
A wind farm or wind park, also called a wind power station or wind power plant, is a group of wind turbines in the same location used to produce electricity. Wind farms vary in size from a small number of turbines to several hundred wind turbines covering an extensive area. Wind farms can be either onshore or offshore.

The United Kingdom is the best location for wind power in Europe and one of the best in the world. The combination of long coastline, shallow water and strong winds make offshore wind unusually effective.

Arklow Bank Wind Park is a 25 megawatt offshore wind farm generating electrical power for the Wicklow region in Ireland. It is the first offshore wind farm in Ireland, and the world's first erection of wind turbines rated over 3 MW. It is located on the Arklow Bank, a shallow water sandbank in the Irish Sea, around 10 kilometers (6.2 mi) off the coast of Arklow with an area of 27 by 2.5 kilometres.
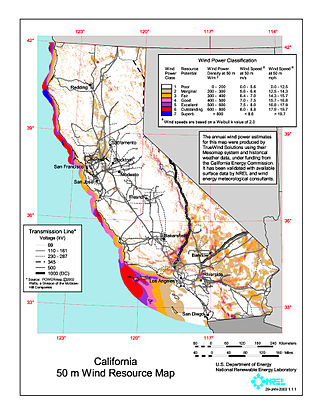
Wind power in California had initiative and early development during Governor Jerry Brown's first two terms in the late 1970s and early 1980s. The state's wind power capacity has grown by nearly 350% since 2001, when it was less than 1,700 MW. In 2016, wind energy supplied about 6.9% of California's total electricity needs, or enough to power more than 1.3 million households. Most of California's wind generation is found in the Tehachapi area of Kern County, California, with some large projects in Solano, Contra Costa and Riverside counties as well. California is among the states with the largest amount of installed wind power capacity. In recent years, California has lagged behind other states when it comes to the installation of wind power. It was ranked 4th overall for wind power electrical generation at the end of 2016 behind Texas, Iowa, and Oklahoma. As of 2019, California had 5,973 megawatts (MW) of wind power generating capacity installed.

Wind power is the fastest-growing renewable energy technology in Scotland, with 11,482 megawatts (MW) of installed wind power capacity by Q1 2023. This included 9,316 MW from onshore wind in Scotland and 2,166 MW of offshore wind generators.

China is the world leader in wind power generation, with the largest installed capacity of any nation and continued rapid growth in new wind facilities. With its large land mass and long coastline, China has exceptional wind power resources: it is estimated China has about 2,380 gigawatts (GW) of exploitable capacity on land and 200GW on the sea. Wind power remained China's third-largest source of electricity at the end of 2021, accounting for 7.5% of total power generation.

In 2021 France reached a total of 18,676 megawatts (MW) installed wind power capacity placing France at that time as the world's seventh largest wind power nation by installed capacity, behind the United Kingdom and Brazil and ahead of Canada and Italy. According to the IEA the yearly wind production was 20.2 TWh in 2015, representing almost 23% of the 88.4 TWh from renewable sources in France during that year. Wind provided 4.3% of the country's electricity demand in 2015.

The Princess Amalia Wind Farm is an offshore wind farm in the Netherlands. Prior to its official opening, it was known as the Q7 Wind Farm.

Wind power in Italy, at the end of 2015, consisted of more than 1,847 wind turbines with a total installed capacity of 8,958 megawatts. Wind power contributed 5.4% of Italy electricity generation in 2015 (14,589 GWh). Italy is ranked as the world's tenth producer of wind power as of the end of 2016. Prospects for Italian wind energy beyond 2020 were positive, with several projects planned to go live before 2030.

Wind power in Belgium depends partially on regional governments and partially on the Belgian federal government. Wind energy producers in both the Flemish and Walloon regions get green certificates but not with the same conditions.

As of October 2023, wind power in the Netherlands has an installed capacity of 10,619 MW, 37.5% of which is based offshore. In 2022, the wind turbines provided the country with 18.37% of its electricity demand during the year. Windmills have historically played a major part in the Netherlands by providing an alternative to water driven mills.
Wind power in Indiana was limited to a few small water-pumping windmills on farms until 2008 with construction of Indiana's first utility-scale wind power facility, Goodland with a nameplate capacity of 130 MW. As of September 2017, Indiana had a total of 1897 MW of wind power capacity installed, ranking it 12th among U.S. states. Wind power was responsible for 4.8% of in-state electricity production in 2016.

The Beatrice Offshore Wind Farm now known as Beatrice Offshore Windfarm Ltd (BOWL) project, is an offshore wind farm close to the Beatrice oil field in the Moray Firth, part of the North Sea 13 km off the north east coast of Scotland.

Teesside Wind Farm, or alternatively referred to as Redcar Wind Farm, is a 27 turbine 62 MW capacity offshore wind farm constructed just to the east of the mouth of the River Tees and 1.5 km north of Redcar off the North Yorkshire coast, in the North Sea, England.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to wind energy:

The Vestas V164 is a three-bladed offshore wind turbine, produced by Vestas, with a nameplate capacity of up to 10 megawatts, a world record. Vestas revealed the V164's design in 2011 with the first prototype unit operated at Østerild in northern Denmark in January 2014. The first industrial units were installed in 2016 at Burbo Bank, off the west coast of the United Kingdom. By 2021, Vestas had produced 500 of the series.

Renewable energy in Taiwan contributed to 8.7% of national electricity generation as of end of 2013. The total installed capacity of renewable energy in Taiwan by the end of 2013 was 3.76 GW. As of 2020, the Taiwan government aims for a renewable share of 20% by 2025, with coal and gas providing the other 80%.
Dogger Bank Wind Farm is a group of offshore wind farms under construction 130 to 200 kilometres off the east coast of Yorkshire, England in the North Sea. It is considered to be the world's largest offshore windfarm. It was developed by the Forewind consortium, with three phases envisioned - first phase, second phase and third phase. In 2015 the third phase was abandoned, while the first and second phases were granted consent. It was initially expected that the Dogger Bank development will consist of four offshore wind farms, each with a capacity of up to 1.2 GW, creating a combined capacity of 4.8 GW. As of 2023, a total of 277 turbines are expected to be built and produce a capacity of 3.6 GW, enough to power 6 million homes.

Wind power is a major industry in Taiwan. Taiwan has abundant wind resources however a lack of space on land means that most major developments are offshore. As of February 2020, there were 361 installed onshore turbines and 22 offshore turbines in operation with the total installed capacity of 845.2 MW.

















