
Wisteria is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae (Leguminosae), that includes ten species of woody twining vines that are native to China, Japan, Korea, Vietnam, Southern Canada, the Eastern United States, and north of Iran. They were later introduced to France, Germany and various other countries in Europe. Some species are popular ornamental plants.

Hibiscus is a genus of flowering plants in the mallow family, Malvaceae. The genus is quite large, comprising several hundred species that are native to warm temperate, subtropical and tropical regions throughout the world. Member species are renowned for their large, showy flowers and those species are commonly known simply as "hibiscus", or less widely known as rose mallow. Other names include hardy hibiscus, rose of sharon, and tropical hibiscus.

Hibiscus rosa-sinensis, known colloquially as Chinese hibiscus, China rose, Hawaiian hibiscus, rose mallow and shoeblack plant, is a species of tropical hibiscus, a flowering plant in the Hibisceae tribe of the family Malvaceae. It is widely cultivated as an ornamental plant in the tropics and subtropics, but its native range is Vanuatu.

The greater coucal or crow pheasant, is a large non-parasitic member of the cuckoo order of birds, the Cuculiformes. A widespread resident in the Indian Subcontinent and Southeast Asia, it is divided into several subspecies, some being treated as full species. They are large, crow-like with a long tail and coppery brown wings and found in a wide range of habitats from jungle to cultivation and urban gardens. They are weak fliers, and are often seen clambering about in vegetation or walking on the ground as they forage for insects, eggs and nestlings of other birds. They have a familiar deep resonant call which is associated with omens in many parts of its range.

Ophiocordyceps sinensis is known in English colloquially as caterpillar fungus, or by its more prominent names dōng chóng xià cǎo, literally "winter worm, summer grass"), or yartsa gunbu (Tibetan: དབྱར་རྩྭ་དགུན་འབུ་, Wylie: dbyar rtswa dgun 'bu, or Yarsa-gumba or Yarcha-gumba, or Keeda Jadi, or ရှီးပတီး. It is an entomopathogenic fungus in the family Ophiocordycipitaceae. It is mainly found in the meadows above 3,500 meters on Tibetan Plateau in Southwest China and Himalayan regions of Bhutan and Nepal. It parasitizes larvae of ghost moths and produces a fruiting body which used to be valued as a herbal remedy and in traditional Chinese medicine. Caterpillar fungus contains the compound cordycepin, an adenosine derivative. However, the fruiting bodies harvested in nature usually contain high amounts of arsenic and other heavy metals so they are potentially toxic and sales have been strictly regulated by the CFDA since 2016.

Clonorchis sinensis, the Chinese liver fluke, is a liver fluke belonging to the class Trematoda, phylum Platyhelminthes. It infects fish-eating mammals, including humans. In humans, it infects the common bile duct and gall bladder, feeding on bile. It was discovered by British physician James McConnell at the Medical College Hospital in Calcutta (Kolkata) in 1874. The first description was given by Thomas Spencer Cobbold, who named it Distoma sinense. The fluke passes its lifecycle in three different hosts, namely freshwater snail as first intermediate hosts, freshwater fish as second intermediate host, and mammals as definitive hosts.

Camellia sinensis is a species of evergreen shrubs or small trees in the flowering plant family Theaceae. Its leaves and leaf buds are used to produce tea. Common names include "tea plant", "tea shrub", and "tea tree".
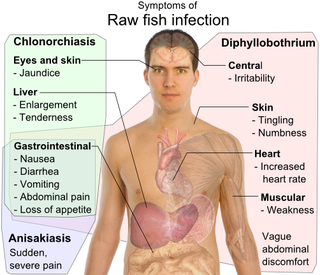
Clonorchiasis is an infectious disease caused by the Chinese liver fluke and two related species. Clonorchiasis is a known risk factor for the development of cholangiocarcinoma, a neoplasm of the biliary system.

Angelica sinensis, commonly known as dong quai or female ginseng, is a herb belonging to the family Apiaceae, indigenous to China. Angelica sinensis grows in cool high altitude mountains in East Asia. The yellowish brown root of the plant is harvested in the fall and is a well-known Chinese medicine which has been used for thousands of years.

Sinosaurus is an extinct genus of theropod dinosaur which lived during the Early Jurassic Period. It was a bipedal carnivore approximately 5.6 metres in length. Fossils of the animal were found at the Lufeng Formation, in the Yunnan Province of China.

Gyposaurus is a genus of basal sauropodomorph dinosaur from the early Jurassic of South Africa. It is usually considered to represent juveniles of other prosauropods, but "G." sinensis is regarded as a possibly valid species.

The Chinese softshell turtle is a species of softshell turtle that is native to China and Taiwan, with records of escapees—some of which have established introduced populations—in a wide range of other Asian countries, as well as Spain, Brazil and Hawaii.

Miscanthus sinensis, the eulalia or Chinese silver grass, is a species of flowering plant in the grass family Poaceae, native to eastern Asia throughout most of China, Japan, Taiwan and Korea.

The South China catshark is a catshark of the family Scyliorhinidae, known only from the holotype, which was taken from the South China Sea at a depth of 537 m. Its length is 42 cm, but this measurement was taken from an immature specimen. The reproduction of the South China catshark is oviparous.

The Asian parti-colored bat is a species of parti-coloured bat. An adult Asian parti-colored bat has a body length of 6–7 cm, a tail of 4.3-4.5 cm, and a wing length of 5 cm. Asian parti-colored bats are distributed across East Asia, from Taiwan through eastern China, eastern Mongolia and Russia (Siberia) to the Korean Peninsula and Japan.

Youngosuchus is an extinct genus of archosaur from the Middle Triassic of China. The type species is Y. sinensis. Y. sinensis was first described in 1973 as a new species of the erythrosuchid Vjushkovia. In 1985, it was reassigned as its own genus of rauisuchid. A 1992 study supported the original classification of Youngosuchus sinensis as an erythrosuchid, but more recent studies classify it as a "rauisuchian"-grade loricatan archosaur completely unrelated to Vjushkovia, which is most likely a synonym of Garjainia.
Neospastis is a genus of moths of the family Xyloryctidae.
Neospastis calpidias is a moth in the family Xyloryctidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1917. It is found in southern India.

Camellia taliensis is a species of evergreen shrub or small tree whose leaves and leaf buds are used to produce tea.
















