
Fattail scorpion or fat-tailed scorpion is the common name given to scorpions of the genus Androctonus, one of the most dangerous groups of scorpions species in the world. They are found throughout the semi-arid and arid regions of the Middle East and Africa. They are a moderate sized scorpion, attaining lengths of 10 cm. Their common name is derived from their distinctly fat metasoma, or tail, while the Latin name originates from Greek and means "man killer". Their venom contains powerful neurotoxins and is especially potent. Stings from Androctonus species are known to cause several human deaths each year. Several pharmaceutical companies manufacture an antivenom for treatment of Androctonus envenomations.

The Buthidae are the largest family of scorpions, containing about 96 genera and over 1230 species as of 2021. Its members are known as, for example, fat-tailed scorpions and bark scorpions. A few very large genera are known, but a high number of species-poor or monotypic ones also exist. New taxa are being described at a rate of several new species per year. They occur in the warmer parts of every major landmass on Earth, except Antarctica and New Zealand. Together with four other families, the Buthidae make up the superfamily Buthoidea. The family was established by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1837.
Buthacus is a genus of scorpion of the family Buthidae. It is distributed across northern and western Africa, Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Syria, the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, and Pakistan.

Hottentotta is a genus of scorpions of the family Buthidae. It is distributed widely across Africa, except for most of the Sahara desert. Species in the genus also occur in the Middle East, the Arabian Peninsula, southeastern Turkey, Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, India, Nepal, Cape Verde Islands, and Sri Lanka (introduced).

Leiurus is a genus of scorpion of the family Buthidae. The most common species, L. quinquestriatus, is also known under the common name Deathstalker. It is distributed widely across North Africa and the Middle East, including the western and southern Arabian Peninsula and southeastern Turkey. At least one species occurs in West Africa.

Pandinus is a genus of large scorpions belonging to the family Scorpionidae. It contains one of the most popular pet scorpions, the emperor scorpion . The genus is distributed widely across tropical Africa and the southeastern Arabian Peninsula.

Compsobuthus is a genus of buthid scorpions.
Uintascorpio is an extinct genus of scorpion in the family Buthidae and containing the single species Uintascorpio halandrasorum. The species is known only from the Middle Eocene Parachute Member, part of the Green River Formation, in the Piceance Creek Basin, Garfield County, northwestern Colorado, USA.

Buthus is a genus of scorpion belonging and being eponymous to the family Buthidae. It is distributed widely across northern Africa, including Morocco, Mauritania, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt, Senegal, Guinea-Bissau, Nigeria, Sudan, Somalia, Ethiopia, Djibouti, as well as the Middle East, including Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon, Iraq, Yemen, and possibly Saudi Arabia and southern Turkey. Its European range includes the Iberian Peninsula, southern France, and Cyprus.
Chaerilus is a genus of scorpions, the only genus in the monotypic family Chaerilidae. They live in tropical parts of South Asia and Southeast Asia. A fossil genus Electrochaerilus is known from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) aged Burmese amber.

Isometrus is a genus of scorpion belonging and being eponymous to the family Buthidae.

Factorio is a construction and management simulation game developed by the Czech studio Wube Software. The game was announced via an Indiegogo crowdfunding campaign in 2013 and released for Microsoft Windows, macOS, and Linux on 14 August 2020 following a four-year long early access phase. The game follows an engineer who crash-landed on an alien planet and must harvest resources and create industry to build a rocket; however, as an open-world game, players can continue the game past the end of the storyline. The game features both single-player and multiplayer modes.

Babycurus is a genus of scorpions of the family Buthidae.

Scorpiops is a genus of scorpions in the family Euscorpiidae. It is distributed throughout much of Asia. The taxonomy of the group is unclear because new species and subgenera are described often, and one subgroup may represent a species complex.
Hottentotta finneganae is a species of scorpion, belonging to the family Buthidae. It was first found in Pakistan.
Hottentotta jalalabadensis is a species of scorpion of the family Buthidae. It was first found in Afghanistan.

Neobuthus factorio is a species of scorpion from the family Buthidae found in Somaliland.
Neobuthus amoudensis is a species of scorpion from the family Buthidae found in Somaliland and Ethiopia. It is named in honor of the Amoud University.

Neobuthus erigavoensis is a species of scorpion from the family Buthidae found in Somaliland.
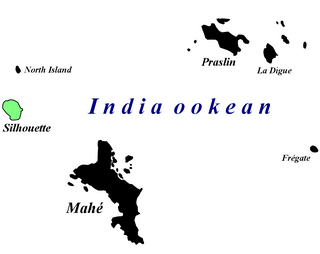
Afrolychas braueri, commonly known as the Seychelles forest scorpion, is a critically endangered species of scorpion in the family Buthidae. It is currently thought to survive only on Silhouette Island, Seychelles, although the species was historically found on two additional Seychellois islands. This scorpion lives in leaf litter in forests that are largely unaffected by invasive plant species. It is a small, yellowish-brown scorpion measuring 25 to 36 mm in length and is best distinguished from similar scorpions by having three conspicuous keels on its mesosoma's dorsal surface. While not much is known about the Seychelles forest scorpion’s ecology due to the paucity of sightings, it is known to rely solely on its venom to capture its prey and to care for its young. Its venom is not dangerous to humans.














