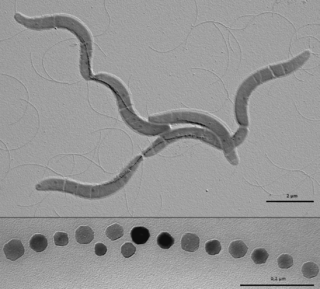
The Rhodospirillales are an order of Pseudomonadota.
The Aurantimonadaceae are a small family of marine bacteria.

The Hyphomicrobiaceae are a family of bacteria. Among others, they include Rhodomicrobium, a genus of purple bacteria.
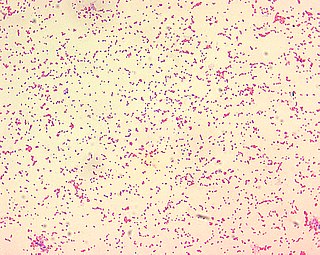
The Brucellaceae are a family of the Gram-negative Hyphomicrobiales. They are named after Sir David Bruce, a Scottish microbiologist. They are aerobic chemoorganotrophes. The family comprises pathogen and soil bacteria

Desulfovibrionales are a taxonomic order of bacteria belonging to the phylum Thermodesulfobacteriota, with four families. They are Gram-negative. The majority are sulfate-reducing, with the exception of Lawsonia and Bilophila. All members of this order are obligately anaerobic. Most species are mesophilic, but some are moderate thermophiles.
The Syntrophobacterales are an order of Thermodesulfobacteriota. All genera are strictly anaerobic. Many of the family Syntrophobacteraceae are sulfate-reducing. Some species are motile by using one polar flagellum.

The Acidimicrobiaceae are a family of Actinomycetota.
The Coriobacteriales are an order of Actinomycetota.
The Actinomycetaceae are a family of bacteria in the order Actinomycetales that contains the medically important genus Actinomyces. These organisms are closely related to the mycobacteria, but were originally classified as fungi because they were thought to be transitional forms between bacteria and fungi.
The Nitrobacteraceae are a family of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria. They include plant-associated bacteria such as Bradyrhizobium, a genus of rhizobia associated with some legumes. It also contains animal-associated bacteria such as Afipia felis, formerly thought to cause cat-scratch disease. Others are free-living, such as Rhodopseudomonas, a purple bacterium found in marine water and soils. The strain Rhodopseudomonas palustris DX-1 can generate an electric current with no hydrogen production, a trait being explored in the development of the microbial fuel cell. The genus Afipia has also been found in the atmosphere, where it uses methylsulfonylmethane as a carbon source.
The Sphingomonadales are an order of the Alphaproteobacteria.
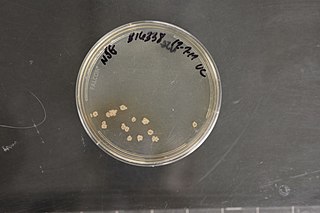
The Glycomycetaceae are a family of bacteria.
Weeksellaceae is a family in the order Flavobacteriales.
Stappiaceae is a family of Alphaproteobacteria.
Tepidamorphaceae is a family of Alphaproteobacteria.
Parvibaculaceae is a family of Alphaproteobacteria.
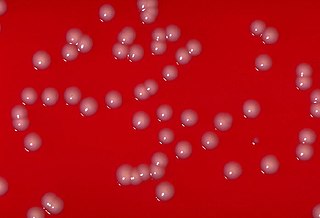
The Mycobacteriales are an order of bacteria.
The Streptosporangiales are an order of bacteria.
The Propionibacteriales are an order of bacteria.
Balneolales is an order of bacteria.






