
Meliaceae, the mahogany family, is a flowering plant family of mostly trees and shrubs in the order Sapindales.

In the botanical classification of plants, Aeridinae Pfitzer is a subtribe of the tribe Vandeae whose representatives all have a monopodial growth habit and do not possess pseudobulbs.

Strobilanthes is a genus of about 350 species of flowering plants in the family Acanthaceae, mostly native to tropical Asia and Madagascar, but with a few species extending north into temperate regions of Asia. Many species are cultivated for their two-lipped, hooded flowers in shades of blue, pink, white and purple. Most are frost-tender and require protection in frost-prone areas. The genus is most famed for its many species which bloom on long cycles of several years, such as Strobilanthes wightii which blooms every thirteen years.

Dysoxylum is a genus of rainforest trees and shrubs in the flowering plant family Meliaceae. About 34 species are recognised in the genus, distributed from India and southern China, through southeast Asia to New Guinea, Solomon Islands, and Australia. The name Dysoxylum derives from the Greek word ‘Dys’ meaning "bad" referring to "ill-smelling" and ‘Xylon’ meaning "wood".

Hydnocarpus is a genus of medium to large trees in the Family Achariaceae; the genus was previously placed in the now defunct family Flacourtiaceae. Species have been recorded from Indochina, Indonesia, Malaysia and the Philippines.

Buchanania is a genus of plants in the mango and cashew family Anacardiaceae, native to areas from India to southern China, and southwards to northern Australia and the western Pacific.

Glycosmis is a genus of flowering plants in the citrus family, Rutaceae and tribe Clauseneae. It is in the subfamily Aurantioideae, which also includes genus Citrus. It is a genus of the subtribe Clauseninae, which are known technically as the remote citroid fruit trees.

Lasianthus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. They are tropical subshrubs, shrubs, or rarely, small trees. They inhabit the understory of primary forests.

Microtropis is a genus of plant in the family Celastraceae. There are about 70 species. They are trees and shrubs, evergreen or deciduous, with oppositely arranged leaves and white or yellowish flowers. Microtropis are distributed in Asia, Africa, and Central America.

Nothopegia is a genus of plants in the family Anacardiaceae, native to India, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka. Out of 11 species only 8 are reported to occur in India. This genus is characterised by small deciduous trees with simple leaves, racemose inflorescence, unisexual tetramerous flowers and drupaceaous fruits Except Nothopegia heyneana Gamble, all other species are restricted to the Western Ghats and SW India.

Saprosma is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. There are about 40 species distributed from south China to tropical Asia.

Syzygium densiflorum is a species of evergreen tree in the family Myrtaceae. It is endemic to the Western Ghats mountains, India. The species is categorised as Vulnerable in the IUCN Red List.

Vatica chinensis is a species of flowering tree in the family Dipterocarpaceae, found in South Asia.

Aurantioideae is the subfamily within the rue and citrus family (Rutaceae) that contains the citrus. The subfamily's center of diversity is in the monsoon region of eastern Australasia, extending west through South Asia into Africa, and eastwards into Polynesia.
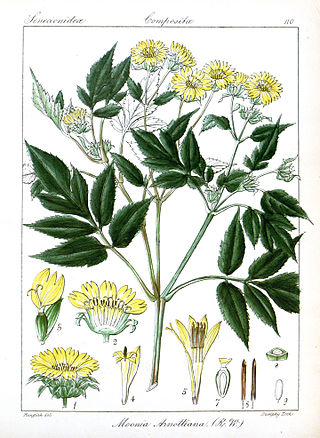
Moonia is a genus of Asian and Australian flowering plants in the daisy family.

Cheirostylis, commonly known as fleshy jewel orchids or velvet orchids, is a genus of about sixty species of flowering plants in the orchid family Orchidaceae. Plants in this genus are terrestrial herbs with a caterpillar-like rhizome and a loose rosette of leaves. Small, white, hairy flowers develop as the leaves wither. They are found in tropical Africa, southern Asia, Southeast Asia, Malesia, New Guinea and Australia.

Bruguiera is a plant genus in the family Rhizophoraceae. It is a small genus of five mangrove species and three hybrids of the Indian and west Pacific Ocean region, its range extending from East Africa and Madagascar through coastal India, Sri Lanka and Southeast Asia to northern Australia, Melanesia and Polynesia. It is characterised by calyces with 8-16 lanceolate, pointed lobes, 16-32 stamens, explosive release of pollen, and viviparous propagules. It is named in honour of French explorer and biologist Jean Guillaume Bruguière (1750–1798). Recently, the eighth taxa of Bruguiera, B. × dungarra was recognised as occurring in northern Australia.

Nothopegia beddomei, also known as Western Ghats Top-Fruit Tree, is a species of plant in the family Anacardiaceae. It is found in India and Sri Lanka. The tree is primarily found in the Western Ghats region of India, which extends along the western coast of the country, spanning states like Maharashtra, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu.

Leptadenia is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1810. It is native to Africa, including Madagascar, as well as southwest Asia and the Indian Subcontinent.
- Leptadenia arborea(Forssk.) Schweinf. - Sudan, Ethiopia
- Leptadenia lancifolia(Schumach. & Thonn.) Decne. - tropical Africa
- Leptadenia madagascariensisDecne. - Madagascar
- Leptadenia pyrotechnica(Forssk.) Decne. - widespread from Algeria to India
- Leptadenia reticulata(Retz.) Wight & Arn. - Madagascar

Macrosolen is a genus of plants in the family Loranthaceae. It includes about 83 species all over the world with ca. 40 species widely distributed in tropical South and Southeast Asia. Some species were described by de Loureiro, Lecomte, Danser (1938) and Hô (2003).


















