Related Research Articles
In theoretical computer science and mathematics, computational complexity theory focuses on classifying computational problems according to their resource usage, and explores the relationships between these classifications. A computational problem is a task solved by a computer. A computation problem is solvable by mechanical application of mathematical steps, such as an algorithm.
Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems, defined as computer systems whose inter-communicating components are located on different networked computers.
In graph theory, an expander graph is a sparse graph that has strong connectivity properties, quantified using vertex, edge or spectral expansion. Expander constructions have spawned research in pure and applied mathematics, with several applications to complexity theory, design of robust computer networks, and the theory of error-correcting codes.
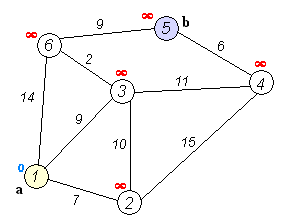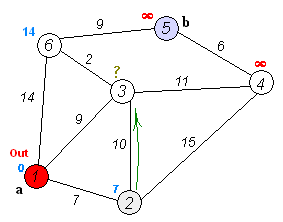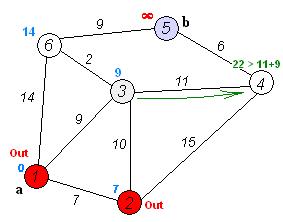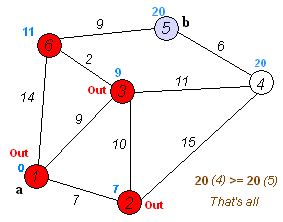
Dijkstra's algorithm is an algorithm for finding the shortest paths between nodes in a weighted graph, which may represent, for example, a road network. It was conceived by computer scientist Edsger W. Dijkstra in 1956 and published three years later.

Theoretical computer science is a subfield of computer science and mathematics that focuses on the abstract and mathematical foundations of computation.
Self-stabilization is a concept of fault-tolerance in distributed systems. Given any initial state, a self-stabilizing distributed system will end up in a correct state in a finite number of execution steps.
Nancy Ann Lynch is a computer scientist affiliated with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. She is the NEC Professor of Software Science and Engineering in the EECS department and heads the "Theory of Distributed Systems" research group at MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory.
In computational complexity theory, the PCP theorem states that every decision problem in the NP complexity class has probabilistically checkable proofs of constant query complexity and logarithmic randomness complexity.

Leslie Gabriel Valiant is a British American computer scientist and computational theorist. He was born to a chemical engineer father and a translator mother. He is currently the T. Jefferson Coolidge Professor of Computer Science and Applied Mathematics at Harvard University. Valiant was awarded the Turing Award in 2010, having been described by the A.C.M. as a heroic figure in theoretical computer science and a role model for his courage and creativity in addressing some of the deepest unsolved problems in science; in particular for his "striking combination of depth and breadth".
ACM SIGACT or SIGACT is the Association for Computing Machinery Special Interest Group on Algorithms and Computation Theory, whose purpose is support of research in theoretical computer science. It was founded in 1968 by Patrick C. Fischer.

Noga Alon is an Israeli mathematician and a professor of mathematics at Princeton University noted for his contributions to combinatorics and theoretical computer science, having authored hundreds of papers.

Avi Wigderson is an Israeli computer scientist and mathematician. He is the Herbert H. Maass Professor in the school of mathematics at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, United States of America. His research interests include complexity theory, parallel algorithms, graph theory, cryptography, and distributed computing. Wigderson received the Abel Prize in 2021 for his work in theoretical computer science. He also received the 2023 Turing Award for his contributions to the understanding of randomness in the theory of computation.
Task systems are mathematical objects used to model the set of possible configurations of online algorithms. They were introduced by Borodin, Linial and Saks (1992) to model a variety of online problems. A task system determines a set of states and costs to change states. Task systems obtain as input a sequence of requests such that each request assigns processing times to the states. The objective of an online algorithm for task systems is to create a schedule that minimizes the overall cost incurred due to processing the tasks with respect to the states and due to the cost to change states.
David Peleg is an Israeli computer scientist. He is a professor at the Weizmann Institute of Science, holding the Norman D. Cohen Professorial Chair of Computer Sciences, and the present dean of the Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science in Weizmann Institute. His main research interests are algorithms, computer networks, and distributed computing. Many of his papers deal with a combination of all three.
Algorithmic game theory (AGT) is an area in the intersection of game theory and computer science, with the objective of understanding and design of algorithms in strategic environments.
Michael Stewart Paterson, is a British computer scientist, who was the director of the Centre for Discrete Mathematics and its Applications (DIMAP) at the University of Warwick until 2007, and chair of the department of computer science in 2005.
Michael Ezra Saks is an American mathematician. He is currently the Department Chair of the Mathematics Department at Rutgers University (2017–) and from 2006 until 2010 was director of the Mathematics Graduate Program at Rutgers University. Saks received his Ph.D. from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1980 after completing his dissertation titled Duality Properties of Finite Set Systems under his advisor Daniel J. Kleitman.
Stathis K. Zachos is a mathematician, logician and theoretical computer scientist.

Noam Nisan is an Israeli computer scientist, a professor of computer science at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. He is known for his research in computational complexity theory and algorithmic game theory.

Michal Parnas is an Israeli theoretical computer scientist known for her work on property testing and sublinear-time algorithms. She is a professor of computer science at the Academic College of Tel Aviv-Yafo in Israel, where she was a founding faculty member and was also the dean of the school of computer science from 2011 to 2016. Since October 2022 she is the vice president of academic affairs of the college.
References
- 1 2 3 4 "2008 Conant Prize" (PDF), Notices of the American Mathematical Society, 55 (4): 491–493, 2008.
- ↑ Linial's home page at the Hebrew University, retrieved 2010-09-08.
- ↑ ISI Web of Knowledge Archived 19 May 2007 at the Wayback Machine , retrieved 2010-09-08.
- ↑ Nati Linial at the Mathematics Genealogy Project
- ↑ List of Fellows of the American Mathematical Society, retrieved 2013-01-27.
- ↑ "FOCS 2019 Award Winners".
- ↑ 2013 Edsger W. Dijkstra Prize in Distributed Computing