
19 Aurigae is a single star located approximately 3,800 light years away from the Sun in the northern constellation Auriga. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, white-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.05. The star is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of 4.3 km/s.

Phi Aurigae, Latinized from φ Aurigae, is a giant star in the northern constellation of Auriga. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.089. It lies 10′ from another faint naked-eye star HD 35520, between the three open clusters M36 and M38, and NGC 1893.
KW Sagittarii is a red supergiant star, located approximately 2,160 parsecs away from the Sun in the direction of the constellation Sagittarius. It is one of the largest known stars, with a diameter about 1,000 times larger than the Sun. If placed at the center of the Solar System, the star's surface would engulf Mars, coming close to Jupiter's orbit.
V354 Cephei is a red supergiant star located within the Milky Way. It is an irregular variable located over 13,000 light-years away from the Sun. It has an estimated radius of 1,139 solar radii. If it were placed in the center of the Solar System, it would extend to between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.

PU Aurigae is an irregular variable star located in the constellation Auriga. A red giant, it varies by 0.1 magnitude around magnitude 5.64. Located around 560 light-years distant, it shines with a luminosity approximately 1,523 times that of the Sun and has a surface temperature of 3,482 K.

V381 Cephei is a triple star system in the northern constellation of Cepheus. Its apparent magnitude is slightly variable between 5.5 and 5.7.

V602 Carinae is a red supergiant and variable star of spectral type M3 in the constellation Carina. It is considered to be one of largest known stars, being around 1,000 times larger than the Sun.
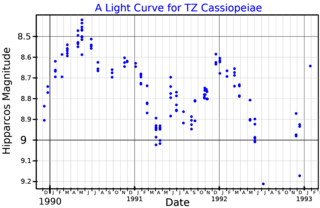
TZ Cassiopeiae(TZ Cas, HIP 117763, SAO 20912) is a variable star in the constellation Cassiopeia with an apparent magnitude of around +9 to +10. It is approximately 8,400 light-years away from Earth. The star is a red supergiant star with a spectral type of M3 and a temperature around 3,600 K.

PZ Cassiopeiae is a red supergiant star located in the constellation of Cassiopeia, and a semi-regular variable star.

Sigma Ophiuchi, Latinized from σ Ophiuchi, is a single, orange-hued star in the equatorial constellation Ophiuchus. Its apparent visual magnitude is 4.31, which is bright enough to be faintly visible to the naked eye. The annual parallax shift of 3.62 mas as seen from Earth provides a distance estimate of roughly 900 light years. It is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −28 km/s.
AH Scorpii is a red supergiant variable star located in the constellation Scorpius. It is one of the largest stars known by radius and is also one of the most luminous red supergiant stars in the Milky Way.

TV Geminorum is a variable red supergiant in the constellation Gemini. Its visual magnitude varies from 6.3 to 7.5.

BC Cygni is a red supergiant and pulsating variable star of spectral type M3.5Ia in the constellation Cygnus.

RW Cygni is a semiregular variable star in the constellation Cygnus, about a degree east of 2nd magnitude γ Cygni. Its apparent magnitude varies between 8.05 and 9.70 and its spectral type between M3 and M4.

V419 Cephei is an irregular variable star in the constellation of Cepheus with an apparent magnitude that varies between 6.54 and 6.89.

CK Carinae is a variable star in the constellation Carina, the keel of Argo Navis. It is a member of the star association Carina OB1-D, at a distance of around 2,300 parsecs or 7,500 light years.

V528 Carinae is a variable star in the constellation Carina.

BO Carinae, also known as HD 93420, is an irregular variable star in the constellation Carina.

6 Geminorum is a variable star in the zodiac constellation of Gemini, located roughly 5,800 light years away from the Sun. It has the variable star designation BU Geminorum; 6 Geminorum is the Flamsteed designation. At its brightest this reddish hued star is barely visible to the naked eye but is readily visible with binoculars, found southeast of M 35, just to the south of WY Geminorum. It is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +27 km/s. The star is a member of the Gemini OB1 association.

IX Carinae is a red supergiant and pulsating variable star of spectral type M2Iab in the constellation Carina. It is a member of the Carina OB1 association along the Carina Nebula.
















