
Lycopene is an organic compound classified as a tetraterpene and a carotene. Lycopene is a bright red carotenoid hydrocarbon found in tomatoes and other red fruits and vegetables.

Carotenoids, also called tetraterpenoids, are yellow, orange, and red organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, and fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, corn, tomatoes, canaries, flamingos, salmon, lobster, shrimp, and daffodils. Carotenoids can be produced from fats and other basic organic metabolic building blocks by all these organisms. It is also produced by endosymbiotic bacteria in whiteflies. Carotenoids from the diet are stored in the fatty tissues of animals, and exclusively carnivorous animals obtain the compounds from animal fat. In the human diet, absorption of carotenoids is improved when consumed with fat in a meal. Cooking carotenoid-containing vegetables in oil and shredding the vegetable both increase carotenoid bioavailability.

Chromoplasts are plastids, heterogeneous organelles responsible for pigment synthesis and storage in specific photosynthetic eukaryotes. It is thought that like all other plastids including chloroplasts and leucoplasts they are descended from symbiotic prokaryotes.

Zeaxanthin is one of the most common carotenoids in nature, and is used in the xanthophyll cycle. Synthesized in plants and some micro-organisms, it is the pigment that gives paprika, corn, saffron, goji (wolfberries), and many other plants and microbes their characteristic color.

Phytofluene is a colorless carotenoid found naturally in tomatoes and other vegetables. It is the second product of carotenoid biosynthesis. It is formed from phytoene in a desaturation reaction leading to the formation of five conjugated double bonds. In the following step, addition of carbon-carbon conjugated double bonds leads to the formation of z-carotene and appearance of visible color.
Tetraterpenes are terpenes consisting of eight isoprene units and have the molecular formula C40H64. Tetraterpenoids (including many carotenoids) are tetraterpenes that have been chemically modified, as indicated by the presence of oxygen-containing functional groups.
γ-Carotene (gamma-carotene) is a carotenoid, and is a biosynthetic intermediate for cyclized carotenoid synthesis in plants. It is formed from cyclization of lycopene by lycopene cyclase epsilon. Along with several other carotenoids, γ-Carotene is a vitamer of vitamin A in herbivores and omnivores. Carotenoids with a cyclized, beta-ionone ring can be converted to vitamin A, also known as retinol, by the enzyme Beta-carotene 15,15'-dioxygenase; however, the bioconversion of gamma-carotene to retinol has not been well-characterized.
CRT is the gene cluster responsible for the biosynthesis of carotenoids. Those genes are found in eubacteria, in algae and are cryptic in Streptomyces griseus.
In enzymology, a carotene 7,8-desaturase (EC 1.14.99.30) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The Cara cara navel orange, or red-fleshed navel orange, is an early-to-midseason navel orange noted for its pinkish-to-reddish-orange flesh.

Phytoene is a 40-carbon intermediate in the biosynthesis of carotenoids. The synthesis of phytoene is the first committed step in the synthesis of carotenoids in plants. Phytoene is produced from two molecules of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) by the action of the enzyme phytoene synthase. The two GGPP molecules are condensed together followed by removal of diphosphate and proton shift leading to the formation of phytoene.
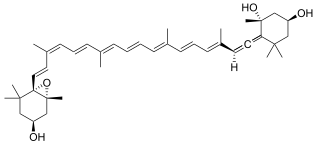
Neoxanthin is a carotenoid and xanthophyll. In plants, it is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of the plant hormone abscisic acid. It is often present in two forms: all-trans and 9-cis isomers. It is produced from violaxanthin, but a suspected neoxanthin synthase is still to be confirmed. Two different genes were confirmed to be implied in violaxanthin conversion to neoxanthin in Arabidopsis and tomato. It has a specific role in protection against photooxidative stress. It is a major xanthophyll found in green leafy vegetables such as spinach.

15-cis-phytoene desaturases, are enzymes involved in the carotenoid biosynthesis in plants and cyanobacteria. Phytoene desaturases are membrane-bound enzymes localized in plastids and introduce two double bonds into their colorless substrate phytoene by dehydrogenation and isomerize two additional double bonds. This reaction starts a biochemical pathway involving three further enzymes called the poly-cis pathway and leads to the red colored lycopene. The homologous phytoene desaturase found in bacteria and fungi (CrtI) converts phytoene directly to lycopene by an all-trans pathway.
9,9'-dicis-zeta-carotene desaturase is an enzyme with systematic name 9,9'-dicis-zeta-corotene:quinone oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Phytoene desaturase (neurosporene-forming) is an enzyme with systematic name 15-cis-phytoene:acceptor oxidoreductase (neurosporene-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Phytoene desaturase (zeta-carotene-forming) is an enzyme with systematic name 15-cis-phytoene:acceptor oxidoreductase (zeta-carotene-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Phytoene desaturase (3,4-didehydrolycopene-forming) is an enzyme with systematic name 15-cis-phytoene:acceptor oxidoreductase (3,4-didehydrolycopene-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Phytoene desaturase (lycopene-forming) are enzymes found in archaea, bacteria and fungi that are involved in carotenoid biosynthesis. They catalyze the conversion of colorless 15-cis-phytoene into a bright red lycopene in a biochemical pathway called the poly-trans pathway. The same process in plants and cyanobacteria utilizes four separate enzymes in a poly-cis pathway.
Demethylspheroidene O-methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:demethylspheroidene O-methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Phytoene desaturase may refer to:









