 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.026.833 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H22N3S:SCl ZnCl2 | |
| Molar mass | 484.22 g/mol |
| Melting point | 239 °C (462 °F; 512 K) |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H302, H312, H332 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P317, P302+P352, P304+P340, P317, P321, P330, P362+P364, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
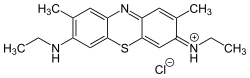
New methylene blue (also NMB, and Basic Blue 24) is an organic compound of the thiazine class of heterocycles. It is used as a stain and as an antimicrobial agent. It is classified as an azine dye, and the chromophore is a cation, the anion is often unspecified. [1]
Contents
New Methylene Blue contains the word "New" in its name to differentiate the effectiveness of staining, between its predecessor methylene blue, the chemical structure of methylene blue, and the colors between the two. [2]