
Bansal, Raj K. (2003). A Textbook of Organic Chemistry. New Age International Limited. p. 644. ISBN 978-81-224-1459-2.

Piperidine is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2)5NH. This heterocyclic amine consists of a six-membered ring containing five methylene bridges (–CH2–) and one amine bridge (–NH–). It is a colorless liquid with an odor described as objectionable, typical of amines. The name comes from the genus name Piper, which is the Latin word for pepper. Although piperidine is a common organic compound, it is best known as a representative structure element within many pharmaceuticals and alkaloids, such as natural-occurring solenopsins.
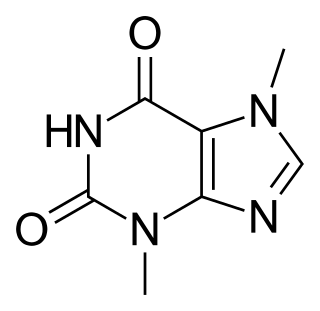
Theobromine, also known as xantheose, is the principal alkaloid of Theobroma cacao. Theobromine is slightly water-soluble (330 mg/L) with a bitter taste. In industry, theobromine is used as an additive and precursor to some cosmetics. It is found in chocolate, as well as in a number of other foods, including the leaves of the tea plant, and the kola nut. It is a white or colourless solid, but commercial samples can appear yellowish.
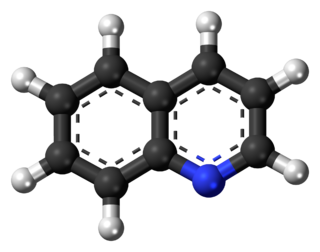
Quinoline is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C9H7N. It is a colorless hygroscopic liquid with a strong odor. Aged samples, especially if exposed to light, become yellow and later brown. Quinoline is only slightly soluble in cold water but dissolves readily in hot water and most organic solvents. Quinoline itself has few applications, but many of its derivatives are useful in diverse applications. A prominent example is quinine, an alkaloid found in plants. Over 200 biologically active quinoline and quinazoline alkaloids are identified. 4-Hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines (HAQs) are involved in antibiotic resistance.
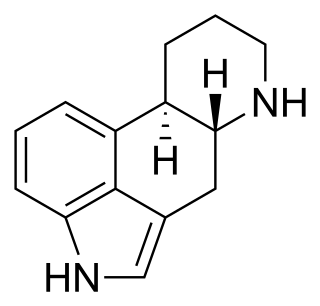
Ergoline is a chemical compound whose structural skeleton is contained in a variety of alkaloids, referred to as ergoline derivatives or ergoline alkaloids. Ergoline alkaloids, one being ergine, were initially characterized in ergot. Some of these are implicated in the condition ergotism, which can take a convulsive form or a gangrenous form. Even so, many ergoline alkaloids have been found to be clinically useful. Annual world production of ergot alkaloids has been estimated at 5,000–8,000 kg of all ergopeptines and 10,000–15,000 kg of lysergic acid, used primarily in the manufacture of semi-synthetic derivatives.
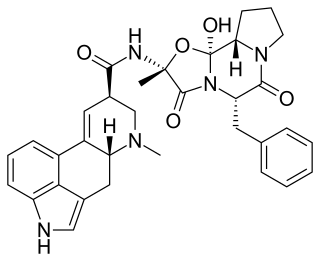
Ergotamine, sold under the brand names Cafergot and Ergomar among others, is an ergopeptine and part of the ergot family of alkaloids; it is structurally and biochemically closely related to ergoline. It is structurally similar to several neurotransmitters, and it acts as a vasoconstrictor.
Total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of a complex molecule, often a natural product, from simple, commercially-available precursors. It usually refers to a process not involving the aid of biological processes, which distinguishes it from semisynthesis. Syntheses may sometimes conclude at a precursor with further known synthetic pathways to a target molecule, in which case it is known as a formal synthesis. Total synthesis target molecules can be natural products, medicinally-important active ingredients, known intermediates, or molecules of theoretical interest. Total synthesis targets can also be organometallic or inorganic, though these are rarely encountered. Total synthesis projects often require a wide diversity of reactions and reagents, and subsequently requires broad chemical knowledge and training to be successful.

Ibogaine is a naturally occurring psychoactive substance found in plants in the family Apocynaceae such as Tabernanthe iboga, Voacanga africana, and Tabernaemontana undulata. It is a psychedelic with dissociative properties.

