
Mycelium is a root-like structure of a fungus consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae. Its normal form is that of branched, slender, entangled, anastomosing, hyaline threads. Fungal colonies composed of mycelium are found in and on soil and many other substrates. A typical single spore germinates into a monokaryotic mycelium, which cannot reproduce sexually; when two compatible monokaryotic mycelia join and form a dikaryotic mycelium, that mycelium may form fruiting bodies such as mushrooms. A mycelium may be minute, forming a colony that is too small to see, or may grow to span thousands of acres as in Armillaria.

Coir, also called coconut fibre, is a natural fibre extracted from the outer husk of coconut, and used in products such as floor mats, doormats, brushes, and mattresses. Coir is the fibrous material found between the hard, internal shell and the outer coat of a coconut. Other uses of brown coir are in upholstery padding, sacking and horticulture. White coir, harvested from unripe coconuts, is used for making finer brushes, string, rope and fishing nets. It has the advantage of not sinking, so can be used in long lengths in deep water without the added weight dragging down boats and buoys.

Polymer degradation is the reduction in the physical properties of a polymer, such as strength, caused by changes in its chemical composition. Polymers and particularly plastics are subject to degradation at all stages of their product life cycle, including during their initial processing, use, disposal into the environment and recycling. The rate of this degradation varies significantly; biodegradation can take decades, whereas some industrial processes can completely decompose a polymer in hours.
Fungiculture is the cultivation of fungi such as mushrooms. Cultivating fungi can yield foods, medicine, construction materials and other products. A mushroom farm is involved in the business of growing fungi.
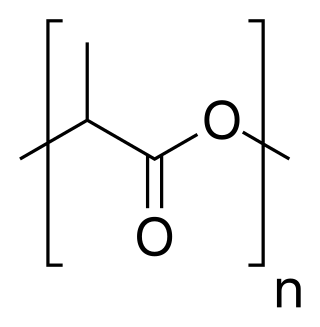
Polylactic acid, also known as poly(lactic acid) or polylactide (PLA), is a plastic material. As a thermoplastic polyester it has the backbone formula (C
3H
4O
2)
n or [–C(CH
3)HC(=O)O–]
n. PLA is formally obtained by condensation of lactic acid C(CH
3)(OH)HCOOH with loss of water. It can also be prepared by ring-opening polymerization of lactide [–C(CH
3)HC(=O)O–]
2, the cyclic dimer of the basic repeating unit. Often PLA is blended with other polymers. PLA can be biodegradable or long-lasting, depending on the manufacturing process, additives and copolymers.

Bioplastics are plastic materials produced from renewable biomass sources. Historically, bioplastics made from natural materials like shellac or cellulose had been the first plastics. Since the end of the 19th century they have been increasingly superseded by fossil-fuel plastics derived from petroleum or natural gas. Today, in the context of bioeconomy and circular economy, bioplastics are gaining interest again. Conventional petro-based polymers are increasingly blended with bioplastics to manufacture "bio-attributed" or "mass-balanced" plastic products - so the difference between bio- and other plastics might be difficult to define.
Polyethylene or polythene film biodegrades naturally, albeit over a long period of time. Methods are available to make it more degradable under certain conditions of sunlight, moisture, oxygen, and composting and enhancement of biodegradation by reducing the hydrophobic polymer and increasing hydrophilic properties.

Biodegradable plastics are plastics that can be decomposed by the action of living organisms, usually microbes, into water, carbon dioxide, and biomass. Biodegradable plastics are commonly produced with renewable raw materials, micro-organisms, petrochemicals, or combinations of all three.
Biotextiles are specialized materials engineered from natural or synthetic fibers. These textiles are designed to interact with biological systems, offering properties such as biocompatibility, porosity, and mechanical strength or are designed to be environmentally friendly for typical household applications. There are several uses for biotextiles since they are a broad category. The most common uses are for medical or household use. However, this term may also refer to textiles constructed from biological waste product. These biotextiles are not typically used for industrial purposes.
PBAT is a biodegradable random copolymer, specifically a copolyester of adipic acid, 1,4-butanediol and terephthalic acid. PBAT is produced by many different manufacturers and may be known by the brand names ecoflex, Wango,Ecoworld, Eastar Bio, and Origo-Bi. It is also called poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) and sometimes polybutyrate-adipate-terephthalate or even just "polybutyrate". It is generally marketed as a fully biodegradable alternative to low-density polyethylene, having many similar properties including flexibility and resilience, allowing it to be used for many similar uses such as plastic bags and wraps. The structure is a random-block polymer consisting of butanediol–adipic acid and butanediol-terephthalic acid blocks.

