
The Esociformes are a small order of ray-finned fish, with two families, Umbridae and Esocidae. The pikes of genus Esox give the order its name.

Desmatophoca is an extinct genus of early pinniped that lived during the Miocene, and is named from the Greek "phoca", meaning seal. A taxon of the family Desmatophocidae, it shares some morphological similarities with modern true seals. Two species are recognized: Desmatophoca oregonensis and Desmatophoca brachycephala. Little information exists regarding Desmatophoca, due to the small number of fossil samples obtained and identified.

Platygonus is an extinct genus of herbivorous peccaries of the family Tayassuidae, endemic to North and South America from the Miocene through Pleistocene epochs, existing for about 10.289 million years. This species grew up to lengths of 3.3 feet long and stood 2.5 feet tall.

Daphoenus is an extinct genus of bear dogs. Daphoenus inhabited North America from the Middle Eocene to the Middle Miocene, 37.2—16.0 Mya, existing for approximately 21 million years.

The northern pikeminnow, or Columbia River dace is a large member of the minnow family, Cyprinidae. This predatory freshwater fish is native to northwestern North America, ranging from the Nass River basin to the Columbia River basin. A good deal of concern has been expressed regarding the impact northern pikeminnow populations may have on salmon in Columbia and Snake river impoundments.
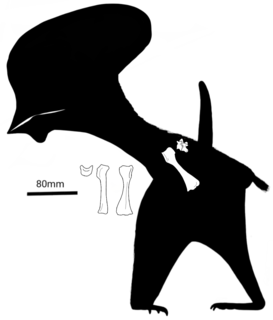
Bennettazhia is a genus of tapejaromorph pterosaur from the Early Cretaceous period of what is now the Hudspeth Formation of the state of Oregon in the United States. Although originally identified as a species of the pteranodontoid pterosaur Pteranodon, Bennettazhia is now thought to have been a different animal. The type and only species is B. oregonensis.

The Rattlesnake Formation is a Miocene to late Pliocene geologic formation found along the John Day River Valley of Oregon, in the Western United States.

The Olympic mudminnow is a fish native to the western lowlands of Washington: the Chehalis River basin, Deschutes River basin, and some Olympic Peninsula basins. It grows to 8 cm in length, and is Washington's only known endemic freshwater fish species. Although they strongly resemble killifish, mudminnows are more closely related to pike and muskellunge.

Batrachotomus is a genus of prehistoric archosaur. Fossils of this animal have been found in southern Germany and dated from the Ladinian stage of the Middle Triassic period, around 242 to 237 million years ago. Batrachotomus was described by palaeontologist David J. Gower 22 years after its discovery.
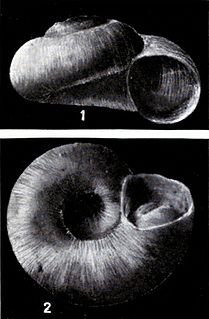
Valvata oregonensis is a species of fossil freshwater snail with a gill and an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Valvatidae, the valve snails.

Livyatan is an extinct genus of macroraptorial sperm whale containing one species: L. melvillei. The genus name was inspired by the biblical sea monster Leviathan, and the species name by Herman Melville, the author of the famous novel Moby-Dick about a white bull sperm whale. It is mainly known from the Pisco Formation of Peru during the Tortonian stage of the Miocene epoch, about 9.9–8.9 million years ago (mya); however, isolated teeth from other locations such as Chile, Argentina, South Africa, and Australia implies that either it or a close relative survived into the Pliocene, around 5 mya, and was present throughout the Southern Hemisphere. It was a member of a group of hyper-predatory macroraptorial sperm whales and was likely an apex predator, preying on whales, seals, and so forth. Characteristic of raptorial sperm whales, Livyatan had functional, enamel-coated teeth on the upper and lower jaws, as well as several adaptations for hunting large prey.

Laccognathus embryi is an extinct species of porolepiform lobe-finned fish recovered from Ellesmere Island, Canada. It existed during the Frasnian age of the Late Devonian epoch.

Paleontology in Oregon refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Oregon. Oregon's geologic record extends back approximately 400 million years ago to the Devonian period, before which time the state's landmass was likely submerged under water. Sediment records show that Oregon remained mostly submerged until the Paleocene period. The state's earliest fossil record includes plants, corals, and conodonts. Oregon was covered by seaways and volcanic islands during the Mesozoic era. Fossils from this period include marine plants, invertebrates, ichthyosaurs, pterosaurs, and traces such as invertebrate burrows. During the Cenozoic, Oregon's climate gradually cooled and eventually yielded the environments now found in the state. The era's fossils include marine and terrestrial plants, invertebrates, fish, amphibians, turtles, birds, mammals, and traces such as eggs and animal tracks.
Acer traini is an extinct maple species in the family Sapindaceae described from isolated fossil samaras. The species was described from Miocene-aged fossils found in Canada and the United States of America. It is one of several extinct species placed in the living section Glabra.

Megacephalosaurus is an extinct genus of short-necked pliosaur that inhabited the Western Interior Seaway of North America about 94 to 93 million years ago during the Turonian stage of the Late Cretaceous, containing the single species M. eulerti. It is named after its large head, which is the largest of any plesiosaur in the continent and measures up to 1.75 meters (5.7 ft) in length. Megacephalosaurus was one of the largest marine reptiles of its time with an estimated length of 6–9 meters (20–30 ft). Its long snout and consistently sized teeth suggest that it preferred a diet on smaller-sized prey.
Actinidia oregonensis is an extinct species of flowering plants in the kiwifruit family, Actinidiaceae, solely known from the middle Eocene sediments exposed in north-central Oregon. The species was first described from a series of isolated fossil seeds in chert.
Paleopanax is an extinct genus of flowering plant in the Ginseng family, Araliaceae, containing the single species Paleopanax oregonensis. The species is solely known from the middle Eocene sediments exposed in north central Oregon and was first described from a series of isolated fossil fruits in siltstones.

Adelolophus is a genus of lambeosaurine dinosaur from Upper Cretaceous rocks in the U.S. state of Utah. The type and only known species is A. hutchisoni; the type specimen consists only of a broken maxilla. It constitutes the oldest known lambeosaur remains from North America, as well as the only known lambeosaur species from the Wahweap Formation, of which it pertains to the Upper Member. Among its relatives, it seems to be particularly similar to Parasaurolophus, rather than animals like Lambeosaurus; phylogenetic analysis confirms this, finding it in Parasaurolophini. It would have lived in a wet environment, bordering on the sea but with a more arid season during some times of the year. This environment would have been shared with a diverse variety of fish and turtles, as well as other dinosaurs like ceratopsids and tyrannosaurids.

Ulmus okanaganensis is an extinct species of flowering plant in the family Ulmaceae related to the modern elms. The species is known from fossil leaves, flowers, and fruits found in the early Eocene deposits of northern Washington state, United States and similar aged formations in British Columbia, Canada.

Comptonia columbiana is an extinct species of sweet fern in the flowering plant family Myricaceae. The species is known from fossil leaves found in the early Eocene deposits of central to southern British Columbia, Canada, plus northern Washington state, United States, and, tentatively, the late Eocene of Southern Idaho and Earliest Oligocene of Oregon, United States.

















