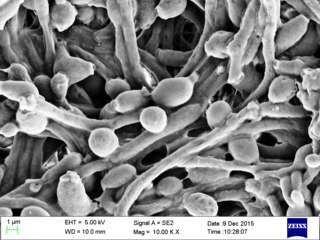
Candida albicans is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usually a commensal organism, but it can become pathogenic in immunocompromised individuals under a variety of conditions. It is one of the few species of the genus Candida that cause the human infection candidiasis, which results from an overgrowth of the fungus. Candidiasis is, for example, often observed in HIV-infected patients. C. albicans is the most common fungal species isolated from biofilms either formed on (permanent) implanted medical devices or on human tissue. C. albicans, C. tropicalis, C. parapsilosis, and C. glabrata are together responsible for 50–90% of all cases of candidiasis in humans. A mortality rate of 40% has been reported for patients with systemic candidiasis due to C. albicans. By one estimate, invasive candidiasis contracted in a hospital causes 2,800 to 11,200 deaths yearly in the US. Nevertheless, these numbers may not truly reflect the true extent of damage this organism causes, given new studies indicating that C. albicans can cross the blood–brain barrier in mice.

Candida is a genus of yeasts. It is the most common cause of fungal infections worldwide and the largest genus of medically important yeast.

Anidulafungin (INN) is a semisynthetic echinocandin used as an antifungal drug. It was previously known as LY303366. It may also have application in treating invasive Aspergillus infection when used in combination with voriconazole. It is a member of the class of antifungal drugs known as the echinocandins; its mechanism of action is by inhibition of (1→3)-β-D-glucan synthase, an enzyme important to the synthesis of the fungal cell wall.
Candida parapsilosis is a fungal species of yeast that has become a significant cause of sepsis and of wound and tissue infections in immunocompromised people. Unlike Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis, C. parapsilosis is not an obligate human pathogen, having been isolated from nonhuman sources such as domestic animals, insects and soil. C. parapsilosis is also a normal human commensal and it is one of the fungi most frequently isolated from human hands. There are several risk factors that can contribute to C. parapsilosis colonization. Immunocompromised individuals and surgical patients, particularly those undergoing surgery of the gastrointestinal tract, are at high risk for infection with C. parapsilosis. There is currently no consensus on the treatment of invasive candidiasis caused by C. parapsilosis, although the therapeutic approach typically includes the removal of foreign bodies such as implanted prostheses and the administration of systemic antifungal therapy. Amphotericin B and Fluconazole are often used in the treatment of C. parapsilosis infection.

Burkholderia pseudomallei is a Gram-negative, bipolar, aerobic, motile rod-shaped bacterium. It is a soil-dwelling bacterium endemic in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide, particularly in Thailand and northern Australia. It was reported in 2008 that there had been an expansion of the affected regions due to significant natural disasters, and it could be found in Southern China, Hong Kong, and countries in America. B. pseudomallei, amongst other pathogens, has been found in monkeys imported into the United States from Asia for laboratory use, posing a risk that the pathogen could be introduced into the country.
Pichia kudriavzevii is a budding yeast involved in chocolate production. P. kudriavzevii is an emerging fungal nosocomial pathogen primarily found in the immunocompromised and those with hematological malignancies. It has natural resistance to fluconazole, a standard antifungal agent. It is most often found in patients who have had prior fluconazole exposure, sparking debate and conflicting evidence as to whether fluconazole should be used prophylactically. Mortality due to P. kudriavzevii fungemia is much higher than the more common C. albicans. Other Candida species that also fit this profile are C. parapsilosis, C. glabrata, C. tropicalis, C. guillermondii and C. rugosa.
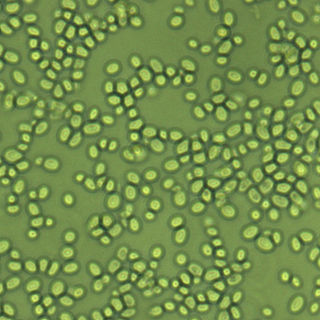
Nakaseomyces glabratus is a species of haploid yeast of the genus Nakaseomyces, previously known as Candida glabrata. Despite the fact that no sexual life cycle has been documented for this species, N. glabratus strains of both mating types are commonly found. C. glabrata is generally a commensal of human mucosal tissues, but in today's era of wider human immunodeficiency from various causes, N. glabratus is often the second or third most common cause of candidiasis as an opportunistic pathogen. Infections caused by N. glabratus can affect the urogenital tract or even cause systemic infections by entrance of the fungal cells in the bloodstream (Candidemia), especially prevalent in immunocompromised patients.