Catharanthus roseus, commonly known as bright eyes, Cape periwinkle, graveyard plant, Madagascar periwinkle, old maid, pink periwinkle, rose periwinkle, is a perennial species of flowering plant in the family Apocynaceae. It is native and endemic to Madagascar, but is grown elsewhere as an ornamental and medicinal plant, and now has a pantropical distribution. It is a source of the drugs vincristine and vinblastine, used to treat cancer. It was formerly included in the genus Vinca as Vinca rosea.

Indole alkaloids are a class of alkaloids containing a structural moiety of indole; many indole alkaloids also include isoprene groups and are thus called terpene indole or secologanin tryptamine alkaloids. Containing more than 4100 known different compounds, it is one of the largest classes of alkaloids. Many of them possess significant physiological activity and some of them are used in medicine. The amino acid tryptophan is the biochemical precursor of indole alkaloids.

Berberine is a quaternary ammonium salt from the protoberberine group of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids

Xanthosine monophosphate (xanthylate) is an intermediate in purine metabolism. It is a ribonucleoside monophosphate. It is formed from IMP via the action of IMP dehydrogenase, and it forms GMP via the action of GMP synthase. Also, XMP can be released from XTP by enzyme deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate pyrophosphohydrolase containing (d)XTPase activity.

Sir Alan Rushton Battersby was an English organic chemist best known for his work to define the chemical intermediates in the biosynthetic pathway to vitamin B12 and the reaction mechanisms of the enzymes involved. His research group was also notable for its synthesis of radiolabelled precursors to study alkaloid biosynthesis and the stereochemistry of enzymic reactions. He won numerous awards including the Royal Medal in 1984 and the Copley Medal in 2000. He was knighted in the 1992 New Year Honours. Battersby died in February 2018 at the age of 92.

Indole is an organic compound with the formula C6H4CCNH3. Indoles are derivatives of indole where one or more H's have been replaced by other groups. Indole is classified as an aromatic heterocycle. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered pyrrole ring. Indoles are widely distributed in nature, most notably as amino acid tryptophan and neurotransmitter serotonin.

Coronaridine, also known as 18-carbomethoxyibogamine, is an alkaloid found in Tabernanthe iboga and related species, including Tabernaemontana divaricata for which it was named.

Ajmalicine, also known as δ-yohimbine or raubasine, is an antihypertensive drug used in the treatment of high blood pressure. It has been marketed under numerous brand names including Card-Lamuran, Circolene, Cristanyl, Duxil, Duxor, Hydroxysarpon, Iskedyl, Isosarpan, Isquebral, Lamuran, Melanex, Raunatin, Saltucin Co, Salvalion, and Sarpan. It is an alkaloid found naturally in various plants such as Rauvolfia spp., Catharanthus roseus, and Mitragyna speciosa.
Biomimetic synthesis is an area of organic chemical synthesis that is specifically biologically inspired. The term encompasses both the testing of a "biogenetic hypothesis" through execution of a series of reactions designed to parallel the proposed biosynthesis, as well as programs of study where a synthetic reaction or reactions aimed at a desired synthetic goal are designed to mimic one or more known enzymic transformations of an established biosynthetic pathway. The earliest generally cited example of a biomimetic synthesis is Sir Robert Robinson's organic synthesis of the alkaloid tropinone.

Erysodienone is a key precursor in the biosynthesis of many Erythrina-produced alkaloids. Early work was done by Derek Barton and co-workers to illustrate the biosynthetic pathways towards erythrina alkaloids. It was demonstrated that erysodienone could be synthesized from simple starting materials by a similar approach as its biosynthetic pathway, which led to the development of the biomimetic synthesis of erysodienone.
Dewan Singh Bhakuni was an Indian natural product chemist, stereochemist who was a director general-grade scientist of the Central Drug Research Institute. He is known for his researches on the biogenesis of alkaloids and is an elected fellow of the Indian Academy of Sciences, the National Academy of Sciences, India and the Indian National Science Academy. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards, in 1975, for his contributions to chemical sciences.

Apparicine is a monoterpenoid indole alkaloid. It is named after Apparicio Duarte, a Brazilian botanist who studied the Aspidosperma species from which apparicine was first isolated. It was the first member of the vallesamine group of alkaloids to be isolated and have its structure established, which was first published in 1965. It has also been known by the synonyms gomezine, pericalline, and tabernoschizine.

















