Related Research Articles

A transcontinental railroad or transcontinental railway is contiguous railroad trackage, that crosses a continental land mass and has terminals at different oceans or continental borders. Such networks can be via the tracks of either a single railroad or over those owned or controlled by multiple railway companies along a continuous route. Although Europe is crisscrossed by railways, the railroads within Europe are usually not considered transcontinental, with the possible exception of the historic Orient Express. Transcontinental railroads helped open up unpopulated interior regions of continents to exploration and settlement that would not otherwise have been feasible. In many cases they also formed the backbones of cross-country passenger and freight transportation networks. Many of them continue to have an important role in freight transportation and some like the Trans-Siberian Railway even have passenger trains going from one end to the other.

Neosho County is a county located in Southeast Kansas. As of the 2020 census, the county population was 15,904. The county seat is Erie.

Labette County is a county located in Southeast Kansas. As of the 2020 census, the county population was 20,184. Its county seat is Oswego, and its most populous city is Parsons. The county was named after LaBette creek, the second-largest creek in the county, which runs roughly NNW-SSE from near Parsons to Chetopa. The creek in turn was named after French-Canadian fur trapper Pierre LaBette who had moved to the area, living along the Neosho River, and marrying into the Osage tribe in the 1830s and 1840s.

Crawford County is a county located in Southeast Kansas. As of the 2020 census, the county population was 38,972. Its county seat is Girard, and its most populous city is Pittsburg. The county was named in honor of Samuel J. Crawford, Governor of Kansas.

Chetopa is a city in Labette County, Kansas, United States. As of the 2010 census, the city population was 1,125. Chetopa was named for Chief Chetopah, an Osage Indian chief. Later, the community name was shortened.

Oswego is a city in and the county seat of Labette County, Kansas, United States, and situated along the Neosho River. As of the 2010 census, the city population was 1,829.

Parsons is a city in Labette County, Kansas, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 9,600. It is the most populous city of Labette County, and the second-most populous city in the southeastern region of Kansas. It is home to Labette Community College.

The Kansas City Southern Railway Company is an American Class I railroad. Founded in 1887, it operates in 10 midwestern and southeastern U.S. states: Illinois, Missouri, Kansas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Tennessee, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana and Texas. KCS hauls freight for seven major government and business sectors: agriculture and minerals, military, automotive, chemical and petroleum, energy, industrial and consumer products and intermodal.

Kansas City Southern (KCS) is a Delaware-registered pure transportation holding company with railroad investments in the United States, Mexico, and Panama.
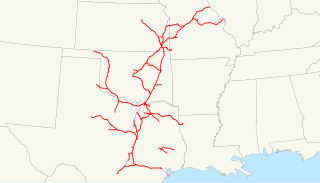
The Missouri–Kansas–Texas Railway is a former Class I railroad company in the United States, with its last headquarters in Dallas, Texas. Established in 1865 under the name Union Pacific Railway, Southern Branch, it came to serve an extensive rail network in Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, and Missouri. In 1988, it merged with the Missouri Pacific Railroad; today, it is part of Union Pacific Railroad.

The St. Louis–San Francisco Railway, commonly known as the "Frisco", was a railroad that operated in the Midwest and South Central United States from 1876 to April 17, 1980. At the end of 1970, it operated 4,547 miles (7,318 km) of road on 6,574 miles (10,580 km) of track, not including subsidiaries Quanah, Acme and Pacific Railway and the Alabama, Tennessee and Northern Railroad; that year, it reported 12,795 million ton-miles of revenue freight and no passengers. It was purchased and absorbed into the Burlington Northern Railroad in 1980. Despite its name, it never came close to San Francisco.
The Kansas Pacific Railway (KP) was a historic railroad company that operated in the western United States in the late 19th century. It was a federally chartered railroad, backed with government land grants. At a time when the first transcontinental railroad was being constructed by the Central Pacific and the Union Pacific, it tried and failed to join the transcontinental ranks. It was originally the "Union Pacific, Eastern Division", although it was completely independent. The Pennsylvania Railroad, working with Missouri financiers, designed it as a feeder line to the transcontinental system. The owners lobbied heavily in Washington for money to build a railroad from Kansas City to Colorado, and then to California. It failed to get funding to go west of Colorado. It operated many of the first long-distance lines in the state of Kansas in the 1870s, extending the national railway network westward across that state and into Colorado. Its main line furnished a principal transportation route that opened up settlement of the central Great Plains, and its link from Kansas City to Denver provided the last link in the coast-to-coast railway network in 1870. The railroad was consolidated with the Union Pacific in 1880, and its mainline continues to be an integral part of the Union Pacific network today.