Sporothrix schenckii, a fungus that can be found worldwide in the environment, is named for medical student Benjamin Schenck, who in 1896 was the first to isolate it from a human specimen. The species is present in soil as well as in and on living and decomposing plant material such as peat moss. It can infect humans as well as animals and is the causative agent of sporotrichosis, commonly known as "rose handler's disease." The most common route of infection is the introduction of spores to the body through a cut or puncture wound in the skin. Infection commonly occurs in otherwise healthy individuals but is rarely life-threatening and can be treated with antifungals. In the environment it is found growing as filamentous hyphae. In host tissue it is found as a yeast. The transition between the hyphal and yeast forms is temperature dependent making S. schenckii a thermally dimorphic fungus.

Trichosporon is a genus of anamorphic fungi in the family Trichosporonaceae. All species of Trichosporon are yeasts with no known teleomorphs. Most are typically isolated from soil, but several species occur as a natural part of the skin microbiota of humans and other animals. Proliferation of Trichosporon yeasts in the hair can lead to an unpleasant but non-serious condition known as white piedra. Trichosporon species can also cause severe opportunistic infections (trichosporonosis) in immunocompromised individuals.

Sabouraud agar or Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA) is a type of agar growth medium containing peptones. It is used to cultivate dermatophytes and other types of fungi, and can also grow filamentous bacteria such as Nocardia. It has utility for research and clinical care.
Vaginal yeast infection, also known as candidal vulvovaginitis and vaginal thrush, is excessive growth of yeast in the vagina that results in irritation. The most common symptom is vaginal itching, which may be severe. Other symptoms include burning with urination, a thick, white vaginal discharge that typically does not smell bad, pain during sex, and redness around the vagina. Symptoms often worsen just before a woman's period.
Candida blankii is a species of budding yeast (Saccharomycotina) in the family Saccharomycetaceae. The yeast may be a dangerous pathogen and resistant to treatment in human hosts. Research on the fungi has therapeutic, medical and industrial implications.
Mycoplasma salivarium is a species of bacteria in the genus Mycoplasma. This genus of bacteria lacks a cell wall around their cell membrane. Without a cell wall, they are unaffected by many common antibiotics such as penicillin or other beta-lactam antibiotics that target cell wall synthesis. Mycoplasma are the smallest bacterial cells yet discovered, can survive without oxygen and are typically about 0. 1 μm in diameter. Mycoplasma salivarium is found in the mouths of 97% of the healthy population, and is generally considered to be a commensal organism and part of the normal oral flora.

Granada medium is a selective and differential culture medium designed to selectively isolate Streptococcus agalactiae and differentiate it from other microorganisms. Granada Medium was developed by Manuel Rosa-Fraile et al. at the Service of Microbiology in the Hospital Virgen de las Nieves in Granada (Spain).

Candida auris is a species of fungus that grows as yeast. It is one of the few species of the genus Candida which cause candidiasis in humans. Often, candidiasis is acquired in hospitals by patients with weakened immune systems. C. auris can cause invasive candidiasis (fungemia) in which the bloodstream, the central nervous system, and internal organs are infected. It has attracted widespread attention because of its multiple drug resistance. Treatment is also complicated because it is easily misidentified as other Candida species.

Trichosporon asteroides is an asexual basidiomycetous fungus first described from human skin but now mainly isolated from blood and urine. T. asteroides is a hyphal fungus with a characteristically yeast-like appearance due to the presence of slimy arthroconidia. Infections by this species usually respond to treatment with azoles and amphotericin B.

Corynebacterium xerosis is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacterium in the genus Corynebacterium. Although it is frequently a harmless commensal organism living on the skin and mucus membranes, C. xerosis is also a clinically-relevant opportunistic pathogen that has been attributed to a number of different infections in animals and humans. However, its actual prominence in human medicine is up for debate due to early difficulties distinguishing it from other Corynebacterium species in clinical isolates.

Corynebacterium striatum is a bacterium that is a member of the Corynebacterium genus. It is classified as non-diphtheritic. The bacterium is a gram-positive prokaryote that assumes a 'club-like' morphology, more formally known as a corynebacteria structure. It is non-lipophilic and undergoes aerobic respiration and is also a facultative anaerobe it is catalase negative and oxidase positive glucose and sucrose fermenter.
Candida catenulata is a yeast-form fungus in the phylum Ascomycota. It is distributed globally and commonly found on the skin of humans and animals, in soil, and in dairy products.
Candida haemulonii is a yeast fungal pathogen that is known to cause infections in humans. C. haemulonii is an emerging opportunistic pathogen that is found in hospitals and healthcare settings. Infections are difficult to treat because the fungus has resistance to antifungal agents. Since its emergence, little research has been conducted on this fungus. However, in recent years, research has been conducted to help identify the various properties of C. haemulonii.













