The pink cusk-eel, Genypterus blacodes, is a demersal species of cusk-eel found in the oceans around southern Australia, Chile, Brazil, and around New Zealand except the east coast of Northland, in depths of 22 to 1,000 metres. Their length is up to 200 centimetres, and they live for up to 30 years. Their maximum weight is 25 kilograms.
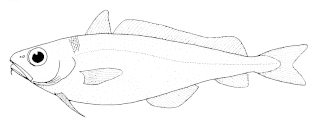
Mora moro, the common mora, is a deep-sea fish, the only species in the genus Mora. It is found worldwide in temperate seas, at depths of between 300 and 2,500 m. Its length is up to about 80 cm. Other names in English include goodly-eyed cod, googly-eyed cod, and ribaldo.

Helicolenus percoides, the reef ocean perch, coral cod, coral perch, Jock Stewart, kuriarki, ocean perch, red gurnard perch, red gurnard scorpionfish, red ocean perch, red perch, red rock perch, scarpee or sea perch, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae, part of the family Scorpaenidae. It is found in the southwestern Pacific Ocean.

Sphaeromatidae is a family of isopods, often encountered on rocky shores and in shelf waters in temperate zones. The family includes almost 100 genera and 619 known marine species. Within these genera, there are groups that share distinctive morphologies; further research may reclassify these genus-groups as separate families.
Ceratoserolis is a genus of isopods in the family Serolidae from the Southern Ocean around Antarctica and some Sub-Antarctic Islands. They prefer to live on soft bottoms and range of least between 24 and 950 m (80–3,120 ft) in depth. They are superficially similar to the unrelated, extinct trilobites and reach up to about 8 cm (3.1 in) in length. They were once considered to be part of the genus Serolis and for a long time only Ceratoserolis trilobitoides was recognized. The validity of the other species has been disputed, but there are some morphological and genetic differences between them and C. trilobitoides, and there are indications that additional, currently unrecognized species of Ceratoserolis exist.

In cryptography, Twofish is a symmetric key block cipher with a block size of 128 bits and key sizes up to 256 bits. It was one of the five finalists of the Advanced Encryption Standard contest, but it was not selected for standardization. Twofish is related to the earlier block cipher Blowfish.

Sphaeromatidea is a suborder of isopod crustaceans.
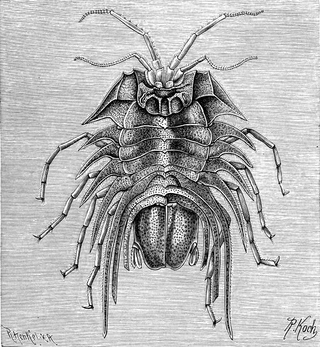
Serolidae is a family of isopod crustaceans. The family encompasses 22 genera with 109 species. These species are exclusively marine and are distributed across the marine realms as follows: one species can be found in the Temperate Northern Atlantic, one species in the Temperate Northern Pacific, seven species in the Tropical Atlantic, six species in the Central Indo-Pacific, 16 species in Temperate South America, one species in Temperate Southern Africa, 20 species in Temperate Australasia, and 31 species in the Southern Ocean.
Tricarina is an extinct genus of crustaceans in order Isopoda, known from a single incomplete fossil specimen from the Cretaceous of western Iran. It has a flattened body with three longitudinal ridges, which give it its name.

Exosphaeroma is a genus of marine isopod of the family Sphaeromatidae. This genus is found in shallow ocean waters worldwide. It is notable for being one of the few genera of sphaeromatid to be found in the southern reaches of the Southern Ocean. The greatest diversity of Exosphaeroma occurs in the Southern Hemisphere.
Dynoides viridis is a species of isopod in the family Sphaeromatidae. It was first found on Heron Island, Great Barrier Reef.

Brucerolis is a genus of isopods in the family Serolidae, found in the Southern Ocean.

Brucerolis brandtae is a species of isopods in the family Serolidae, found in the Southern Ocean in the waters around New Zealand.
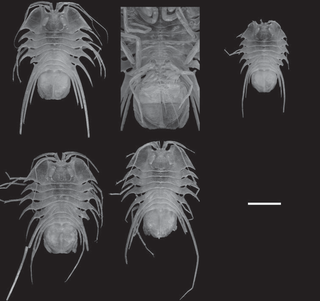
Brucerolis nowra is a species of isopods in the family Serolidae, found in marine waters off Nowra in New South Wales.

Brucerolis bromleyana is a benthic species of isopods in the family Serolidae, found in the Southern Ocean.

Rocinela is a genus of isopods in the family Aegidae, and was first described in 1818 by William Elford Leach. The type species is Rocinela danmoniensis Leach, 1818.
Rocinela kapala is a species of isopod in the family Aegidae, and was first described in 1988 by Niel L. Bruce. The species was first described in detail as R. oculata. The species is named for the FRV Kapala, the vessel from which the holotype was collected at a depth of 450 metres.
Aegiochus bertrandi is a species of isopod in the family Aegidae, and was first described in 2009 by Niel L. Bruce. The species epithet, bertrandi, honours the French zoologist Bertrand Richer de Forges.

Aegiochus piihuka is a species of isopod in the family Aegidae, and was first described in 2009 by Niel L. Bruce. The species epithet, piihuka, is a Mäori word meaning hook, and refers to the hooked anterior legs.
The Norfolk Ridge / Lord Howe Rise Biodiversity Discovery Survey (NORFANZ) was an expedition undertaken in May to June 2003 to research the biodiversity found in and around the Norfolk Ridge and the Lord Howe Rise.










