
Cesare Bonesana di Beccaria, Marquis of Gualdrasco and Villareggio was an Italian criminologist, jurist, philosopher, economist and politician, who is widely considered one of the greatest thinkers of the Age of Enlightenment. He is well remembered for his treatise On Crimes and Punishments (1764), which condemned torture and the death penalty, and was a founding work in the field of penology and the Classical School of criminology. Beccaria is considered the father of modern criminal law and the father of criminal justice.

Juvenile delinquency, also known as juvenile offending, is the act of participating in unlawful behavior as a minor or individual younger than the statutory age of majority. These acts would otherwise be considered crimes if the individuals committing them were older. The term delinquent usually refers to juvenile delinquency, and is also generalised to refer to a young person who behaves an unacceptable way.
The Chicago school refers to a school of thought in sociology and criminology originating at the University of Chicago whose work was influential in the early 20th century.
Articles related to criminology and law enforcement.

In criminology, subcultural theory emerged from the work of the Chicago School on gangs and developed through the symbolic interactionism school into a set of theories arguing that certain groups or subcultures in society have values and attitudes that are conducive to crime and violence. The primary focus is on juvenile delinquency because theorists believe that if this pattern of offending can be understood and controlled, it will break the transition from teenage offender into habitual criminal. Some of the theories are functionalist, assuming that criminal activity is motivated by economic needs, while others posit a social class rationale for deviance.

Right realism, in criminology, also known as New Right Realism, Neo-Classicism, Neo-Positivism, or Neo-Conservatism, is the ideological polar opposite of left realism. It considers the phenomenon of crime from the perspective of political conservatism and asserts that it takes a more realistic view of the causes of crime and deviance, and identifies the best mechanisms for its control. Unlike the other schools of criminology, there is less emphasis on developing theories of causality in relation to crime and deviance. The school employs a rationalist, direct and scientific approach to policy-making for the prevention and control of crime. Some politicians who subscribe to the perspective may address aspects of crime policy in ideological terms by referring to freedom, justice, and responsibility. For example, they may be asserting that individual freedom should only be limited by a duty not to use force against others. This, however, does not reflect the genuine quality in the theoretical and academic work and the real contribution made to the nature of criminal behaviour by criminologists of the school.

In criminology, the classical school usually refers to the 18th-century work during the Enlightenment by the utilitarian and social-contract philosophers Jeremy Bentham and Cesare Beccaria. Their interests lay in the system of criminal justice and penology and indirectly through the proposition that "man is a calculating animal," in the causes of criminal behavior. The classical school of thought was premised on the idea that people have free will in making decisions, and that punishment can be a deterrent for crime, so long as the punishment is proportional, fits the crime, and is carried out promptly.

In criminology, social control theory proposes that exploiting the process of socialization and social learning builds self-control and reduces the inclination to indulge in behavior recognized as antisocial. It derived from functionalist theories of crime and was developed by Ivan Nye (1958), who proposed that there were three types of control:

The Positivist School was founded by Cesare Lombroso and led by two others: Enrico Ferri and Raffaele Garofalo. In criminology, it has attempted to find scientific objectivity for the measurement and quantification of criminal behavior. Its method was developed by observing the characteristics of criminals to observe what may be the root cause of their behavior or actions. Since the Positivist's school of ideas came around, research revolving around its ideas has sought to identify some of the key differences between those who were deemed "criminals" and those who were not, often without considering flaws in the label of what a “criminal” is.

In the fields of sociology and criminology, strain theory is a theoretical perspective that aims to explain the relationship between social structure, social values or goals, and crime. Strain theory was originally introduced by Robert King Merton (1938), and argues that society's dominant cultural values and social structure causes strain, which may encourage citizens to commit crimes. Following on the work of Émile Durkheim's theory of anomie, strain theory has been advanced by Robert King Merton (1938), Albert K. Cohen (1955), Richard Cloward, Lloyd Ohlin (1960), Neil Smelser (1963), Robert Agnew (1992), Steven Messner, Richard Rosenfeld (1994) and Jie Zhang (2012).

In criminology, rational choice theory adopts a utilitarian belief that humans are reasoning actors who weigh means and ends, costs and benefits, in order to make a rational choice. This method was designed by Cornish and Clarke to assist in thinking about situational crime prevention.

Deterrence in relation to criminal offending is the idea or theory that the threat of punishment will deter people from committing crime and reduce the probability and/or level of offending in society. It is one of five objectives that punishment is thought to achieve; the other four objectives are denunciation, incapacitation, retribution and rehabilitation.
Techniques of neutralization are a theoretical series of methods by which those who commit illegitimate acts temporarily neutralize certain values within themselves which would normally prohibit them from carrying out such acts, such as morality, obligation to abide by the law, and so on. In simpler terms, it is a psychological method for people to turn off "inner protests" when they do, or are about to do something they themselves perceive as wrong.
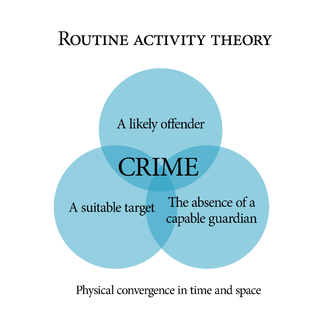
Routine activity theory is a sub-field of crime opportunity theory that focuses on situations of crimes. It was first proposed by Marcus Felson and Lawrence E. Cohen in their explanation of crime rate changes in the United States between 1947 and 1974. The theory has been extensively applied and has become one of the most cited theories in criminology. Unlike criminological theories of criminality, routine activity theory studies crime as an event, closely relates crime to its environment and emphasizes its ecological process, thereby diverting academic attention away from mere offenders.

Deviance or the sociology of deviance explores the actions and/or behaviors that violate social norms across formally enacted rules as well as informal violations of social norms. Although deviance may have a negative connotation, the violation of social norms is not always a negative action; positive deviation exists in some situations. Although a norm is violated, a behavior can still be classified as positive or acceptable.

Travis Warner Hirschi was an American sociologist and an emeritus professor of sociology at the University of Arizona. He helped to develop the modern version of the social control theory of crime and later the self-control theory of crime.
Robert Agnew is the Samuel Candler Dobbs Professor of Sociology at Emory University and past president of the American Society of Criminology.
The self-control theory of crime, often referred to as the general theory of crime, is a criminological theory about the lack of individual self-control as the main factor behind criminal behavior. The self-control theory of crime suggests that individuals who were ineffectually parented before the age of ten develop less self-control than individuals of approximately the same age who were raised with better parenting. Research has also found that low levels of self-control are correlated with criminal and impulsive conduct.

Criminology is the interdisciplinary study of crime and deviant behaviour. Criminology is a multidisciplinary field in both the behavioural and social sciences, which draws primarily upon the research of sociologists, political scientists, economists, legal sociologists, psychologists, philosophers, psychiatrists, social workers, biologists, social anthropologists, scholars of law and jurisprudence, as well as the processes that define administration of justice and the criminal justice system.

Mendota Juvenile Treatment Center (MJTC) is a juvenile psychiatric facility of the Wisconsin Department of Health Services, located in the Lorenz Hall Annex on the grounds of the Mendota Mental Health Institute (MMHI) in Madison, Wisconsin. It has space for 29 patients. The inmates at Mendota usually have anti-social personality disorders who do not feel empathy, guilt, nor remorse. It uses the Mendota Juvenile Treatment Center Program.







