
A windmill is a structure that converts wind power into rotational energy using vanes called sails or blades, by tradition specifically to mill grain (gristmills), but in some parts of the English-speaking world, the term has also been extended to encompass windpumps, wind turbines, and other applications. The term wind engine is also sometimes used to describe such devices.
Fiberglass or fibreglass is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass cloth. The plastic matrix may be a thermoset polymer matrix—most often based on thermosetting polymers such as epoxy, polyester resin, or vinyl ester resin—or a thermoplastic.
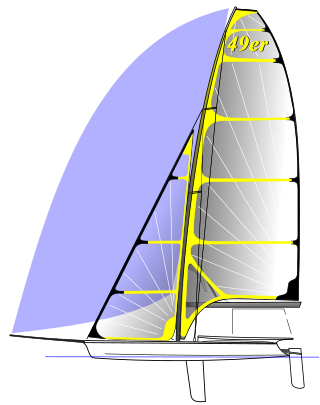
The 49er and 49er FX is a two-handed skiff-type high-performance sailing dinghy. The two crew work on different roles with the helm making many tactical decisions, as well as steering, and the crew doing most of the sail control. Both of the crew are equipped with their own trapeze and sailing is done while cantilevered over the water to the fullest extent to balance against the sails.

Sail components include the features that define a sail's shape and function, plus its constituent parts from which it is manufactured. A sail may be classified in a variety of ways, including by its orientation to the vessel and its shape,. Sails are typically constructed out of flexible material that is shaped by various means, while in use, to offer an appropriate airfoil, according to the strength and apparent direction of the wind. A variety of features and fittings allow the sail to be attached to lines and spars.

The International 505 is a One-Design high-performance two-person monohull planing sailing dinghy, with spinnaker, utilising a trapeze for the crew.
Filament winding is a fabrication technique mainly used for manufacturing open (cylinders) or closed end structures. This process involves winding filaments under tension over a rotating mandrel. The mandrel rotates around the spindle while a delivery eye on a carriage traverses horizontally in line with the axis of the rotating mandrel, laying down fibers in the desired pattern or angle to the rotational axis. The most common filaments are glass or carbon and are impregnated with resin by passing through a bath as they are wound onto the mandrel. Once the mandrel is completely covered to the desired thickness, the resin is cured. Depending on the resin system and its cure characteristics, often the mandrel is autoclaved or heated in an oven or rotated under radiant heaters until the part is cured. Once the resin has cured, the mandrel is removed or extracted, leaving the hollow final product. For some products such as gas bottles, the 'mandrel' is a permanent part of the finished product forming a liner to prevent gas leakage or as a barrier to protect the composite from the fluid to be stored.

Sailcloth is cloth used to make sails. It can be made of a variety of materials, including natural fibers such as flax, hemp, or cotton in various forms of sail canvas, and synthetic fibers such as nylon, polyester, aramids, and carbon fibers in various woven, spun, and molded textiles.

Dyneema Composite Fabric (DCF), also known as Cuben Fiber (CTF3), is a high-performance non-woven composite material used in high-strength, low-weight applications. It is constructed from a thin sheet of ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene laminated between two sheets of polyester.

A sailmaker makes and repairs sails for sailboats, kites, hang gliders, wind art, architectural sails, or other structures using sails. A sailmaker typically works on shore in a sail loft; the sail loft has other sailmakers. Large ocean-going sailing ships often had sailmakers in the crew. The sailmaker maintained and repaired sails. This required knowledge of the sailmaker's craft and the tools of the sailmakers loft on shore.
Lowell Orton North was an American sailor and Olympic gold medalist. He competed at the 1968 Summer Olympics in Mexico City, where he received a gold medal in the Star class with the boat North Star, together with Peter Barrett.
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers, carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers, carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon-fiber reinforced-thermoplastic, also known as carbon fiber, carbon composite, or just carbon, are extremely strong and light fiber-reinforced plastics that contain carbon fibers. CFRPs can be expensive to produce, but are commonly used wherever high strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness (rigidity) are required, such as aerospace, superstructures of ships, automotive, civil engineering, sports equipment, and an increasing number of consumer and technical applications.

Waxed cotton is cotton impregnated with a paraffin or natural beeswax based wax, woven into or applied to the cloth. Popular from the 1920s to the mid-1950s, the product, which developed from the sailing industry in England and Scotland, became commonly used for waterproofing. It has been replaced by more modern materials but is still used by the country sports community. There are two main drawbacks: waxed fabric is not very breathable, and it tends to be heavier and bulkier than modern synthetic waterproof materials.
Three-dimensional composites use fiber preforms constructed from yarns or tows arranged into complex three-dimensional structures. These can be created from a 3D weaving process, a 3D knitting process, a 3D braiding process, or a 3D lay of short fibers. A resin is applied to the 3D preform to create the composite material. Three-dimensional composites are used in highly engineered and highly technical applications in order to achieve complex mechanical properties. Three-dimensional composites are engineered to react to stresses and strains in ways that are not possible with traditional composite materials composed of single direction tows, or 2D woven composites, sandwich composites or stacked laminate materials.

Thomas A. Whidden is one of the most-acclaimed sailors of all-time. He is a member of both the America's Cup Hall of Fame and the National Sailing Hall of Fame. Whidden joined North Sails, the world's largest sailmaker, in 1986, just before being part of the crew of the yacht Stars & Stripes in the victory over Australia in the 1987 America's Cup. He became CEO and co-owner of North Technology Group, formerly known as North Marine Group, parent company to North Sails, when it was established several years later.

Tailored fiber placement (TFP) is a textile manufacturing technique based on the principle of sewing for a continuous placement of fibrous material for composite components. The fibrous material is fixed with an upper and lower stitching thread on a base material. Compared to other textile manufacturing processes fiber material can be placed near net-shape in curvilinear patterns upon a base material in order to create stress adapted composite parts.

A sail is a tensile structure, which is made from fabric or other membrane materials, that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails may be made from a combination of woven materials—including canvas or polyester cloth, laminated membranes or bonded filaments, usually in a three- or four-sided shape.
G-10 or garolite is a high-pressure fiberglass laminate, a type of composite material. It is created by stacking multiple layers of glass cloth, soaked in epoxy resin, then compressing the resulting material under heat until the epoxy cures. It is manufactured in flat sheets, most often a few millimeters thick.
The C&C 44 and the C&C 44 Custom are a series of Canadian sailboats, that were designed by Robert W. Ball and first built in 1985.
The Tech Dinghy is an American sailing dinghy that was designed by George Owen, a professor at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), as a one-design racer and for sail training. It was first built in 1935.
The Alerion Express 19 is an American trailerable sailboat that was designed by Gary Hoyt as a cruiser and first built in 1998.











