
John White was an English colonial governor, explorer, artist, and cartographer. White was among those who sailed with Richard Grenville in the first attempt to colonize Roanoke Island in 1585, acting as artist and mapmaker to the expedition. He would most famously briefly serve as the governor of the second attempt to found Roanoke Colony on the same island in 1587 and discover the colonists had mysteriously vanished.

Roanoke Island is an island in Dare County, bordered by the Outer Banks of North Carolina. It was named after the historical Roanoke, a Carolina Algonquian people who inhabited the area in the 16th century at the time of English colonization.

The Roanoke Colony was an attempt by Sir Walter Raleigh to found the first permanent English settlement in North America. The colony was founded in 1585, but when it was visited by a ship in 1590, the colonists had inexplicably disappeared. It has come to be known as the Lost Colony, and the fate of the 112 to 121 colonists remains unknown.
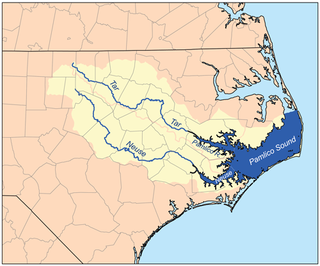
The Neuse River is a river rising in the Piedmont of North Carolina and emptying into Pamlico Sound below New Bern. Its total length is approximately 275 miles (443 km), making it the longest river entirely contained in North Carolina. The Trent River joins the Neuse at New Bern. Its drainage basin, measuring 5,630 square miles (14,600 km2) in area, also lies entirely inside North Carolina. It is formed by the confluence of the Flat and Eno rivers prior to entering the Falls Lake reservoir in northern Wake County. Its fall line shoals, known as the Falls of the Neuse, lie submerged under the waters of Falls Lake. This River also creates the beauty of the Neuse River Trail, a 34.5 miles (55.5 km) long greenway that stretches from Falls Lake Dam, Raleigh, North Carolina to Legend Park, Clayton, North Carolina.
The Waccamaw people were an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, who lived in villages along the Waccamaw and Pee Dee rivers in North and South Carolina in the 18th century.

The Meherrin people are an Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands, who spoke an Iroquian language. They lived between the Piedmont and coastal plains at the border of Virginia and North Carolina.

The Saponi are a Native American tribe historically based in the Piedmont of North Carolina and Virginia. They spoke a Siouan language, related to the languages of the Tutelo, Biloxi, and Ofo.

The Pedee people, also Pee Dee and Peedee, were a historic Native American tribe of the Southeastern United States. Historically, their population has been concentrated in the Piedmont of present-day South Carolina. It is believed that in the 17th and 18th centuries, English colonists named the Pee Dee River and the Pee Dee region of South Carolina for the tribe. Today four state-recognized tribes, one state-recognized group, and several unrecognized groups claim descent from the historic Pedee people. Presently none of these organizations are recognized by the Bureau of Indian Affairs, with the Catawba Indian Nation being the only federally recognized tribe within South Carolina.
The Machapunga were a small Algonquian language–speaking Native American tribe from coastal northeastern North Carolina. They were part of the Secotan people. They were a group from the Powhatan Confederacy who migrated from present-day Virginia.

The Tutelo were Native American people living above the Fall Line in present-day Virginia and West Virginia. They spoke a dialect of the Siouan Tutelo language thought to be similar to that of their neighbors, the Monacan and Manahoac nations.

The Croatan were a small Native American ethnic group living in the coastal areas of what is now North Carolina. They might have been a branch of the larger Roanoke people or allied with them.
The Sissipahaw or Haw were a Native American tribe of North Carolina. They are also variously recorded as Saxahapaw, Sauxpa, Sissipahaus, etc. Their settlements were generally located in the vicinity of modern-day Saxapahaw, North Carolina on the Haw River in Alamance County upstream from Cape Fear. They are possibly first recorded by the Spaniard Vendera in the 16th century as the Sauxpa in South Carolina. Their last mention in history is that the tribe joined the Yamasee against the English colonists in the Yamasee War of 1715. Some scholars speculate that they may have been a branch of the Shakori due to being so closely associated with that tribe but others disagree with this assumption.

The Neusiok Trail is a 20.4-mile (32.8 km) hiking trail located in the Croatan National Forest in Carteret County, North Carolina. The trail traverses the forest from a sandy beach on the Neuse River to a salt marsh on the Newport River, and along the way, it crosses cypress swamps, hardwood ridges, longleaf-pine savannah and pocosin—shrubby bogs The entire Neusiok is part of the Mountains-to-Sea Trail (MST) which spans North Carolina, and the MST in the Croatan is a designated National Recreation Trail.

The Secotans were one of several groups of Native Americans dominant in the Carolina sound region, between 1584 and 1590, with which English colonists had varying degrees of contact. Secotan villages included the Secotan, Aquascogoc, Dasamongueponke, Pomeiock (Pamlico) and Roanoac. Other local groups included the Chowanoke, Weapemeoc, Chesapeake, Ponouike, Neusiok, and Mangoak (Tuscarora), and all resided along the banks of the Albemarle and Pamlico sounds.

The Dasamongueponke is the name given to a Native American tribe of Secotan people and also the name of a village encountered by the English during their late 16th century attempts to settle and establish permanent colonies in what is now North Carolina, known at the time as Virginia. Together with the rest of Secotan people they formed a part of the Native American group known as the Carolina Algonquian Indians, and spoke the now extinct Carolina Algonquian language. Dasamongueponke in Carolina Algonquin means "where the extended land is surrounded by water.
Arthur Barlowe (1550–1620) was one of two British captains who, under the direction of Sir Walter Raleigh, left England in 1584 to find land in North America to claim for Queen Elizabeth I of England. His account survives in a letter written to Raleigh as a report on their journey. It is one of the earliest detailed English commercial reports written from direct observation about any place in North America and has been called "one of the clearest contemporary pictures of the contact of Europeans with North American Indians."

Wingina, also known as Pemisapan, was a Secotan weroance who was the first Native American leader to be encountered by English colonists in North America. During the late 16th century, English explorers Philip Amadas and Arthur Barlowe explored the region inhabited by Wingina and his people, detailing conflicts between Wingina's tribe, the Secotan and a rival tribe known as the Neusiok. When English colonization of the region began, relations between the colonists and the Secotan quickly broke down. On 1 June 1586, in an effort to gain more stocks of food for the colony, Sir Ralph Lane led an attack on the Secotan; Wingina was decapitated during the attack by one of Lane's men. This attack and crime doomed the Roanoke colony.

The Kiawah were a tribe of Cusabo people, an alliance of Indigenous groups in lowland regions of the coastal region of what became Charleston, South Carolina.
The Hatteras Indians were a tribe of Native Americans in the United States who lived in the North Carolina Outer Banks. They inhabited a village on what is now called Hatteras Island called Croatoan.

The Weapemeoc Indians were a small Native American tribe from northeastern North Carolina. They lived on the north shore of Albemarle Sound. that was first noted in literature in 1585/1586. At that time, they approximately had 700 to 800 people. They had a maritime culture. However, their culture changed rapidly as European settlers introduced diseases and ultimately forced them from their lands by 1780.












