| Name | Year | Rank | Synonym of: | Notes |
|---|
| Camellia angustifoliaHung T.Chang | 1981 | species | var. pubilimba | = het. |
| Camellia arborescensHung T.Chang, F.L.Yu & P.S.Wang | 1983 | species | var. sinensis | = het. |
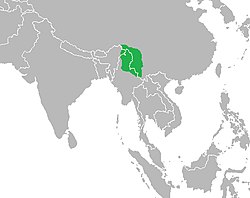
| Camellia assamica(Royle ex Hook.) C.D.Darl & Jan.Ammal | 1945 | species | var. assamica | ≡ hom. |
| Camellia assamica var. kuchaHung T.Chang, H.S.Wang & B.H.Chen | 1983 | variety | var. assamica | = het. |
| Camellia assamica subsp. lasiocalyx(G.Watt) W.Wight | 1962 | subspecies | var. assamica | = het. |
| Camellia assamica var. polyneura(Hung T.Chang, Y.J.Tan & P.S.Wang) Hung T.Chang | 1998 | variety | var. assamica | = het. |
| Camellia bohea(L.) Sweet | 1818 | species | var. viridis | = het. |
| Camellia dehungensisHung T.Chang, H.S.Wang & B.H.Chen | 1983 | species | var. dehungensis | ≡ hom. |
| Camellia dehungensisHung T.Chang & B.H.Chen | 1984 | species | var. dehungensis | = het., nom. illeg. |
| Camellia dishiensisF.C.Zhang, X.Y.Chen & G.B.Chen | 1990 | species | var. pubilimba | = het. |
| Camellia formosensis(Masam. & S.Suzuki) M.H.Su, C.F.Hsieh & C.H.Tsou | 2009 | species | var. viridis | = het. |
| Camellia kucha(Hung T.Chang, H.S.Wang & B.H.Chen) Hung T.Chang | 2008 | species | var. assamica | = het. |
| Camellia longlingensisF.C.Zhang, G.B.Chen & M.D.Tang | 1990 | species | var. viridis | = het. |
| Camellia manglaensisHung T.Chang, Y.J.Tan & P.S.Wang | 1983 | species | var. dehungensis | = het. |
| Camellia multisepalaHung T.Chang, Y.J.Tan & P.S.Wang | 1983 | species | var. assamica | = het. |
| Camellia oleosa(Lour.) Rehder | 1937 | species | var. virescens | ≡ hom. |
| Camellia parvisepalaHung T.Chang | 1981 | species | var. pubilimba | = het. |
| Camellia parvisepaloidesHung T.Chang, H.S.Wang & B.H.Chen | 1983 | species | var. dehungensis | = het. |
| Camellia polyneuraHung T.Chang, Y.J.Tan & P.S.Wang | 1983 | species | var. assamica | = het. |
| Camellia scottianaChoisy | 1855 | species | var. assamica | = het., not validly publ. |
| Camellia sinensis var. dulcamaraQ.U.Le & D.L.Nguyen | 2020 | variety | var. assamica | = het. |
| Camellia sinensis f. formosensis(Masam. & S.Suzuki) Kitam. | 1950 | form | var. virescens | ≡ hom. |
| Camellia sinensis var. kuchaHung T.Chang & S.S.Wang | 1984 | variety | var. assamica | = het. |
| Camellia sinensis var. lasiocalyx(G.Watt) A.P.Das & C.Ghosh | 2016 | variety | var. assamica | = het. |
| Camellia sinensis f. macrophylla(C.Morren) Kitam. | 1950 | form | var. virescens | = het. |
| Camellia sinensis f. parvifolia(Miq.) Sealy | 1958 | form | D. viridis | ≡ hom. |
| Camellia sinensis f. rosea(Makino) Kitam. | 1950 | form | D. viridis | ≡ hom. |
| Camellia sinensis f. ticinensis(Pollacci & Gallotti) Ardenghi | 2020 | form | var. virescens | = het., cited basionym not validly publ. |
| Camellia sinensis var. waldenae(S.Y.Hu) Hung T.Chang | 1981 | variety | var. virescens | ≡ hom. |
| Camellia tenuistipaOrel, Curry & Luu | 2015 | species | var. assamica | = het. |
| Camellia theaLink | 1822 | species | C. sinensis | ≡ hom., nom. superfl. |
| Camellia thea var. assamica(Royle ex Hook.) Boerl. | 1901 | variety | var. assamica | ≡ hom. |
| Camellia thea var. bohea(L.) G.Watt | 1907 | variety | D. viridis | ≡ hom. |
| Camellia thea var. lasiocalyxG.Watt | 1907 | variety | var. assamica | = het. |
| Camellia thea var. stricta(Hayne) G.Watt | 1907 | variety | var. virescens | = het. |
| Camellia thea f. ticinensisPollacci & Gallotti | 1940 | form | var. virescens | = het., nom. nud. |
| Camellia thea var. viridis(L.) G.Watt | 1907 | variety | var. virescens | = het. |
| Camellia theiferaGriff. | 1854 | species | var. assamica | = het. |
| Camellia theifera var. assamica(Royle ex Hook.) Greshoff | 1893 | variety | var. assamica | ≡ hom. |
| Camellia theifera var. macrophylla(C.Morren) Matsum. | 1883 | variety | var. viridis | = het. |
| Camellia viridisSweet | 1818 | species | D. viridis | ≡ hom. |
| Camellia waldenaeS.Y.Hu | 1977 | species | var. viridis | = het. |
| Thea assamicaRoyle ex Hook. | 1847 | species | var. assamica | ≡ hom. |
| Thea boheaL. | 1762 | species | var. virescens | = het. |
| Thea bohea var. laxaAiton | 1789 | variety | var. virescens | = het. |
| Thea bohea var. strictaAiton | 1789 | variety | var. virescens | = het. |
| Thea cantoniensisLour. | 1790 | species | var. viridis | = het. |
| Thea chinensisSims | 1807 | species | var. virescens | ≡ hom., orth. var. |
| Thea cochinchinensisLour. | 1790 | species | var. assamica | = het. |
| Thea formosensisMasam. & S.Suzuki | 1937 | species | var. virescens | = het. |
| Thea grandifoliaSalisb. | 1796 | species | var. viridis | = het. |
| Thea latifoliaLodd. ex Sweet | 1839 | species | var. virescens | ≡ hom. |
| Thea laxaStaunton | 1798 | species | D. viridis | ≡ hom. |
| Thea longifoliaNois. ex Steud. | 1821 | species | var. viridis | = het., not validly publ. |
| Thea macrophylla(C.Morren) Makino | 1918 | species | var. viridis | = het. |
| Thea oleariaLour. ex Gomes Mach. | 1868 | species | var. viridis | = het. |
| Thea oleosaLour. | 1790 | species | var. viridis | = het. |
| Thea parvifoliaSalisb. | 1796 | species | var. virescens | = het. |
| Thea sasanqua var. oleosa(Lour.) Pierre | 1887 | variety | var. viridis | = het. |
| Thea sinensisL. | 1753 | species | C. sinensis | ≡ hom. |
| Thea sinensis var. assamica(Royle ex Hook.) Pierre | 1887 | variety | var. assamica | ≡ hom., nom. illeg. |
| Thea sinensis var. assamicaGuilf. | 1883 | variety | var. assamica | = het. |
| Thea sinensis var. bohea(L.) K.Koch | 1853 | variety | var. viridis | = het. |
| Thea sinensis var. cantoniensis(Lour.) Pierre | 1887 | variety | var. virescens | ≡ hom. |
| Thea sinensis var. diffusaC.Morren | 1835 | variety | D. viridis | ≡ hom. |
| Thea sinensis var. macrophyllaC.Morren | 1835 | variety | var. virescens | = het. |
| Thea sinensis var. parvifoliaMiq. | 1867 | variety | var. viridis | = het. |
| Thea sinensis var. pubescensPierre | 1887 | variety | var. virescens | = het. |
| Thea sinensis var. roseaMakino | 1905 | variety | var. viridis | = het. |
| Thea sinensis var. rugosaC.Morren | 1835 | variety | var. viridis | = het. |
| Thea sinensis var. strictaC.Morren | 1835 | variety | D. viridis | ≡ hom. |
| Thea sinensis var. viridisPierre | 1887 | variety | var. virescens | = het. |
| Thea strictaHayne | 1821 | species | var. viridis | = het. |
| Thea viridisL. | 1762 | species | var. viridis | = het. |
| Thea viridis var. assamica(Royle ex Hook.) Choisy | 1855 | variety | var. assamica | ≡ hom. |
| Thea viridis var. bohea(L.) Vent. | 1799 | variety | var. virescens | = het. |
| Thea viridis variegataJ.Dix | 1861 | | var. viridis | = het. |
| Thea yersiniiA.Chev. ex Gagnep. | 1943 | species | var. assamica | = het., without a Latin descr. |
| Theaphylla anamensisRaf. | 1838 | species | var. viridis | = het. |
| Theaphylla cantoniensis(Lour.) Raf. | 1838 | species | var. viridis | = het. |
| Theaphylla laxa(Aiton) Raf. | 1838 | species | var. viridis | = het. |
| Theaphylla viridis(Sweet) Raf. | 1838 | species | var. virescens | ≡ hom. |
| Notes: ≡ homotypic synonym; = heterotypic synonym |
|---|