Related Research Articles

The Yukon River is a major watercourse of northwestern North America. From its source in British Columbia, it flows through Canada's territory of Yukon. The lower half of the river continues westward through the U.S. state of Alaska. The river is 3,190 kilometres (1,980 mi) long and empties into the Bering Sea at the Yukon–Kuskokwim Delta. The average flow is 6,400–7,000 m3/s (230,000–250,000 cu ft/s). The total drainage area is 854,700 km2 (330,000 sq mi), of which 323,800 km2 (125,000 sq mi) lies in Canada. The total area is more than 25% larger than Texas or Alberta.

Vice-Admiral Sir George Strong Nares was a Royal Navy officer and Arctic explorer. He commanded the Challenger Expedition, and the British Arctic Expedition. He was highly thought of as a leader and scientific explorer. In later life he worked for the Board of Trade and as Acting Conservator of the River Mersey.

Bennett Lake is a lake in the Province of British Columbia and Yukon Territory in northwestern Canada, at an elevation of 656 m (2,152 ft). It is just north of the border with the United States state of Alaska, near the Alaskan port of Skagway. The lake has an area of either 90.68 or 96.8 km2. The average depth is 61.9 m (203 ft) and the maximum depth is 123 m (404 ft).

Carcross, originally known as Caribou Crossing, is an unincorporated community in Yukon, Canada, on Bennett Lake and Nares Lake. It is home to the Carcross/Tagish First Nation.

Tagish Lake is a lake in Yukon and northern British Columbia, Canada. The lake is 119 kilometres (74 mi) long and averages 3.2 km (2 mi) wide with an area of 354.48 km2 (136.87 sq mi), about two thirds of which is in British Columbia. The average depth is 62 m (203 ft) and maximum depth is 307 m (1,007 ft).

Nares Lake is a 107.15 km2 (41.37 sq mi) lake in the southern Yukon between Bennett Lake and Tagish Lake that lies below Nares Mountain. Nares Lake is in fact an arm of Tagish Lake. The community of Carcross is on the Nares Narrows between Bennett and Tagish Lake, along the Klondike Highway. The primary inflow to and outflow from the lake is the Nares River. Both the river and the lake are named after Admiral George Nares.

Atlin Lake is the largest natural lake in the Canadian province of British Columbia. The lake is 6.44 kilometres (4.00 mi) wide and 137 kilometres (85 mi) long. The northern tip of the lake is in the Yukon, as is Little Atlin Lake. However, most of the lake lies within the Atlin District of British Columbia. Atlin Lake is generally considered to be the source of the Yukon River although it is drained via the short Atlin River into Tagish Lake. Atlin Lake was named by the Tlingit First Nation people of the region.
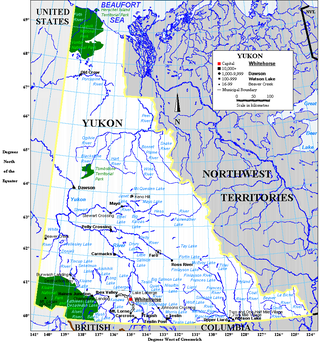
Yukon is in the northwestern corner of Canada and is bordered by Alaska, British Columbia and the Northwest Territories. The sparsely populated territory abounds with natural scenery, snowmelt lakes and perennial white-capped mountains, including many of Canada's highest mountains. The territory's climate is Arctic in territory north of Old Crow, subarctic in the region, between Whitehorse and Old Crow, and humid continental climate south of Whitehorse and in areas close to the British Columbia border. Most of the territory is boreal forest with tundra being the main vegetation zone only in the extreme north and at high elevations.

The Kwanlin Dün First Nation (KDFN) or Kwänlin Dän kwächʼǟn is located in and around Whitehorse in Yukon, Canada.
Tagish is an extinct language spoken by the Tagish or Carcross-Tagish, a First Nations people that historically lived in the Northwest Territories and Yukon in Canada. The name Tagish derives from /ta:gizi dene/, or "Tagish people", which is how they refer to themselves, where /ta:gizi/ is a place name meaning "it is breaking up.

Tagish is an unincorporated community in Yukon, Canada. It is 30 kilometres (19 mi) east of Carcross, Yukon, on the Tagish Road at the northern end of Tagish Lake. The greater Tagish area also includes the Tagish Estates, Tagish Beach and Taku subdivisions, the latter two developed for cottages but now serving for many year-round homes. Tagish Beach and Taku have their own community hall. The Tagish Road was built in 1942 as part of an oil pipeline project, and the community sprouted around a bridge built over the narrow water between Tagish Lake and Marsh Lake.

The Tagish Highland is an upland area on the inland side of the northernmost Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains, spanning far northwestern British Columbia from Atlin Lake to the area of the pass at Champagne, Yukon between the Alsek and Yukon Rivers. In some classification systems, and in local terminology, the Tagish Highland is considered to be part of the Boundary Ranges, as is the neighbouring Tahltan Highland to its south. As classified by the Canadian Mountain Encyclopedia per S. Holland, the Tagish Highland is part of the system unofficially described as the Interior Mountains.

Steamboats on the Yukon River played a role in the development of Alaska and Yukon. Access to the interior of Alaska and Yukon was hindered by large mountains and distance, but the wide Yukon River provided a feasible route. The first steamers on the lower Yukon River were work boats for the Collins Overland Telegraph in 1866 or 1867, with a small steamer called Wilder. The mouth of the Yukon River is far to the west at St. Michael and a journey from Seattle or San Francisco covered some 4,000 miles (6,400 km).

Teslin Lake is a large lake spanning the border between British Columbia and Yukon, Canada. It is one of a group of large lakes in the region of far northwestern BC, east of the upper Alaska Panhandle, which are the southern extremity of the basin of the Yukon River, and which are known in Yukon as "the Southern Lakes". The lake is fed and drained primarily by the Teslin River, south and north, but is also fed from the east by the Jennings River and the Swift River, and from the west by the Hayes River.

The Yukon Plateau is a plateau located in the Yukon Territory, comprising much of the central and southern Yukon Territory and the far northern part of British Columbia, Canada between Tagish Lake (W) and the Cassiar Mountains (E) and north of the Nakina River.
The Wolf River is a river in Yukon, Canada. It is in the Bering Sea drainage basin and is a left tributary of the Nisutlin River.
The Partridge River is a river in the Yukon and British Columbia, Canada. It is in the Bering Sea drainage basin and is a tributary of Bennett Lake.
Partridge Lake is a lake in the Yukon and British Columbia, Canada that is part of the Bering Sea drainage basin. The primary inflow, at the south, and outflow, at the north, is the Partridge River, which flows via Bennett Lake, the Nares River, Tagish Lake, the Tagish River and the Yukon River to the Bering Sea. A secondary inflow, at the southwest, is Jones Creek.
References
- ↑ "Nares River". Geographical Names Data Base . Natural Resources Canada . Retrieved 2014-07-28.