The music of Croatia, like the divisions of the country itself, has two major influences: Central European, present in central and northern parts of the country including Slavonia, and Mediterranean, present in coastal regions of Dalmatia and Istria.

Trogir is a historic town and harbour on the Adriatic coast in Split-Dalmatia County, Croatia, with a population of 10,923 (2011) and a total municipal population of 13,192 (2011). The historic city of Trogir is situated on a small island between the Croatian mainland and the island of Čiovo. It lies 27 kilometres west of the city of Split.

Korčula is a Croatian island in the Adriatic Sea. It has an area of 279 km2 (108 sq mi), is 46.8 km (29.1 mi) long and on average 7.8 km (4.8 mi) wide, and lies just off the Dalmatian coast. Its 15,522 inhabitants (2011) make it the second most populous Adriatic island after Krk. The population are almost entirely ethnic Croats (95.74%). The island is twinned with Rothesay in Scotland. It is known for Grk, a white wine that is only produced here and not exported due to limited production.

Vis is a town on the eponymous island in the Adriatic Sea in southern Croatia. Its population was 1,934 as of 2011. The town is the seat of the eponymous Vis municipality, one of the island's two municipalities. Both belong administratively to Split-Dalmatia County.

Hvar is a Croatian island in the Adriatic Sea, located off the Dalmatian coast, lying between the islands of Brač, Vis and Korčula. Approximately 68 kilometres (42.25 mi) long, with a high east–west ridge of Mesozoic limestone and dolomite, the island of Hvar is unusual in the area for having a large fertile coastal plain, and fresh water springs. Its hillsides are covered in pine forests, with vineyards, olive groves, fruit orchards and lavender fields in the agricultural areas. The climate is characterized by mild winters, and warm summers with many hours of sunshine. The island has 10,678 residents according to the 2021 census, making it the 4th most populated of the Croatian islands.
Stari Grad is a town on the northern side of the island of Hvar in Dalmatia, Croatia. One of the oldest towns in Europe, its position at the end of a long, protected bay and next to prime agricultural land has long made it attractive for human settlement. Stari Grad is also a municipality within the Split-Dalmatia County.

Hvar is a town and port on the island of Hvar, part of Split-Dalmatia County, Croatia. The municipality has a population of 4,251 (2011) while the town itself is inhabited by 3,771 people, making it the largest settlement on the island of Hvar. It is situated on a bay in the south coast of the island, opposite from the other nearby towns of Stari Grad and Jelsa.

The Uskoks were irregular soldiers in Habsburg Croatia that inhabited areas on the eastern Adriatic coast and surrounding territories during the Ottoman wars in Europe. Bands of Uskoks fought a guerrilla war against the Ottomans, and they formed small units and rowed swift boats. Since the uskoks were checked on land and were rarely paid their annual subsidy, they resorted to acts of piracy.
The History of Dalmatia concerns the history of the area that covers eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea and its inland regions, from the 2nd century BC up to the present day. The earliest mention of Dalmatia as a province came after its establishment as part of the Roman Empire. Dalmatia was ravaged by barbaric tribes in the beginning of the 4th century. Slavs settled in the area in the 6th century, the White Croats settled Dalmatia the following century.

Supetar is a town on the northern part of the Dalmatian island of Brač, in the Split-Dalmatia County, in Croatia. It became the island's official centre in 1827. The town of Supetar includes Supetar itself and the three villages of Splitska, Škrip and Mirca.

Andrea Antico was a music printer, editor, publisher and composer of the Renaissance born in the Republic of Venice, of Istrian birth, active in Rome and in Venice. He was the first printer of sacred music in Rome, and the earliest competitor of Venetian Ottaviano Petrucci, who is regarded as the first significant music printer.

Dalmatian Italians are the historical Italian national minority living in the region of Dalmatia, now part of Croatia and Montenegro.
Croatian art describes the visual arts in Croatia, and art by Croatian artists from prehistoric times to the present. In Early Middle Ages, Croatia was an important centre for art and architecture in south eastern Europe. There were many Croatian artists during the Medieval period, and the arts flourished during the Renaissance. Later styles in Croatia included Baroque and Rococo.
Renaissance Ensemble Serbia is the first early music ensemble in Serbia and the second in south-eastern Europe, having been founded in 1968. Ensemble Renaissance usually focuses on the music of the Middle Ages, Renaissance and Baroque. Occasionally, however, Ensemble performs modern music on ancient instruments.

The Renaissance in Croatia is a period of cultural enrichment in Croatia that began at the middle of the 15th century and lasted until the end of the 16th century.
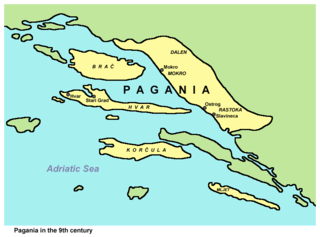
The Narentines were a South Slavic tribe that occupied an area of southern Dalmatia centered at the river Neretva, active in the 9th and 10th centuries, noted as pirates on the Adriatic. Named Narentani in Venetian sources, Greek sources call them Paganoi, "pagans", as they were for long pagan, in a time when neighbouring tribes were Christianized. The tribe were fierce enemies of the Republic of Venice, having attacked Venetian merchants and clergy passing on the Adriatic, and even raided close to Venice itself, as well as defeated the doge several times. Venetian–Narentine peace treaties did not last long, as the Narentines quickly returned to piracy. They were finally defeated in a Venetian crackdown at the turn of the 10th century and disappeared from sources by the 11th century.

The Theme of Dalmatia was a Byzantine theme on the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea in Southeastern Europe, headquartered at Jadera.

Journey Through Dalmatia is album by Ensemble Renaissance, released on 14 March 1999 on the Al Segno label. It is their 14th album overall, dealing with early music of Dalmatia and Adriatic, from the earliest medieval manuscripts with Beneventan chant and church music, to the first authentic Dalmatian Renaissance composers, such as Petar Hektorović, who wrote down two songs, one bugarštica Kada mi se Radosave vojevoda and one song I kliče devojka, both of which were printed in Venice; also are included the first composers active in Republic of Ragusa, like Vincenzo Comnen, the renaissance printers like Andrea Antico, Julije Skjavetić, Marcantonio Romano, renaissance dances, music of nobility, up to the early baroque and late baroque sonatas and motets by Tomaso Cecchini, Ivan Lukačić, Vinko Jelić. The tracks included on the album are also first renaissance dances. One of the members of the Ensemble, Dragan Mlađenović, cites the album as their greatest success. The Journey through Dalmatia was their second album dealing with early music of Dalmatia and Adriatic, the first being Music of the Old Adriatic from the 1983.

Venetian Dalmatia refers to parts of Dalmatia under the rule of the Republic of Venice, mainly from the 15th to the 18th centuries. Dalmatia was first sold to Venice in 1409 but Venetian Dalmatia was not fully consolidated until 1420. It lasted until 1797, when the Republic of Venice fell to the forces of Napoleon Bonaparte and Habsburg Austria.

Dalmatian city-states were the Dalmatian localities where the local Romance population survived the Barbarian invasions after the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 400s CE. Eight little cities were created by indigenous inhabitants who maintained political links with the Eastern Roman Empire which defended these cities, enabling their commercial trade.















