COUNT][COLLIDEABLE_COUNT]={{&collisionAsteroidAsteroid,&collisionAsteroidSpaceship},{&collisionSpaceshipAsteroid,&collisionSpaceshipSpaceship}};voidcollide(Collideablea,Collideableb){(*collisionCases[a][b])();}intmain(void){collide(COLLIDEABLE_SPACESHIP,COLLIDEABLE_ASTEROID);}With the C Object System library, [19] C does support dynamic dispatch similar to CLOS. It is fully extensible and does not need any manual handling of the methods. Dynamic message (methods) are dispatched by the dispatcher of COS, which is faster than Objective-C. Here is an example in COS:
#include<stdio.h>#include<cos/Object.h>#include<cos/gen/object.h>// classesdefclass(Asteroid)// data membersendclassdefclass(Spaceship)// data membersendclass// genericsdefgeneric(_Bool,collide_with,_1,_2);// multimethodsdefmethod(_Bool,collide_with,Asteroid,Asteroid)// deal with asteroid hitting asteroidendmethoddefmethod(_Bool,collide_with,Asteroid,Spaceship)// deal with asteroid hitting spaceshipendmethoddefmethod(_Bool,collide_with,Spaceship,Asteroid)// deal with spaceship hitting asteroidendmethoddefmethod(_Bool,collide_with,Spaceship,Spaceship)// deal with spaceship hitting spaceshipendmethod// example of useintmain(void){OBJa=gnew(Asteroid);OBJs=gnew(Spaceship);printf("<a,a> = %d\n",collide_with(a,a));printf("<a,s> = %d\n",collide_with(a,s));printf("<s,a> = %d\n",collide_with(s,a));printf("<s,s> = %d\n",collide_with(s,s));grelease(a);grelease(s);}C++
As of 2021 [update] , C++ natively supports only single dispatch, though adding multi-methods (multiple dispatch) was proposed by Bjarne Stroustrup (and collaborators) in 2007. [20] The methods of working around this limit are analogous: use either the visitor pattern, dynamic cast or a library:
// Example using run time type comparison via dynamic_castclassCollideable{public:virtualvoidcollideWith(Collideable&other)=0;};classAsteroid:publicCollideable{public:voidcollideWith(Collideable&other){// dynamic_cast to a pointer type returns nullptr if the cast fails// (dynamic_cast to a reference type would throw an exception on failure)if(Asteroid*asteroid=dynamic_cast<Asteroid*>(&other)){// handle Asteroid-Asteroid collision}elseif(Spaceship*spaceship=dynamic_cast<Spaceship*>(&other)){// handle Asteroid-Spaceship collision}else{// default collision handling here}}};classSpaceship:publicCollideable{public:voidcollideWith(Collideable&other){if(Asteroid*asteroid=dynamic_cast<Asteroid*>(&other)){// handle Spaceship-Asteroid collision}elseif(Spaceship*spaceship=dynamic_cast<Spaceship*>(&other)){// handle Spaceship-Spaceship collision}else{// default collision handling here}}};or pointer-to-method lookup table:
importstd;usingstd::unordered_map;classCollideable{protected:explicitCollideable(uint32_tcid):tid{cid}{}virtual~Collideable()=default;constuint32_ttid;// type idusingCollisionHandler=void(Collideable::*)(Collideable&other);usingCollisionHandlerMap=unordered_map<uint64_t,CollisionHandler>;staticvoidaddHandler(uint32_tid1,uint32_tid2,CollisionHandlerhandler){collisionCases.insert(CollisionHandlerMap::value_type(key(id1,id2),handler));}staticuint64_tkey(uint32_tid1,uint32_tid2){returnuint64_t(id1)<<32|id2;}staticCollisionHandlerMapcollisionCases;public:voidcollideWith(Collideable&other){autohandler=collisionCases.find(key(tid,other.tid));if(handler!=collisionCases.end()){(this->*handler->second)(other);// pointer-to-method call}else{// default collision handling}}};classAsteroid:publicCollideable{private:voidasteroidCollision(Collideable&other){// handle Asteroid-Asteroid collision }voidspaceshipCollision(Collideable&other){// handle Asteroid-Spaceship collision}public:Asteroid():Collideable(cid){}~Asteroid()=default;staticvoidinitCases();staticconstuint32_tcid;};classSpaceship:publicCollideable{private:voidasteroidCollision(Collideable&other){// handle Spaceship-Asteroid collision}voidspaceshipCollision(Collideable&other){// handle Spaceship-Spaceship collision}public:Spaceship():Collideable(cid){}~Spaceship()=default;staticvoidinitCases();staticconstuint32_tcid;// class id};Collideable::CollisionHandlerMapCollideable::collisionCases;constuint32_tAsteroid::cid=typeid(Asteroid).hash_code();constuint32_tSpaceship::cid=typeid(Spaceship).hash_code();voidAsteroid::initCases(){addHandler(cid,cid,CollisionHandler(&Asteroid::asteroidCollision));addHandler(cid,Spaceship::cid,CollisionHandler(&Asteroid::spaceshipCollision));}voidSpaceship::initCases(){addHandler(cid,Asteroid::cid,CollisionHandler(&Spaceship::asteroidCollision));addHandler(cid,cid,CollisionHandler(&Spaceship::spaceshipCollision));}intmain(intargc,char*argv[]){Asteroid::initCases();Spaceship::initCases();Asteroida1;Asteroida2;Spaceships1;Spaceships2;a1.collideWith(a2);a1.collideWith(s1);s1.collideWith(s2);s1.collideWith(a1);}The YOMM2 library [21] provides a fast, orthogonal implementation of open multimethods.
