
The Sunda Islands are a group of islands in the Indonesian Archipelago.

Sundaland is a biogeographical region of Southeastern Asia corresponding to a larger landmass that was exposed throughout the last 2.6 million years during periods when sea levels were lower. It includes the Malay Peninsula on the Asian mainland, as well as the large islands of Borneo, Java, and Sumatra and their surrounding small islands.

Wallacea is a biogeographical designation for a group of mainly Indonesian islands separated by deep-water straits from the Asian and Australian continental shelves. Wallacea includes Sulawesi, the largest island in the group, as well as Lombok, Sumbawa, Flores, Sumba, Timor, Halmahera, Buru, Seram, and many smaller islands. The islands of Wallacea lie between the Sunda Shelf to the west, and the Sahul Shelf including Australia and New Guinea to the south and east. The total land area of Wallacea is 347,000 km2 (134,000 sq mi).
The Burma Plate is a minor tectonic plate or microplate located in Southeast Asia, sometimes considered a part of the larger Eurasian Plate. The Andaman Islands, Nicobar Islands, and northwestern Sumatra are located on the plate. This island arc separates the Andaman Sea from the main Indian Ocean to the west.

Geologically, the Sunda Shelf is a southeast extension of the continental shelf of Southeast Asia. Major landmasses on the shelf include the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, Borneo, Java, Madura, Bali and their surrounding smaller islands. It covers an area of approximately 1.85 million km2. Sea depths over the shelf rarely exceed 50 metres and extensive areas are less than 20 metres resulting in strong bottom friction and strong tidal friction. Steep undersea gradients separate the Sunda Shelf from the Philippines, Sulawesi, and the Lesser Sunda Islands.

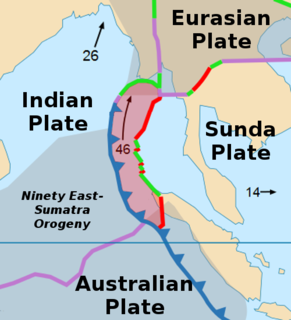
The Sunda Trench, earlier known as and sometimes still indicated as the Java Trench, is an oceanic trench located in the Indian Ocean near Sumatra, formed where the Australian-Capricorn plates subduct under a part of the Eurasian Plate. It is 3,200 kilometres (2,000 mi) long with a maximum depth of 7,290 metres. Its maximum depth is the deepest point in the Indian Ocean. The trench stretches from the Lesser Sunda Islands past Java, around the southern coast of Sumatra on to the Andaman Islands, and forms the boundary between Indo-Australian Plate and Eurasian plate. The trench is considered to be part of the Pacific Ring of Fire as well as one of a ring of oceanic trenches around the northern edges of the Australian Plate.

Breynia is a plant genus in the family Phyllanthaceae, first described in 1776. It is native to Southeast Asia, China, the Indian Subcontinent, Papuasia, Australia, and the island of Réunion.

Deudorix epijarbas, the cornelian or hairy line blue, is a species of lycaenid or blue butterfly found in south and southeast Asia from India to Fiji, including the Philippines, and also the tropical coast of Queensland in Australia. The species was first described by Frederic Moore in 1857.

Euplocia is a monotypic moth genus in the family Erebidae erected by Jacob Hübner in 1819. Its only species, Euplocia membliaria, was first described by Pieter Cramer in 1780. It is found from the northeastern Himalayas to Sundaland, the Philippines, Sulawesi and the Lesser Sundas.
Pinacia is a genus of moths of the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Jacob Hübner in 1831.

Ozola is a genus of moths in the family Geometridae first described by Francis Walker in 1861.

Neochera dominia is a species of moth in the family Erebidae. It is found from the Indo-Australian tropics from India to Queensland and the Solomons.

Neochera inops is a moth in the family Erebidae. It is found from the north-eastern Himalaya to Sundaland and Palawan, including Bangladesh (Silhet), China, India, Indonesia (Borneo), Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Sikkim, Thailand and northern Vietnam.

Pseudojana perspicuifascia is a species of moth of the family Eupterotidae first described by Rothschild in 1917. It is found in Sundaland and on Nias.
Eugoa bipuncta is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Franciscus J. M. Heylaerts in 1891. It is found in Sundaland and on Sulawesi and the Lesser Sunda Islands. The habitat consists of lowland forests.

The Lesser Sunda Islands are an archipelago in Maritime Southeast Asia, north of Australia. Together with the Greater Sunda Islands to the west they make up the Sunda Islands. The islands are part of a volcanic arc, the Sunda Arc, formed by subduction along the Sunda Trench in the Java Sea.
Lymantria subrosea is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Francis Walker in 1855. It is found from Sri Lanka to China and Sundaland, the Philippines, Sulawesi, Seram, the Lesser Sundas to Timor. The Sumatran population is categorized under the subspecies, Lymantria subrosea singapura.

Cleora alienaria is a moth of the family Geometridae first described by Francis Walker in 1860. It is found in Sri Lanka, the Indian subregion to the Andaman Islands, Thailand, Sundaland, Taiwan, and Lesser Sundas as far east as Timor and Christmas Island.












