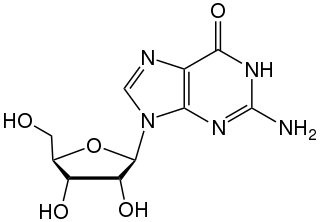
Guanosine (symbol G or Guo) is a purine nucleoside comprising guanine attached to a ribose (ribofuranose) ring via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Guanosine can be phosphorylated to become guanosine monophosphate (GMP), cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), guanosine diphosphate (GDP), and guanosine triphosphate (GTP). These forms play important roles in various biochemical processes such as synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, photosynthesis, muscle contraction, and intracellular signal transduction (cGMP). When guanine is attached by its N9 nitrogen to the C1 carbon of a deoxyribose ring it is known as deoxyguanosine.
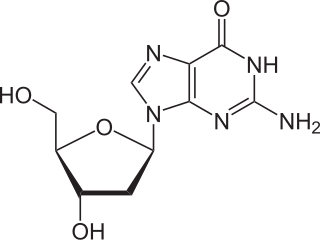
Deoxyguanosine is composed of the purine nucleobase guanine linked by its N9 nitrogen to the C1 carbon of deoxyribose. It is similar to guanosine, but with one hydroxyl group removed from the 2' position of the ribose sugar. If a phosphate group is attached at the 5' position, it becomes deoxyguanosine monophosphate.
Small GTPases, also known as small G-proteins, are a family of hydrolase enzymes that can bind and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP). They are a type of G-protein found in the cytosol that are homologous to the alpha subunit of heterotrimeric G-proteins, but unlike the alpha subunit of G proteins, a small GTPase can function independently as a hydrolase enzyme to bind to and hydrolyze a guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to form guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The best-known members are the Ras GTPases and hence they are sometimes called Ras subfamily GTPases.

Guanosine-5'-triphosphate (GTP) is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It is one of the building blocks needed for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process. Its structure is similar to that of the guanosine nucleoside, the only difference being that nucleotides like GTP have phosphates on their ribose sugar. GTP has the guanine nucleobase attached to the 1' carbon of the ribose and it has the triphosphate moiety attached to ribose's 5' carbon.

Guanosine diphosphate, abbreviated GDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GDP consists of a pyrophosphate group, a pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine.

Nucleoside-diphosphate kinases are enzymes that catalyze the exchange of terminal phosphate between different nucleoside diphosphates (NDP) and triphosphates (NTP) in a reversible manner to produce nucleotide triphosphates. Many NDP serve as acceptor while NTP are donors of phosphate group. The general reaction via ping-pong mechanism is as follows: XDP + YTP ←→ XTP + YDP. NDPK activities maintain an equilibrium between the concentrations of different nucleoside triphosphates such as, for example, when guanosine triphosphate (GTP) produced in the citric acid (Krebs) cycle is converted to adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Other activities include cell proliferation, differentiation and development, signal transduction, G protein-coupled receptor, endocytosis, and gene expression.

ADP ribosylation factors (ARFs) are members of the ARF family of GTP-binding proteins of the Ras superfamily. ARF family proteins are ubiquitous in eukaryotic cells, and six highly conserved members of the family have been identified in mammalian cells. Although ARFs are soluble, they generally associate with membranes because of N-terminus myristoylation. They function as regulators of vesicular traffic and actin remodelling.

Deoxyguanosine monophosphate (dGMP), also known as deoxyguanylic acid or deoxyguanylate in its conjugate acid and conjugate base forms, respectively, is a derivative of the common nucleic acid guanosine triphosphate (GTP), in which the –OH (hydroxyl) group on the 2' carbon on the nucleotide's pentose has been reduced to just a hydrogen atom. It is used as a monomer in DNA.

In molecular biology, adenylosuccinate synthase is an enzyme that plays an important role in purine biosynthesis, by catalysing the guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-dependent conversion of inosine monophosphate (IMP) and aspartic acid to guanosine diphosphate (GDP), phosphate and N(6)-(1,2-dicarboxyethyl)-AMP. Adenylosuccinate synthetase has been characterised from various sources ranging from Escherichia coli to vertebrate tissues. In vertebrates, two isozymes are present: one involved in purine biosynthesis and the other in the purine nucleotide cycle.

GTPgammaS is a non-hydrolyzable or slowly hydrolyzable G-protein-activating analog of guanosine triphosphate (GTP). Many GTP binding proteins demonstrate activity when bound to GTP, and are inactivated via the hydrolysis of the phosphoanhydride bond that links the γ-phosphate to the remainder of the nucleotide, leaving a bound guanosine diphosphate (GDP) and releasing an inorganic phosphate. This usually occurs rapidly, and the GTP-binding protein can then only be activated by exchanging the GDP for a new GTP molecule. The substitution of sulfur for one of the oxygens of the γ-phosphate of GTP creates a nucleotide that either cannot be hydrolyzed or is only slowly hydrolyzed. This prevents the GTP-binding proteins from being inactivated, and allows the cellular processes that they carry out when active to be more easily studied.
In enzymology, an acid—CoA ligase (GDP-forming) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Guanosine diphosphate mannose or GDP-mannose is a nucleotide sugar that is a substrate for glycosyltransferase reactions in metabolism. This compound is a substrate for enzymes called mannosyltransferases.
In enzymology, a GTP cyclohydrolase II (EC 3.5.4.25) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a fucose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glucose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a GTP diphosphokinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a guanosine-triphosphate guanylyltransferase (EC 2.7.7.45) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a mannose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a nucleoside-triphosphate-aldose-1-phosphate nucleotidyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
A biphosphate is any of the following :











