In calculus, the chain rule is a formula that expresses the derivative of the composition of two differentiable functions f and g in terms of the derivatives of f and g. More precisely, if is the function such that for every x, then the chain rule is, in Lagrange's notation,

In mathematics, convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions that produces a third function that expresses how the shape of one is modified by the other. The term convolution refers to both the result function and to the process of computing it. It is defined as the integral of the product of the two functions after one is reflected about the y-axis and shifted. The choice of which function is reflected and shifted before the integral does not change the integral result. The integral is evaluated for all values of shift, producing the convolution function.

G, or g, is the seventh letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is gee, plural gees.

In mathematics, an integral is the continuous analog of a sum, which is used to calculate areas, volumes, and their generalizations. Integration, the process of computing an integral, is one of the two fundamental operations of calculus, the other being differentiation. Integration started as a method to solve problems in mathematics and physics, such as finding the area under a curve, or determining displacement from velocity. Today integration is used in a wide variety of scientific fields.

In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the form of energy that it possesses due to its motion.

In physics and mathematics, the phase of a wave or other periodic function of some real variable is an angle-like quantity representing the fraction of the cycle covered up to . It is expressed in such a scale that it varies by one full turn as the variable goes through each period. It may be measured in any angular unit such as degrees or radians, thus increasing by 360° or as the variable completes a full period.

The uncertainty principle, also known as Heisenberg's indeterminacy principle, is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics. It states that there is a limit to the precision with which certain pairs of physical properties, such as position and momentum, can be simultaneously known. In other words, the more accurately one property is measured, the less accurately the other property can be known.
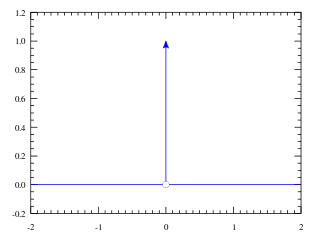
In mathematical analysis, the Dirac delta distribution, also known as the unit impulse, is a generalized function or distribution over the real numbers, whose value is zero everywhere except at zero, and whose integral over the entire real line is equal to one.
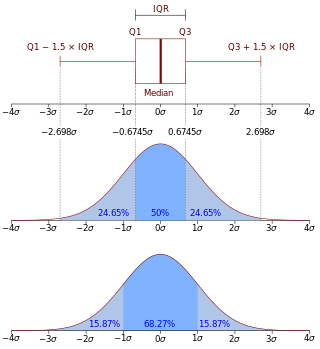
In probability theory, a probability density function (PDF), density function, or density of an absolutely continuous random variable, is a function whose value at any given sample in the sample space can be interpreted as providing a relative likelihood that the value of the random variable would be equal to that sample. Probability density is the probability per unit length, in other words, while the absolute likelihood for a continuous random variable to take on any particular value is 0, the value of the PDF at two different samples can be used to infer, in any particular draw of the random variable, how much more likely it is that the random variable would be close to one sample compared to the other sample.
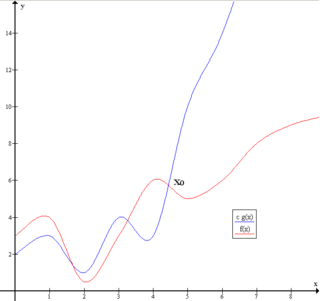
Big O notation is a mathematical notation that describes the limiting behavior of a function when the argument tends towards a particular value or infinity. Big O is a member of a family of notations invented by German mathematicians Paul Bachmann, Edmund Landau, and others, collectively called Bachmann–Landau notation or asymptotic notation. The letter O was chosen by Bachmann to stand for Ordnung, meaning the order of approximation.

In physics, engineering and mathematics, the Fourier transform (FT) is an integral transform that converts a function into a form that describes the frequencies present in the original function. The output of the transform is a complex-valued function of frequency. The term Fourier transform refers to both this complex-valued function and the mathematical operation. When a distinction needs to be made the Fourier transform is sometimes called the frequency domain representation of the original function. The Fourier transform is analogous to decomposing the sound of a musical chord into the intensities of its constituent pitches.

The orbital period is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets, exoplanets orbiting other stars, or binary stars. It may also refer to the time it takes a satellite orbiting a planet or moon to complete one orbit.
In chemistry, the molar mass of a chemical compound is defined as the ratio between the mass and the amount of substance of any sample of said compound. The molar mass is a bulk, not molecular, property of a substance. The molar mass is an average of many instances of the compound, which often vary in mass due to the presence of isotopes. Most commonly, the molar mass is computed from the standard atomic weights and is thus a terrestrial average and a function of the relative abundance of the isotopes of the constituent atoms on Earth. The molar mass is appropriate for converting between the mass of a substance and the amount of a substance for bulk quantities.

In mathematics, a function from a set X to a set Y assigns to each element of X exactly one element of Y. The set X is called the domain of the function and the set Y is called the codomain of the function.

In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum amount of work, other than pressure-volume work, that may be performed by a thermodynamically closed system at constant temperature and pressure. It also provides a necessary condition for processes such as chemical reactions that may occur under these conditions. The Gibbs free energy is expressed as

In signal processing, cross-correlation is a measure of similarity of two series as a function of the displacement of one relative to the other. This is also known as a sliding dot product or sliding inner-product. It is commonly used for searching a long signal for a shorter, known feature. It has applications in pattern recognition, single particle analysis, electron tomography, averaging, cryptanalysis, and neurophysiology. The cross-correlation is similar in nature to the convolution of two functions. In an autocorrelation, which is the cross-correlation of a signal with itself, there will always be a peak at a lag of zero, and its size will be the signal energy.

Neomachlotica is a genus of sedge moths. It was described by John B. Heppner in 1981.
Neomachlotica actinota is a species of sedge moth in the genus Neomachlotica. It was described by Walsingham in 1914. It is found in Central America.
Neomachlotica spiraea is a species of sedge moth in the genus Neomachlotica. It was described by John B. Heppner in 1981. It is found in the US state of Florida.

Laphriinae is a subfamily of robber flies in the family Asilidae. There are more than 110 genera and 1,000 described species in Laphriinae. Larvae of the genus Hyperechia are known to grow inside the cells of Xylocopa bees, feeding on their larvae.