The syntax for declaring open methods is inspired by a proposal for a native C++ implementation. The library requires that the user registers all the classes used as virtual arguments (and their sub-classes), but does not require any modifications to existing code. Methods are implemented as ordinary inline C++ functions; they can be overloaded and they can be passed by pointer. There is no limit on the number of virtual arguments, and they can be arbitrarily mixed with non-virtual arguments.
The library uses a combination of techniques (compressed dispatch tables, collision free integer hash table) to implement method calls in constant time, while mitigating memory usage. Dispatching a call to an open method with a single virtual argument takes only 15–30% more time than calling an ordinary virtual member function, when a modern optimizing compiler is used.
The Asteroids example can be implemented as follows:
#include<yorel/yomm2/keywords.hpp>importstd;usingstd::unique_ptr;classCollideable{public:virtual~Collideable()=default;};classAsteroid:publicCollideable{// ...};classSpaceship:publicCollideable{// ...};register_classes(Collideable,Spaceship,Asteroid);declare_method(void,collideWith,(virtual_<Collideable&>,virtual_<Collideable&>));define_method(void,collideWith,(Collideable&left,Collideable&right)){// default collision handling}define_method(void,collideWith,(Asteroid&left,Asteroid&right)){// handle Asteroid-Asteroid collision}define_method(void,collideWith,(Asteroid&left,Spaceship&right)){// handle Asteroid-Spaceship collision}define_method(void,collideWith,(Spaceship&left,Asteroid&right)){// handle Spaceship-Asteroid collision}define_method(void,collideWith,(Spaceship&left,Spaceship&right)){// handle Spaceship-Spaceship collision}intmain(intargc,char*argv[]){yorel::yomm2::update_methods();unique_ptr<Collideable>a1(std::make_unique<Asteroid>());unique_ptr<Collideable>a2(std::make_unique<Asteroid>());unique_ptr<Collideable>s1(std::make_unique<Spaceship>());unique_ptr<Collideable>s2(std::make_unique<Spaceship>());// note: types partially erasedcollideWith(*a1,*a2);// Asteroid-Asteroid collisioncollideWith(*a1,*s1);// Asteroid-Spaceship collisioncollideWith(*s1,*a1);// Spaceship-Asteroid collisioncollideWith(*s1,*s2);// Spaceship-Spaceship collisionreturn0;}Stroustrup mentions in The Design and Evolution of C++ that he liked the concept of multimethods and considered implementing it in C++ but claims to have been unable to find an efficient sample implementation (comparable to virtual functions) and resolve some possible type ambiguity problems. He then states that although the feature would still be nice to have, that it can be approximately implemented using double dispatch or a type based lookup table as outlined in the C/C++ example above so is a low priority feature for future language revisions. [22]
D
As of 2021 [update] , as do many other object-oriented programming languages, D natively supports only single dispatch. However, it is possible to emulate open multimethods as a library function in D. The openmethods library [23] is an example.
// DeclarationMatrixplus(virtual!Matrix,virtual!Matrix);// The override for two DenseMatrix objects@methodMatrix_plus(DenseMatrixa,DenseMatrixb){constintnr=a.rows;constintnc=a.cols;assert(a.nr==b.nr);assert(a.nc==b.nc);autoresult=newDenseMatrix;result.nr=nr;result.nc=nc;result.elems.length=a.elems.length;result.elems[]=a.elems[]+b.elems[];returnresult;}// The override for two DiagonalMatrix objects@methodMatrix_plus(DiagonalMatrixa,DiagonalMatrixb){assert(a.rows==b.rows);double[]sum;sum.length=a.elems.length;sum[]=a.elems[]+b.elems[];returnnewDiagonalMatrix(sum);}Java
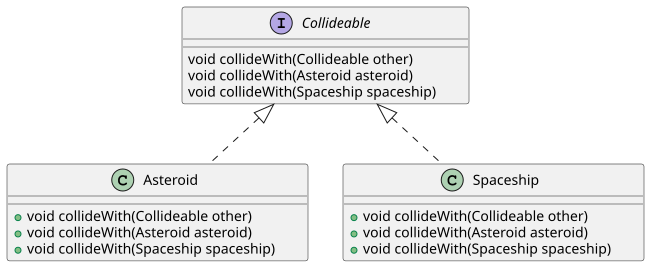
In a language with only single dispatch, such as Java, multiple dispatch can be emulated with multiple levels of single dispatch:
interfaceCollideable{voidcollideWith(finalCollideableother);/* These methods would need different names in a language without method overloading. */voidcollideWith(finalAsteroidasteroid);voidcollideWith(finalSpaceshipspaceship);}classAsteroidimplementsCollideable{publicvoidcollideWith(finalCollideableother){// Call collideWith on the other object.other.collideWith(this);}publicvoidcollideWith(finalAsteroidasteroid){// Handle Asteroid-Asteroid collision.}publicvoidcollideWith(finalSpaceshipspaceship){// Handle Asteroid-Spaceship collision.}}classSpaceshipimplementsCollideable{publicvoidcollideWith(finalCollideableother){// Call collideWith on the other object.other.collideWith(this);}publicvoidcollideWith(finalAsteroidasteroid){// Handle Spaceship-Asteroid collision.}publicvoidcollideWith(finalSpaceshipspaceship){// Handle Spaceship-Spaceship collision.}}Run time instanceof checks at one or both levels can also be used.