
A bridge piercing is a facial piercing through the skin on the bridge of the nose, usually directly between the eyes of the wearer. A variation on this piercing, the vertical bridge piercing is a surface piercing, with all of the risks or potential complications related to surface piercings.

A navel piercing is a type of piercing located through, in, or around, the navel. It may heal quickly and with no problems, like an ear piercing, or may heal more like a surface piercing with the associated extended healing time. Healing usually takes around 6-9 months, or even more and as long as it is cleaned, it will heal nicely. Unlike most surface piercings, this is one of the few that do not normally reject, although the rejection rate is higher than non-surface piercings, such as ear piercing. The actual navel is not pierced when a navel piercing is performed. The most common form of navel piercing is through the upper rim of the navel. It is worn by a lot of female celebrities including Britney Spears and Beyoncé.
A clitoral hood piercing is a female genital piercing through the clitoral hood surrounding the clitoris. There are two main types of hood piercing: the vertical clitoral hood piercing and the horizontal clitoral hood piercing. As the name indicates, the difference is in the direction the piercing is oriented in the skin above the clitoris. Neither of these piercings penetrates the clitoris itself.

Nose piercing is the piercing of the skin or cartilage which forms any part of the nose, normally for the purpose of wearing jewelry, called a nose-jewel. Among the different varieties of nose piercings, the nostril piercing is the most common. Nose piercing is the third most common variety of piercing after earlobe piercing and tongue piercing.

An eyebrow piercing is a vertical surface piercing, wherein a twelve to eighteen gauge cannula needle is inserted through the bottom of the eyebrow and exits through the top of the eyebrow to permit insertion of jewellery. Those performing the piercing may use a pennington clamp to better guide the needle through the skin. A curved barbell is the most common jewellery inserted post-piercing.

Cheek piercing is facial body piercing through the cheek. The most common variation of the cheek piercing penetrates the facial tissue into the oral cavity. The usual placement is symmetrical on either side of the face, either penetrating or imitating dimples. The piercing can cause the wearer slight nerve damage and will result in "man-made dimples". An alternative is microdermal implants, placed in the intended dimple location. This method avoids drawbacks of full cheek piercings, which have a tendency to leak or secrete lymph fluid, which has a saliva-like texture and can create an unpleasant odor. Though microdermals do have a slightly larger chance to leave a scar than a piercing, they will heal eventually and be almost unnoticeable. The rate of infection is also lower in the long run. Because the piercing does not penetrate the cheek completely, there is little to no chance of tooth or gum damage. Microdermals are like a 'one hole' piercing, where the 'foot' of the jewelry sits below the skin and the decorative jewel or flat disc is above the skin.

A Christina piercing, also known as a Venus piercing, is a female genital piercing. It is located where the outer labia meet, below the pubic mound. The Christina piercing is anatomy dependant; it has a high rejection rate, and is not possible for all women due to anatomical variation. The piercing does not facilitate sexual stimulation and can be found uncomfortable when pressure is applied. It is usually pierced with either a custom made curved barbell or surface bar to reduce the risk of rejection.
In modern Western body piercing, a wide variety of materials are used. Some cannot be autoclaved, and others may induce allergic reactions, or harbour bacteria. Certain countries, such as those belonging to the EU, have legal regulations specifying which materials can be used in new piercings.
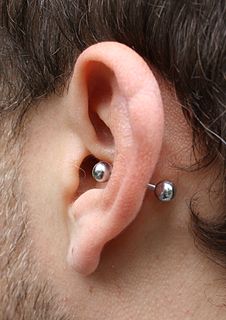
A conch piercing is a perforation of the cartilage of the ear for the purpose of inserting and wearing jewelry. There are two types of conch piercings, inner and outer. The name is derived from the resemblance of this part of the ear to a conch shell.

A clitoris piercing is a female genital piercing placed directly through the head (glans) of the clitoris itself. It is a relatively uncommon piercing by choice because of the potential for nerve damage, and because women may find it too stimulating to allow the constant wearing of a small ring or barbell. It is often confused with the more common clitoral hood piercing, which pierces only the hood covering the clitoral glans, allowing the jewellery to make only occasional contact with the most sensitive area.

A rook piercing is a perforation of the antihelix of the ear for the purpose of wearing jewelry. It is located just above the tragus on the ridge between the inner and outer conch with the piercing passing from the underside to the top of this ridge, differing from many ear piercings that essentially span between a "front" and "back" surface. Erik Dakota, a well known professional piercer and the individual responsible for originating and popularizing the rook piercing, is said to have named this modification after a shortened version of his first name. The piercing was first named in issue #4 of the magazine Body Play and Modern Primitives Quarterly around 1992 alongside the first printed reference to the industrial piercing, then termed "industrial ear project".

A corset piercing is a body piercing that is pierced multiple times mostly side to side to look like a corset being laced up the body. Two rows of bilaterally symmetrical piercings are performed and can be composed of as few as four piercings or as many as the length of the area being pierced and the vertical space between piercings will allow space for. Due to the difficulty and risks associated with permanently healing single surface piercings, most corset piercings are intended to be temporary.

A Madison piercing is a body piercing going through the skin at the front of the neck. They are surface piercings, and have a high rate of migration and rejection. They have a long healing period, if they heal at all. The Madison piercing is named after the first person publicly associated with it, the porn star Madison Stone.

A hip piercing is a piercing in the pelvic area through the skin near the hip bone. Hip piercings are often done in couplets with one on each hip, but it is not unusual to see only one. Hips piercing are a type of surface piercing. Microdermals or skin divers can be implanted in the hip area to give a similar appearance.

In body modification, an implant is a device is placed under the human skin for decorative purposes. Such implants may be subdermal or transdermal. In the context of body modification, some may consider injections of silicone and other substances a type of implant as well.

A neck piercing is a series of surface piercings done to emulate the appearance of a bite on the side of a person's neck. A barbell is placed in the skin of the side of the neck. When the earring/barbell is removed it looks like a vampire bite.
A wrist piercing is a piercing through the surface of the wrist, first popularized by Jon Cobb in PFIQ. Wrist piercings are a type of surface piercing. They carry a high rate of rejection and migration, unless they are properly measured and placed. They may reject if they are not pierced properly, as they are in a part of the body that moves constantly and are easy to irritate, catching on clothing or other objects. People with wrist piercings are advised to put on short sleeved t-shirts, singlets so as to prevent the surface barbell from catching onto the threads of the clothing. Also, wrist piercings can only be done with a special tool and thus, it is of high difficulty for it to be home-made. Piercers would also advise that, after getting a wrist piercing, the person is to soak and moisten the wound with mild salted solution so as to disinfect the area, preventing bacteria from entering the unclotted wound. The span of a wrist piercing ranges approximately from as short as 2 weeks to 6 or 7 months.




