The Missouri and Northern Arkansas Railroad, LLC is a Class III shortline railroad headquartered in Carthage, Missouri. It is not to be confused with the Missouri and North Arkansas Railroad which connected Joplin, Missouri with Helena, Arkansas from 1906 to 1946.

The Central Branch Union Pacific Railroad was a railroad in the U.S. state of Kansas. Originally planned as a line from Atchison west into Colorado, and given federal land grants by the Pacific Railway Act of 1862 as one of the branches of the Union Pacific Railroad, it was left with a hanging end at Waterville, Kansas when the Union Pacific Railway, Eastern Division, with which it was to connect, changed its route. The line was acquired by the Union Pacific through a stock purchase by Jay Gould and leased to the Missouri Pacific Railroad in 1880. In 1909 the Central Branch was merged into the Missouri Pacific; the latter company came back into the Union Pacific system in 1982. In 1991 the remaining trackage west of Frankfort was leased to the Kyle Railroad.
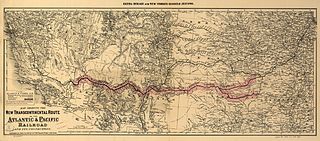
The Atlantic and Pacific Railroad was a U.S. railroad that owned or operated two disjointed segments, one connecting St. Louis, Missouri with Tulsa, Oklahoma, and the other connecting Albuquerque, New Mexico with Southern California. It was incorporated by the U.S. Congress in 1866 as a transcontinental railroad connecting Springfield, Missouri and Van Buren, Arkansas with California. The central portion was never constructed, and the two halves later became parts of the St. Louis-San Francisco Railway and Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway systems, now both merged into the BNSF Railway.

The Great Southwest railroad strike of 1886 was a labor union strike involving more than 200,000 workers. Beginning on March 1, 1886, railroad workers in five states struck against the Union Pacific and Missouri Pacific railroads, owned by Jay Gould. At least ten people were killed. The unravelling of the strike within two months led directly to the collapse of the Knights of Labor and the formation of the American Federation of Labor.

The California Southern Railroad was a subsidiary railroad of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway in Southern California. It was organized July 10, 1880, and chartered on October 23, 1880, to build a rail connection between what has become the city of Barstow and San Diego, California.

The Kansas City Terminal Railway is a Class III terminal railroad that serves as a joint operation of the trunk railroads that serve the Kansas City metropolitan area, the United States' second largest rail hub after Chicago. It is operated by the Kaw River Railroad.
The Omaha Belt Line was a 15-mile (24 km) long railroad that circumnavigated Omaha, Nebraska, starting in 1885. The organization behind the line, called the Omaha Belt Railway, was incorporated two years earlier, in 1883. Carrying passengers and cargo, the original line was operated by the Missouri Pacific Railroad, with the first line from the Sarpy County line into Downtown Omaha.
The Southwest Missouri Railroad Company was a rail carrier in the tri-state mining region of southwestern Missouri, southeastern Kansas and northeastern Oklahoma. An outgrowth of passenger streetcar lines with 94 miles of track, it became a smaller but full-fledged electric freight railway by the time it ceased operations effective May 31, 1939.
References
- ↑ "Annual Report of the Railroad and Warehouse Commissioners of the State of Missouri for the year ended December 31st, 1884, p.75". 1885. Retrieved November 10, 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 "The history of railway development in Kansas". Leonard Wilson Thompson, February, 1942 (accessed on document.pub). Retrieved November 9, 2021.
- 1 2 "History of Labette County, Kansas, p.226" (PDF). Nelson Case, Crane & Company, 1893. Retrieved November 9, 2021.
- ↑ "Town named for Civil War veteran". James R. Campbell, Nevada Daily Mail, January 25, 2012. Retrieved November 9, 2021.
- ↑ "An Ordinance annexing land into the limits and boundaries of the City of Pittsburg, Kansas, pursuant to K.S.A. 12-520(a)(7), as amended" (PDF). The Morning Sun, August 27, 2021 (accessed on the City of Pittsburg website). Retrieved November 9, 2021.
- ↑ "Tenth Annual Report of the Board of Transportation for the year ended June 30, 1896, p.356". 1897. Retrieved November 10, 2021.
- 1 2 "Coffeyville Rail Bridge (East)". John Marvig Railroad Bridge Photography. Retrieved November 10, 2021.