Algoriphagus is a genus in the phylum Bacteroidota (Bacteria).
Algibacter is a genus in the phylum Bacteroidota (Bacteria).
Nitratireductor is a genus of bacteria.
Nitratireductor aquibiodomus is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria from the genus of Nitratireductor which was isolated from a marine denitrification system in Canada.
Nitratireductor basaltis is a Gram-negative, oxidase- and catalase-positive bacteria from the genus of Nitratireductor which was isolated from black sand from the Soesoggak beach on the Jeju Island in South Korea.
Nitratireductor indicus is a Gram-negative, oxidase- and catalase-positive mobile bacteria from the genus of Nitratireductor which was isolated from deep-sea water of the Indian Ocean.
Nitratireductor kimnyeongensis is a Gram-negative, aerobic, oxidase- and catalase-positive bacteria from the genus of Nitratireductor which was isolated from the Kimnyeong Beach in Jeju from the Republic of Korea.
Nitratireductor lucknowense is a bacterium from the genus of Nitratireductor which was isolated from pesticide contaminated soil in Lucknow in India.
Nitratireductor pacificus is a Gram-negative and motile bacteria from the genus of Nitratireductor which was isolated from enriched sediment from the Pacific Ocean.
Skeletonema dohrnii is a diatom. Together with S. marinoi, this species has flattened extremities of the processes of the fultoportulae, which interlock with those of succeeding valves without forming knuckles. It is a species of the genus Skeletonema that can be found in many waters across the globe. In the coastal waters of South Korea, their cell diameters are about 3 to 6 micrometers.
Skeletonema grethae is a species of diatom. Together with S. pseudocostatum, S. tropicum, and S. japonicum, it possesses external processes of its fultoportulae that have narrow tips which connect with those of sibling cells via fork-, knot-, or knuckle-like unions.
Skeletonema japonicum is a diatom. Together with S. pseudocostatum, S. tropicum, and S. grethae, it possesses external processes of its fultoportulae that have narrow tips which connect with those of sibling cells via fork-, knot-, or knuckle-like unions.
Skeletonema marinoi is a diatom. Together with S. dohrnii, this species has flattened extremities of the processes of the fultoportulae, which interlock with those of succeeding valves without forming knuckles.
Nitratireductor lacus is a Gram-negative bacteria from the genus of Nitratireductor which has been isolated from the Yuncheng Salt Lake in China.
Polaribacter is a genus in the family Flavobacteriaceae. They are gram-negative, aerobic bacteria that can be heterotrophic, psychrophilic or mesophilic. Most species are non-motile and species range from ovoid to rod-shaped. Polaribacter forms yellow- to orange-pigmented colonies. They have been mostly adapted to cool marine ecosystems, and their optimal growth range is at a temperature between 10 and 32 °C and at a pH of 7.0 to 8.0. They are oxidase and catalase-positive and are able to grow using carbohydrates, amino acids, and organic acids.
Flaviramulus aquimarinus is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Flaviramulus which has been isolated from seawater from the Suncheon Bay in Korea.
Linda Karen Medlin is a molecular biologist known for her work on diatoms. She is an elected member of the Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters.
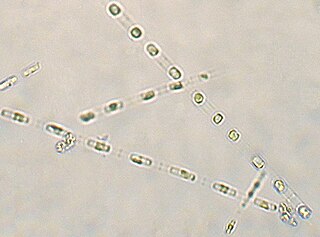
Skeletonema costatum is a cosmopolitan centric diatom that belongs to the genus Skeletonema. It was first described by R. K. Greville, who originally named it Melosira costata, in 1866. It was later renamed by Cleve in 1873 and was more narrowly defined by Zingone et al. and Sarno et al. Skeletonemacostatum is the most well known species of the genus Skeletonema and is often one of the dominant species responsible for red tide events.
Algibacter aquimarinus is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped and aerobic bacterium from the genus of Algibacter which has been isolated from seawater from the Gwangyang Bay.
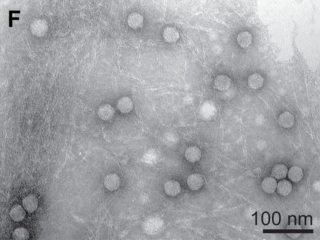
Algal viruses are the viruses infecting algae, which are photosynthetic single-celled eukaryotes. As of 2020, there were 61 viruses known to infect algae. Algae are integral components of aquatic food webs and drive nutrient cycling, so the viruses infecting algal populations also impacts the organisms and nutrient cycling systems that depend on them. Thus, these viruses can have significant, worldwide economic and ecological effects. Their genomes varied between 4.4 to 560 kilobase pairs (kbp) long and used double-stranded Deoxyribonucleic Acid (dsDNA), double-stranded Ribonucleic Acid (dsRNA), single-stranded Deoxyribonucleic Acid (ssDNA), and single-stranded Ribonucleic Acid (ssRNA). The viruses ranged between 20 and 210 nm in diameter. Since the discovery of the first algae-infecting virus in 1979, several different techniques have been used to find new viruses infecting algae and it seems that there are many algae-infecting viruses left to be discovered