Sustainable packaging is packaging materials and methods that result in improved sustainability. This involves increased use of life cycle inventory (LCI) and life cycle assessment (LCA) to help guide the use of packaging which reduces the environmental impact and ecological footprint. It includes a look at the whole of the supply chain: from basic function, to marketing, and then through to end of life (LCA) and rebirth. Additionally, an eco-cost to value ratio can be useful The goals are to improve the long term viability and quality of life for humans and the longevity of natural ecosystems. Sustainable packaging must meet the functional and economic needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. Sustainability is not necessarily an end state but is a continuing process of improvement.

Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semisynthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be molded, extruded, or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptability, combined with a wide range of other properties, such as being lightweight, durable, flexible, nontoxic, and inexpensive to produce, has led to their widespread use around the world. Most plastics are derived from natural gas and petroleum, and a small fraction from renewable materials. One such material polylactic acid.

Mycoforestry is an ecological forest management system implemented to enhance forest ecosystems and plant communities, by introducing the mycorrhizal and saprotrophic fungi. Mycoforestry is considered a type of permaculture and can be implemented as a beneficial component of an agroforestry system. It can enhance the yields of tree crops and produce edible mushrooms, an economically valuable product. By integrating plant-fungal associations into a forestry management system, native forests can be preserved, wood waste can be recycled back into the ecosystem, carbon sequestration can be increased, planted restoration sites are enhanced, and the sustainability of forest ecosystems are improved. Mycoforestry is an alternative to the practice of clearcutting, which removes dead wood from forests, thereby diminishing nutrient availability and reducing soil depth.

Ecovative Design LLC is a materials company headquartered in Green Island, New York, that provides sustainable alternatives to plastics and polystyrene foams for packaging, building materials and other applications by using mushroom technology.
Zeoform is a material developed by the Australian company, Zeo IP Pty made from water and cellulose. Polymeric lignocellulosic fibres from industrial biomass are used to produce a structural material suitable for various applications in the industrial sector. Depending on the source material it is non-toxic, biodegradable, and that it could replace many forms of hard plastics, synthetic compounds and other polymers.
A living building material (LBM) is a material used in construction or industrial design that behaves in a way resembling a living organism. Examples include: self-mending biocement, self-replicating concrete replacement, and mycelium-based composites for construction and packaging. Artistic projects include building components and household items.
Biofoams are biological or biologically derived foams, making up lightweight and porous cellular solids. A relatively new term, its use in academia began in the 1980s in relation to the scum that formed on activated sludge plants.

Mycelium, a root-like structure that comprises the main vegetative growth of fungi, has been identified as an ecologically friendly substitute to a litany of materials throughout different industries, including but not limited to packaging, fashion and building materials. Such substitutes present a biodegradable alternative to conventional materials.

Fungi are a common theme and working material in art. Fungi appear in nearly all art forms, including literature, paintings, and graphic arts; and more recently, contemporary art, music, photography, comic books, sculptures, video games, dance, cuisine, architecture, fashion, and design. There are some exhibitions dedicated to fungi, as well as an entire museum.
Plant-based leather, also known as vegan leather or eco-leather, is a type of material made from plant-based sources as an alternative to traditional leather, which is typically made from animal hides. Plant-based leather can be made from a variety of sources, including pineapple leaves, mushrooms, corn, apple peels, and recycled plastic. The growing interest in sustainable and environmentally friendly products has led to increased demand for plant-based leather in recent years.











