
Amanita fulva, commonly called the tawny grisette or the orange-brown ringless amanita, is a basidiomycete mushroom of the genus Amanita. It is found frequently in deciduous and coniferous forests of Europe, and possibly North America.

Amanita orientifulva, also known as the Asian orange-brown ringless amanita, is a species of agaric fungus found at altitudes ranging from 1,300–4,200 m (4,300–13,800 ft) in south-western China. It is associated with trees, especially Abies, Quercus, Salix, and occasionally Castanopsis. It fruits singly or scattered from June to September.
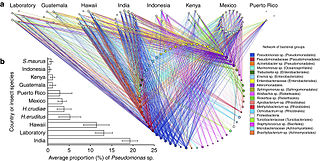
Pseudomonas fulva is a Gram-negative environmental bacterium, originally isolated from rice and commonly associated with rice plants, grains and paddy fields. It is rod-shaped and motile using one to three polar flagella.

The red climbing mouse, also known as Vernay's climbing mouse, is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is named after explorer and antiques dealer, Arthur Vernay, who sponsored the expedition during which the animal was first discovered. It is the only living species in the genus Vernaya, and has no subspecies.

The fulvous babbler or fulvous chatterer is a species of bird in the family Leiothrichidae. It is 25 cm long with a wingspan of 27–30.5 cm. It is warm brown above with very faint streaking on the crown and back. The throat is whitish and the rest of the underparts are pale brown.

The incurvate emerald is a species of dragonfly in the family Corduliidae. It is found in Canada and the United States. Its natural habitat is fens.
Nectandra fulva is a species of plant in the family Lauraceae. It is endemic to Venezuela.

The North American red fox is a North American subspecies of the red fox. It is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the order Carnivora, occurring in North America. It is listed as least concern by the IUCN.

The tawny crazy ant or Rasberry crazy ant, Nylanderia fulva, is an ant originating from South America. Like the longhorn crazy ant, this species is called "crazy ant" because of its quick, unpredictable movements. It is sometimes called the "Rasberry crazy ant" in Texas after the exterminator Tom Rasberry, who noticed that the ants were increasing in numbers in 2002. Scientists have reorganised the genera taxonomy within this clade of ants, and now it is identified as Nylanderia fulva.
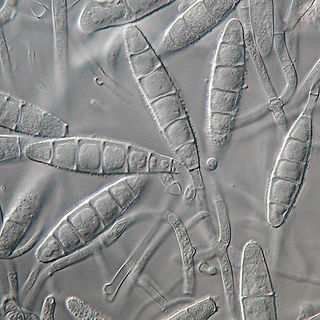
Microsporum gypseum is a soil-associated dermatophyte that occasionally is known to colonise and infect the upper dead layers of the skin of mammals. The name refers to an asexual "form-taxon" that has been associated with four related biological species of fungi: the pathogenic taxa Arthroderma incurvatum, A. gypsea, A. fulva and the non-pathogenic saprotroph A. corniculata. More recent studies have restricted M. gypseum to two teleomorphic species A. gypseum and A. incurvatum. The conidial states of A. fulva and A. corniculata have been assigned to M. fulvum and M. boullardii. Because the anamorphic states of these fungi are so similar, they can be identified reliably only by mating. Two mating strains have been discovered, "+" and "–". The classification of this species has been based on the characteristically rough-walled, blunt, club-shaped, multicelled macroconidia. Synonyms include Achorion gypseum, Microsporum flavescens, M. scorteum, and M. xanthodes. There has been past nomenclatural confusion in the usage of the generic names Microsporum and Microsporon.
The Brachypsectridae are a family of beetles commonly known as the Texas beetles. There are only two extant genera, Brachypsectra and Asiopsectra. The type species, Brachypsectra fulva, occurs in North America. Other species in the genus have a cosmopolitan distribution. Two other extant and fossil species have been described from the Dominican Republic. While formerly considered monogeneric, in 2016 Asiopsectra was described from specimens found in Iran and Tajikistan. Two extinct genera, Vetubrachypsectra and Hongipsectra, known from adults, and a larval genus, Cretopsectra are known from Cenomanian aged Burmese amber.
Nannizzia incurvata is a species of fungus. It is a heterothallic species.

Iris fulva, also known as copper iris, is a species in the genus Iris, it is also in the subgenus Limniris and in the series Hexagonae. It is a rhizomatous perennial, endemic to the southern and central United States. It has copper-red to deep red flowers and bright green leaves.
Petrophile incurvata is a species of flowering plant in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to southwestern Western Australia. It is a shrub with flattened, sometimes pinnately-divided leaves with up to five sharply pointed lobes, and cylindrical to oval heads of silky-hairy, cream-coloured to yellowish-white flowers.
Longispora fulva is a bacterium from the genus of Longispora which has been isolated from soil from a Zelkova forest from Ohnuma, Fukushima Prefecture, Japan.

Pyrenomonadaceae is a family of cryptomonads which includes three or four known genera. They are distinguished from other cryptomonads by their nucleomorphs being imbedded into the pyrenoid, and the presence of distinctive pigment phycoerythrin 545.
Microsporum fulvum is a wildly-distributed dermatophyte species in the Fungi Kingdom. It is known to be a close relative to other dermatophytes such as Trichophyton andEpidermophyton. The fungus is common within soil environments and grows well on keratinized material, such as hair, nails and dead skin. It is recognized as an opportunistic fungal pathogen capable of causing cutaneous mycoses in humans and animals. Originally, the fungus was thought to be Microsporum gypseum until enhanced genetic examination separated the two as distinct species in 1963.

Durvillaea incurvata is a large, robust species of southern bull kelp endemic to Chile.
Nannizzia is a genus of fungus in the family Arthrodermataceae.
Catenulispora fulva is a bacterium from the genus of Catenulispora which has been isolated from forest soil from Chungnam in Korea.











