
In astronomy, a galactic bulge is a tightly packed group of stars within a larger star formation. The term almost exclusively refers to the central group of stars found in most spiral galaxies. Bulges were historically thought to be elliptical galaxies that happened to have a disk of stars around them, but high-resolution images using the Hubble Space Telescope have revealed that many bulges lie at the heart of a spiral galaxy. It is now thought that there are at least two types of bulges: bulges that are like ellipticals and bulges that are like spiral galaxies.

NGC 1300 is a barred spiral galaxy located about 65 million light-years away in the constellation Eridanus. The galaxy is about 110,000 light-years across. It is a member of the Eridanus Cluster, a cluster of 200 galaxies, in a subgroup of 2-4 galaxies in the cluster known as the NGC 1300 Group. It was discovered by John Herschel in 1835.

NGC 3783 is a barred spiral galaxy located about 135 million light years away in the constellation Centaurus. It is inclined by an angle of 23° to the line of sight from the Earth along a position angle of about 163°. The morphological classification of SBa indicates a bar structure across the center (B) and tightly-wound spiral arms (a). Although not shown by this classification, observers note the galaxy has a luminous inner ring surrounding the bar structure. The bright compact nucleus is active and categorized as a Seyfert 1 type. This nucleus is a strong source of X-ray emission and undergoes variations in emission across the electromagnetic spectrum.

NGC 5643 is an intermediate spiral galaxy in the constellation Lupus. Based on the tip of the red-giant branch distance indicator, it is located at a distance of about 40 million light-years. NGC 5643 has an active galactic nucleus and is a type II Seyfert galaxy.

NGC 3642 is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. The galaxy has a low-ionization nuclear emission-line region. It is located at a distance of circa 30 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 3642 is about 50,000 light years across. The galaxy is characterised by an outer pseudoring, which was probably formed after the accretion of a gas rich dwarf galaxy.

NGC 4494 is an elliptical galaxy located in the constellation Coma Berenices. It is located at a distance of circa 45 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 4494 is about 60,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1785.

NGC 3675 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Ursa Major. It is located at a distance of circa 50 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 3675 is about 100,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1788.

NGC 3941 is a barred lenticular galaxy located in the constellation Ursa Major. It is located at a distance of circa 40 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 3941 is about 40,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1787.

NGC 3631 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Ursa Major. It is located at a distance of about 35 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 3631 is about 60,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on April 14, 1789. It is a grand design spiral galaxy seen face on.

NGC 3081 is a barred lenticular ring galaxy in the constellation of Hydra. NGC 3081 is located about 85 million light-years away from Earth, which means, given its apparent dimensions, that NGC 3081 is approximately 60,000 light-years across. It is a type II Seyfert galaxy, characterised by its bright nucleus. It was discovered by William Herschel on 21 December 1786.

NGC 3147 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Draco. It is located at a distance of about 130 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 3147 is about 140,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on April 3, 1785.

NGC 5084 is a lenticular galaxy in the constellation of Virgo. It is located at a distance of about 80 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 5084 is at least 200,000 light years across. It is one of the largest and most massive galaxies in the Virgo Supercluster. William Herschel discovered it on March 10, 1785. It is a member of the NGC 5084 Group of galaxies, which is a member of the Virgo II Groups, a series of galaxies and galaxy clusters strung out from the southern edge of the Virgo Supercluster. The galaxy is seen nearly edge-on, with inclination 86°, and features a warped disk and large quantities of HI gas extending along the disk, probably accumulated after multiple accretions of smaller galaxies.

NGC 7606 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Aquarius. It is located at a distance of circa 100 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 7606 is about 165,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on September 28, 1785. The galaxy is included in the Herschel 400 Catalogue. It lies 45 arcminutes northeast from psi2 Aquarii. It can be seen with a 4 inch telescope but its visibility is greatly affected by light pollution.

NGC 7213 is a lenticular galaxy located in the constellation Grus. It is located at a distance of circa 70 million light-years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 7213 is about 75,000 light-years across. It was discovered by John Herschel on September 30, 1834. It is an active galaxy with characteristics between a type I Seyfert galaxy and LINER.

NGC 5982 is an elliptical galaxy located in the constellation Draco. It is located at a distance of circa 130 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 5982 is about 100,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on May 25, 1788.

NGC 3585 is an elliptical or a lenticular galaxy located in the constellation Hydra. It is located at a distance of circa 60 million light-years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 3585 is about 80,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on December 9, 1784.

IC 1459 is an elliptical galaxy located in the constellation Grus. It is located at a distance of circa 85 million light-years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that IC 1459 is about 130,000 light-years across. It was discovered by Edward Emerson Barnard in 1892.

NGC 4278 is an elliptical galaxy located in the constellation Coma Berenices. It is located at a distance of circa 55 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 4278 is about 65,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on March 13, 1785. NGC 4278 is part of the Herschel 400 Catalogue and can be found about one and 3/4 of a degree northwest of Gamma Comae Berenices even with a small telescope.

NGC 2974 is a lenticular galaxy located in the constellation Sextans. It is located at a distance of circa 90 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 2974 is about 90,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on January 6, 1785. NGC 2974 is located in the sky about 2 and a half degrees south-south east of Iota Hydrae and more than 6 degrees northeast of Alphard. A 10th magnitude star lies next to the galaxy, thus making it a challenging object at low magnifications. NGC 2974 is part of the Herschel 400 Catalogue.
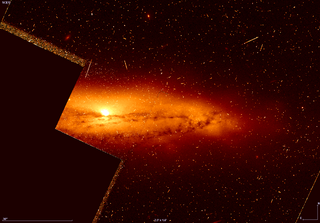
NGC 5506 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Virgo. It is located at a distance of about 75 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 5506 is about 80,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on April 15, 1787. It is a Seyfert galaxy.




















