
Dentistry, also known as dental medicine and oral medicine, is the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and conditions of the mouth, most commonly focused on dentition as well as the oral mucosa. Dentistry may also encompass other aspects of the craniofacial complex including the temporomandibular joint. The practitioner is called a dentist.
A dentist, also known as a dental surgeon, is a health care professional who specializes in dentistry, the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. The dentist's supporting team aids in providing oral health services. The dental team includes dental assistants, dental hygienists, dental technicians, and sometimes dental therapists.
Cosmetic dentistry is generally used to refer to any dental work that improves the appearance of teeth, gums and/or bite. It primarily focuses on improvement in dental aesthetics in color, position, shape, size, alignment and overall smile appearance. Many dentists refer to themselves as "cosmetic dentists" regardless of their specific education, specialty, training, and experience in this field. This has been considered unethical with a predominant objective of marketing to patients. The American Dental Association does not recognize cosmetic dentistry as a formal specialty area of dentistry. However, there are still dentists that promote themselves as cosmetic dentists.

A bridge is a fixed dental restoration used to replace one or more missing teeth by joining an artificial tooth definitively to adjacent teeth or dental implants.
Dental restoration, dental fillings, or simply fillings are treatments used to restore the function, integrity, and morphology of missing tooth structure resulting from caries or external trauma as well as to the replacement of such structure supported by dental implants. They are of two broad types—direct and indirect—and are further classified by location and size. A root canal filling, for example, is a restorative technique used to fill the space where the dental pulp normally resides.

A dental technician is a member of the dental team who, upon prescription from a dental clinician, constructs custom-made restorative and dental appliances.

A dental implant is a prosthesis that interfaces with the bone of the jaw or skull to support a dental prosthesis such as a crown, bridge, denture, or facial prosthesis or to act as an orthodontic anchor. The basis for modern dental implants is a biological process called osseointegration, in which materials such as titanium or zirconia form an intimate bond to the bone. The implant fixture is first placed so that it is likely to osseointegrate, then a dental prosthetic is added. A variable amount of healing time is required for osseointegration before either the dental prosthetic is attached to the implant or an abutment is placed which will hold a dental prosthetic/crown.
Osseointegration is the direct structural and functional connection between living bone and the surface of a load-bearing artificial implant. A more recent definition defines osseointegration as "functional ankylosis ", where new bone is laid down directly on the implant surface and the implant exhibits mechanical stability. Osseointegration has enhanced the science of medical bone and joint replacement techniques as well as dental implants and improving prosthetics for amputees.

In dentistry, a crown or a dental cap is a type of dental restoration that completely caps or encircles a tooth or dental implant. A crown may be needed when a large dental cavity threatens the health of a tooth. Some dentists will also finish root canal treatment by covering the exposed tooth with a crown. A crown is typically bonded to the tooth by dental cement. They can be made from various materials, which are usually fabricated using indirect methods. Crowns are used to improve the strength or appearance of teeth and to halt deterioration. While beneficial to dental health, the procedure and materials can be costly.
Prosthodontics, also known as dental prosthetics or prosthetic dentistry, is the area of dentistry that focuses on dental prostheses. It is one of 12 dental specialties recognized by the American Dental Association (ADA), Royal College of Surgeons of England, Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh, Royal College of Surgeons of Ireland, Royal College of Surgeons of Glasgow, Royal College of Dentists of Canada, and Royal Australasian College of Dental Surgeons. The ADA defines it as "the dental specialty pertaining to the diagnosis, treatment planning, rehabilitation and maintenance of the oral function, comfort, appearance and health of patients with clinical conditions associated with missing or deficient teeth or oral and maxillofacial tissues using biocompatible substitutes."

In dentistry, inlays and onlays are used to fill cavities, and then cemented in place in the tooth. This is an alternative to a direct restoration, made out of composite, amalgam or glass ionomer, that is built up within the mouth.

The UCLA School of Dentistry is the dental school of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) located in the Center for Health Sciences building in the Westwood neighborhood of Los Angeles, California, United States. The school has several educational and training programs, conducts oral and dental health research, and offers affordable dental care at three locations: Westwood, Venice, and Inglewood. The school also participates in several outreach endeavors, including numerous health fairs during the year, STEM pipeline programs and provides dental care for underserved populations in the region. The School of Dentistry is considered among the nation's best research-intensive dental schools.
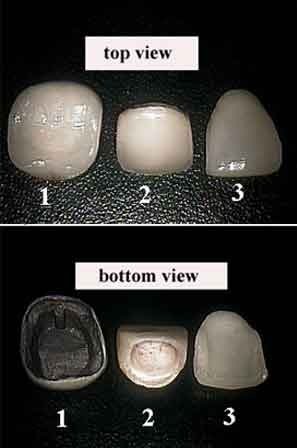
In dentistry, a veneer is a layer of material placed over a tooth. Veneers can improve the aesthetics and function of a smile and protect the tooth's surface from damage.

Nobel Biocare is a Swiss company originally founded in Sweden for manufacturing dental implants. It is now headquartered in Kloten, Switzerland near the Zürich Airport. Nobel Biocare in its current form was founded in 2002. It originates from a partnership formed in 1978 between Swedish medical researcher Professor Per-Ingvar Brånemark and Bofors, a Swedish company, to industrialize Brånemark's discovery of osseointegration. Beside dental implants, it also presently develops and commercializes CAD/CAM-based prosthetics equipments to scan teeth and to fabricate individualized dental prosthesis using digital technologies in place of silicone molding.
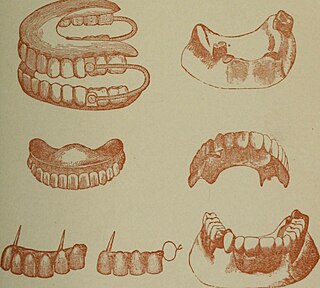
A denturist in the United States and Canada, clinical dental technologist in the United Kingdom and Ireland, dental prosthetist in Australia, or a clinical dental technician in New Zealand is a member of the oral health care team and role as primary oral health care provider who provides an oral health examination, planning treatment, takes impressions of the surrounding oral tissues, constructs and delivers removable oral prosthesis treatment directly to the patient.
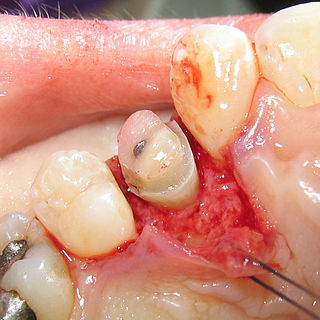
Crown lengthening is a surgical procedure performed by a dentist, or more frequently a periodontist, where more tooth is exposed by removing some of the gingival margin (gum) and supporting bone. Crown lengthening can also be achieved orthodontically by extruding the tooth.
A post and core crown is a type of dental restoration required where there is an inadequate amount of sound tooth tissue remaining to retain a conventional crown. A post is cemented into a prepared root canal, which retains a core restoration, which retains the final crown.

The Nankali post system is a post and cores prosthesis, which is used in prosthodontology and dental restoration. This post and core consists of a single smooth or serrated post and core which has an additional circle ring around it.

Nankali’s masticatory force systematization categorizes the locations of the forces on different part of mandible/maxilla, which are important in designing a prosthetic and implant treatment in dentistry.
A root-analog dental implant (RAI) – also known as a truly anatomic dental implant, or an anatomical/custom implant – is a medical device to replace one or more roots of a single tooth immediately after extraction. In contrast to common titanium screw type implants, these implants are custom-made to exactly match the extraction socket of the specific patient. Thus there is usually no need for surgery.














